Once you find a geoprocessing tool and open it, specify its parameter values and run it.
To get help for an open tool in the Geoprocessing pane, hover over the Help button  to access a summary and illustration of the tool, or click the button to open the tool reference page.
to access a summary and illustration of the tool, or click the button to open the tool reference page.
Parameters
After the tool opens, you specify the tool's parameter values. Parameters are a set of options or settings, such as the input data to process, output dataset, and other options that modify how the tool runs. Every geoprocessing tool has a unique set of parameters. For information about each tool parameter, hover on the information button  that appears next to the parameter's label.
that appears next to the parameter's label.
Parameters can be required or optional and are treated as follows:
- Required parameters must be filled in for the tool to run and are indicated by a red asterisk
 .
. - Optional parameters can be left blank or unmodified to use a default behavior.
Geoprocessing tools have both input and output parameters. Input parameters can reference data or be options that control what the tool does. There are a number of ways to specify the input data to be processed by the tool, including the following:
- Select a layer from a list of map layers. If the layer has a selection, only the selected features will be processed. Likewise, if the layer has a definition query, time filter, or range filter, only the features included in the filter will be processed.
- Browse to a dataset that is in a project database or connection using the browse button
 .
. - Create input features interactively using the interactive input button
 .
.

For input parameters that are not data, you typically only need to specify a number, check a box, or select an option from a list.
Some parameters require more interaction, such as multiple values, geographic extent, expression, or field map.
An output parameter is typically the location of a new dataset or resulting value to be created by the tool. For output dataset parameters, an output location and name are usually automatically assigned, but you can change the path of the dataset or browse using the output browse button  . The output location that is automatically assigned is based on your current or scratch workspace.
. The output location that is automatically assigned is based on your current or scratch workspace.
Reset parameter settings
To reset a tool to its default parameter state, open the Run menu at the bottom of the Geoprocessing pane and select Reset Parameters.
Override default parameter values
You can override the default parameter values of system geoprocessing tools using the Pro.settingsConfig file. Include the ToolParameters element in the file to set and, optionally, lock tool parameter values. Tools that have been configured with parameter overrides open with the specified value, rather than system-defined default values. For example, you can set the Calculate Field tool’s Expression Type parameter to use Arcade as the default rather than Python using the following syntax.
<Geoprocessing>
<ToolParameters>
<Parameter toolName="calculatefield" toolboxAlias="management" name="expression_type" isLocked="true">ARCADE</Parameter>
</ToolParameters>
</Geoprocessing>
Note:
Parameter overrides only apply to tools opened in the Geoprocessing pane and in a floating window. The overrides are not used when a tool is run in Python or ModelBuilder unless the parameter value is specified.
Environments
You can modify additional options that affect tool performance on the tool Environments tab. All environment settings are optional. Only the geoprocessing environments that apply to the specific open tool will be displayed on the Environments tab.
Environment options set from the tool Environments tab will only be applied to that specific instance of running the tool. If you reopen the tool from geoprocessing history, the environment settings will be retained; otherwise, all environment settings will be the default. To set geoprocessing environments that should be applied to all geoprocessing performed in the project, set environments from the Environments window opened by clicking Analysis > Geoprocessing > Environments.
Learn more about geoprocessing environment settings
Note:
The tool Environments tab may not display when a tool is opened in a floating window from a ribbon button or UI command. Set the project environments from the Environments window described above to apply environment settings when necessary.
Run a tool
To run a geoprocessing tool, click the Run button  at the bottom of the Geoprocessing pane.
at the bottom of the Geoprocessing pane.
Status banner, progress, and messages
After you run a tool, a status banner is added to the bottom of the Geoprocessing pane with a progress bar that shows completion percentage, and a cancel button to stop processing.
You can hover over the banner or progress bar to display a pop-up containing information about the tool that is running, such as messages, run time, and the specified tool parameters and environments. You can click View Details to access the same detailed information in a detached window, or click Open History to open the project's geoprocessing history.
The status banner also has a link you can click to access the Suggestions list, which includes tools that may help you get to the next step in your geoprocessing workflow. Suggestions are based on the previous tools you ran in the current project, which are logged in the geoprocessing history.
Learn more about geoprocessing tool suggestions
When the tool is finished running, any output layers are added to the open map and the progress bar displays an icon and message to indicate the tool status as follows:
| Icon | Status |
|---|---|
 | The tool completed successfully. |
 | The tool completed with warnings. Click View Details or hover over the status icon |
 | The tool failed. Click View Details or hover over the status icon |
When you finish running a geoprocessing tool, click the Back button  at the top of the Geoprocessing pane to return to the last page you viewed.
at the top of the Geoprocessing pane to return to the last page you viewed.
