Zusammenfassung
The Parse Path tool parses the input into its file, path, name, or extension. The output can be used as inline variable in the output name of other tools.
Ältere Versionen:
This is a deprecated tool. This functionality has been replaced by the new Parse Path tool.
Verwendung
Dieses Werkzeug ist nur für die Verwendung in ModelBuilder, nicht in Python-Skripten vorgesehen.
Parsing results are controlled by the Parse Type parameter. Example: If the input to the Parse Path tool is C:\ToolData\InputFC.shp, then
Parse Type Result File name and extension InputFC.shp File path C:\ToolData File name InputFC File extension shp The same functionality can be accessed in scripting with the Python os module. For example if you pass an input variable:
Input = "C:\ToolData\InputFC.shp", then
- To get the file InputFC.shp
import os os.path.basename(Input) - To get the file path C:\ToolData
import os os.path.dirname(Input) - To get the file name InputFC
import os os.path.basename(Input).rstrip(os.path.splitext(Input)[1]) - To get the file extension shp
import os os.path.splitext(Input)[1].lstrip(".")
- To get the file InputFC.shp
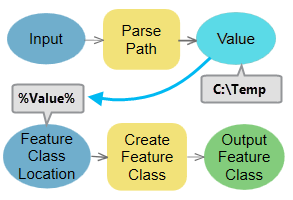
The output of Parse Path is a string and cannot be connected directly as an input to the tools such as Create Feature Class in parameters like Feature Class Location which requires a workspace data type as input. Use %Value% inline variable substitution in such cases as shown below:
Syntax
ParsePath(in_data_element, {parse_type})| Parameter | Erklärung | Datentyp |
in_data_element | Input values that you want to parse. | Any value |
parse_type (optional) | The parse type. Given the input value of C:\ToolData\InputFC.shp:
| String |
Abgeleitete Ausgabe
| Name | Erklärung | Datentyp |
| value |
Umgebungen
Lizenzinformationen
- Basic: Ja
- Standard: Ja
- Advanced: Ja