| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Source Features
| The line features that will be used as edgematching source features. All edgematch links start at source features. | Feature Layer |
Adjacent Features
| The line features that are adjacent to the source features. All edgematch links end at matched adjacent features. | Feature Layer |
Output Feature Class
| The output feature class containing lines representing edgematch links. | Feature Class |
Search Distance
| The distance that will be used to search for match candidates. A distance must be specified and it must be greater than zero. You can choose a preferred unit. The default is the feature unit. | Linear Unit |
Match Fields
(Optional) | The fields from the source and target features in which the target fields are from the adjacent features. If provided, each pair of fields will be checked for match candidates to help determine the right match. | Value Table |
Summary
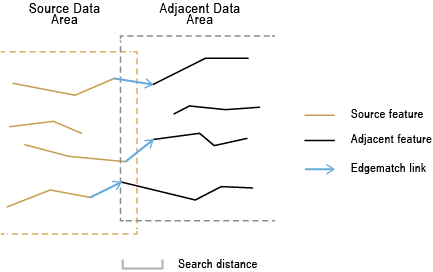
Finds matching but disconnected line features along the edges of the source data's area and its adjacent data's area, and generates edgematch links from the source lines to the matched adjacent lines.
Illustration
Usage
Line features of separate adjacent datasets, such as roads of neighboring countries, may have gaps or be shifted along their meeting edges due to inconsistent data collections or other reasons. You can resolve the edgematching problem between two datasets at a time using this tool to generate edgematch links. Then use the Edgematch Features tool to adjust features so they connect. The two sets of line features are referred to as source features and adjacent features. This tool finds disjoint but corresponding source and adjacent lines within the specified search distance and generates lines representing edgematch links (also known as displacement links) between them.
When two disconnected corresponding features along the edge area are within the search distance to each other, but their endpoints are more than the search distance apart, they will not be considered for edgematching.
Note:
All inputs must be in the same coordinate system.
The output feature class uses the same coordinate system as the inputs.
The output feature class contains line features representing edgematch links with the following fields:
- SRC_FID—The source feature ID at the starting points of the links.
- ADJ_FID—The adjacent feature ID at the ending points of the links.
- EM_CONF—Values representing the edgematching level of confidence. These values account for the number of candidates found within the search distance, the attribute match situations, and continuities between source and adjacent features. The value ranges from greater than 0 to 100 in which 100 represents the highest level of confidence. The higher the EM_CONF value, the better chance the link will be correct. See examples in About edgematching.
The Search Distance parameter is used in finding match candidates. Use a distance large enough to catch most of the shifts between corresponding features, but not too large to cause unnecessary processing of too many candidates and potentially getting wrong matches.
Once match candidates are found, the characteristics of their shapes are analyzed. A match is determined between the source and adjacent features that make the best continuation. A line representing the edgematch link is generated from the end of the source line to the end of the matched adjacent line.
You can display these links on a map as you would any other line features. The lines can be drawn with an arrow at each end to produce a map similar to the illustration above.
If you specify one or more pairs of fields for the Match Fields parameter, spatially matched features will be compared to the field values. For example, the update and base features both have a STREET_NAME field containing street names. If a source feature spatially matches two adjacent features but only one adjacent candidate has the same STREET_NAME value as the source feature, it is the better match. The comparison of text strings is not case sensitive, meaning that First St is considered the same as first st.
The attribute match conditions affect the values in the EM_CONF field as described above.
Edgematching accuracy relies on data quality and complexity along the edges of the two inputs.
Minimize data errors and select relevant features as input through preprocessing. In general, it is helpful when the features in an input dataset are topologically correct, have valid geometry, and are singlepart and not duplicate; otherwise, unexpected results may occur.
It is recommended that you review the results and make necessary corrections. During postinspection and postediting, you can use the existing editing tools to edit the links, for example, to delete a link, alter a link by moving its start or end vertex, or add a new link. Update the SRC_FID and TGT_FID field values accordingly.
Parameters
arcpy.edit.GenerateEdgematchLinks(source_features, adjacent_features, out_feature_class, search_distance, {match_fields})| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
source_features | The line features that will be used as edgematching source features. All edgematch links start at source features. | Feature Layer |
adjacent_features | The line features that are adjacent to the source features. All edgematch links end at matched adjacent features. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The output feature class containing lines representing edgematch links. | Feature Class |
search_distance | The distance that will be used to search for match candidates. A distance must be specified and it must be greater than zero. You can choose a preferred unit. The default is the feature unit. | Linear Unit |
match_fields [[source_field, target_field],...] (Optional) | The fields from the source and target features in which the target fields are from the adjacent features. If provided, each pair of fields will be checked for match candidates to help determine the right match. | Value Table |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the GenerateEdgematchLinks function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.edit.GenerateEdgematchLinks("countyA_Roads.shp",
"countyB_Roads.shp", "em_Links.shp"
"25 Feet")The following stand-alone script is a simple example of how to apply the GenerateEdgematchLinks function in a scripting environment.
"""
Name: EdgematchFeatures_example_script2.py
Description: Performs edgematching spatial adjustment using links produced by
GenerateEdgematchLinks. The links go from input features to adjacent
features. The links are then checked for intersecting conditions, which
may not be desired. They are then used to adjust input features
(a copy is made) to connect to the matched adjacent features.
"""
# Import system modules.
import arcpy
# Set environment settings.
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
arcpy.env.workspace = r"D:\conflationTools\ScriptExamples\data.gdb"
# Set local variables.
inFeatures = "roads1"
adjFeatures = "roads2"
gelOutput = "gelinks_out"
search_distance = "200 Feet"
match_fields = "NAME ROAD_NAME"
qaLocations = "qa_locations"
# Generate rubbersheet links.
arcpy.edit.GenerateEdgematchLinks(inFeatures, adjFeatures, gelOutput, search_distance, match_fields)
"""
Note 1: The result of GenerateEdgematchLinks may contain errors; see the tool reference.
Inspection and editing may be necessary to ensure correct links before using
them for edgematching.
One of the possible errors is intersecting or touching links.
Their locations can be found by the process below.
"""
# Find locations where links intersect or touch. The result contains coincident points.
arcpy.analysis.Intersect(gelOutput, qaLocations, "", "", "POINT")
# Delete coincident points.
arcpy.management.DeleteIdentical(qaLocations, "Shape")
"""
Note 2: You can manually inspect locations in qaLocations and delete or
modify links as needed.
"""
# Make a copy of the inFeatures for edgematching.
inFeature_Copy = inFeatures + "_Copy"
arcpy.management.CopyFeatures(inFeatures, inFeature_Copy)
# Use the links to adjust the copy of the input features.
arcpy.edit.EdgematchFeatures(inFeature_Copy, gelOutput, "MOVE_ENDPOINT")Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: No
- Standard: No
- Advanced: Yes