| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
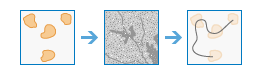
Input Regions Raster or Features | The input regions that are to be connected by the least-cost network. Regions can be defined by either an image service or a feature service. If the region input is a raster, the regions are defined by groups of contiguous (adjacent) cells of the same value. Each region must be uniquely numbered. The cells that are not part of any region must be NoData. The raster type must be integer, and the values can be either positive or negative. If the region input is a feature, it can be polygons, lines, or points. Polygon feature regions cannot be composed of multipart polygons. | Raster Layer; Image Service; Feature Layer; String |
Input Cost Raster | A raster defining the impedance or cost to move planimetrically through each cell. The value at each cell location represents the cost-per-unit distance for moving through the cell. Each cell location value is multiplied by the cell resolution while also compensating for diagonal movement to obtain the total cost of passing through the cell. The values of the cost raster can be integer or floating point, but they cannot be negative or zero (you cannot have a negative or zero cost). | Raster Layer; Image Service; String |
Output Optimum Network Name | The name of the output optimum network feature service. The polyline feature service of the optimum (least-cost) network of paths necessary to connect each of the input regions. Each path (or line) is uniquely numbered, and additional fields in the attribute table store specific information about the path. Those fields include the following:
This information provides you insight into the paths within the network. Since each path is represented by a unique line, there will be multiple lines in locations where paths travel the same route. | String |
Output Neighbor Network Name (Optional) | The name of the output Neighbor network feature service. The polyline feature service identifying all paths from each region to each of its closest-cost neighbors. Each path (or line) is uniquely numbered, and additional fields in the attribute table store specific information about the path. Those fields include the following:
This information provides you insight into the paths within the network and is particularly useful when deciding which paths should be removed if necessary. Since each path is represented by a unique line, there will be multiple lines in locations where paths travel the same route. | String |
Derived Output
| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
| Output Optimum Network Features | The output optimum network features. | Raster Layer |
| Output Neighbor Network Features | The output neighbor network features. | Feature Class |