Suggestions
Geoprocessing tool suggestions are tools that may help you get to the next step in your geoprocessing workflow. Suggestions are based on the previous tools you ran in the current project, which are logged in the geoprocessing history. If you clear the geoprocessing history or you have a new project, no suggestions will be listed.
Suggestions are available in the following locations:
- After you run a tool, the Suggestions list is in the tool status banner.
- The Favorites tab of the Geoprocessing pane.
Suggestions use a prediction model that has been trained with tool usage sequences from the Esri User Experience Improvement program. The suggested tools have been used in sequences with the tools you previously ran by the ArcGIS Pro user community.
There is some randomization that occurs in the prediction, and you can retrieve alternative suggestions. If none of the suggestions apply to your workflow, click Try Again to get alternative suggestions.
Note:
Suggestions are available if you have chosen to install the AI Models > Tool Suggestions file during ArcGIS Pro installation.
Note:
Suggestions require a processor supporting the AVX2 instruction set. If this hardware requirement is not met, even if the tool suggestions model file is installed, suggestions will not be available.
Schedule a tool
From the Run menu, select Schedule to run the tool at a later date and time and, optionally, with recurrence. All required parameters must be specified to schedule a tool.
Copy Python command
To copy a Python command snippet that you can use to run the tool in Python with the currently specified parameters and environments, from the Run menu select Copy Python Command. The Python code is copied to the clipboard, and you can paste it into the Python window, a notebook, or other Python interface.
Note:
It is not necessary to run the tool before copying the Python command. However, all required parameter values must be specified to enable the Copy Python Command option.
Python commands can also be copied from geoprocessing history entries.
Geoprocessing threads
When you run a geoprocessing tool, it typically runs in a background thread dedicated to geoprocessing. This enables the application and map to remain available for other tasks while the tool is running, which is especially important if you are running a tool that takes a long time to complete. There are several cases when a geoprocessing tool does not run in this geoprocessing thread, which causes the tool to run in the main application thread and lock the application for the duration of the tool run time. In this situation, other tasks cannot be performed until the tool has completed. The following cases lock the application until the geoprocessing tool has completed:
- Running a geoprocessing tool in the Python window..
- Running a geoprocessing tool in an ArcGIS Pro add-in may lock the application depending on the methods and properties of the tools set in the add-in.
- Running a geoprocessing tool when there are pending edits.
- Running a model interactively in ModelBuilder.
- Running a geoprocessing tool from a floating window opened from a ribbon button or UI command may lock the application depending on the methods and properties of the tools set by the button or command developer.
History and recent tools
When a geoprocessing tool is run an entry is added to the project's geoprocessing history with details on when the tool was run, the settings that were used, whether the tool completed successfully, and any information, warning, or error messages.
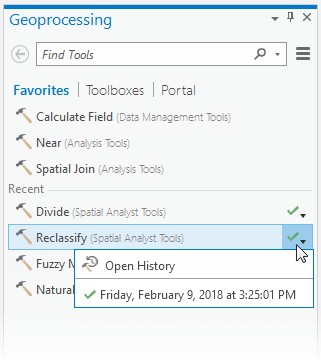
The Favorites tab in the Geoprocessing pane also has a Recent section that lists the tools you have recently run.
Tools that have been recently run display a status indication icon and a list of recent instances of the tool. You can hover over the entries in the list to see details, and click to open the selected tool with the parameter settings that were previously used.
Open and run multiple tools
The Geoprocessing pane allows you to open multiple geoprocessing tools, see a list of the open tools, and switch between them. To open multiple tools, complete the following steps:
- Open a geoprocessing tool.
- Click the Add button
 in the upper right corner of the Geoprocessing pane to open a menu that lists all the open geoprocessing tools.
in the upper right corner of the Geoprocessing pane to open a menu that lists all the open geoprocessing tools. - Select Open Another Tool.
The Geoprocessing pane returns to the previous page and adds the name of the first opened tool to the list of open tools. All changes to the previous tool are saved and will be loaded when the tool is reopened from this menu.
- Search for or select another tool and open it.
- Click the Add button
 in the Geoprocessing pane to see the list of multiple open tools.
in the Geoprocessing pane to see the list of multiple open tools.
You can switch between all open tools without losing any progress, as the parameter and environment settings are maintained as long as the tool remains in the open tool list.
You can run multiple tools, and they will be added to a queue of running tools that can be viewed in the geoprocessing history. If you run a tool while another tool is running, the second tool will be in a pending state until the first tool completes, at which time the next pending tool will run automatically.