To use ArcGIS Bathymetry tools in ArcGIS Pro, you need to create at least one Bathymetric Information System (BIS) workspace. The BIS is a geodatabase that contains a catalog of spatial data. Since the BIS manages the location of datasets rather than loading the datasets directly into the geodatabase, file system data storage requirements are reduced, resulting in a highly scalable information model.
You can create a BIS using the Create BIS tool in the Bathymetry toolbox. The BIS must be created in an existing database; it can be created in either a file or enterprise geodatabase and can reference data stored locally or on a network.
Learn more about creating a Bathymetry workspace in an enterprise geodatabase
There are four schema templates provided with the ArcGIS Bathymetry extension that you can use to create a BIS: the basic BisCatalog schema containing default metadata fields, the Bathymetric Attributed Grid (BAG) schema, the S-102 schema, and the combined BAG plus S-102 schema. You can expand the preconfigured BIS templates to create the most relevant and useful BIS geodatabase for your organization. Custom BIS metadata allows you to produce high-quality authoritative content that can be used to publish maps, perform analysis, and share the results throughout your organization.
When creating a BIS, the coordinate system you choose is used to store and manage the BisCatalog and Bathymetric Data Index (BisBDI) mosaic dataset. If no coordinate system is chosen when the BIS is created, the BIS uses GCS WGS84.
Hinweis:
A BIS created at ArcGIS Pro 3.1 is not compatible with ArcGIS Bathymetry tools at ArcGIS Pro 3.2 and later. A new BIS must be created with the Create BIS tool to use with Bathymetry tools at version 3.2 and later.
To create a BIS, complete the following steps:
- Start ArcGIS Pro.
- Open a new or existing project.
- On the Analysis tab, in the Geoprocessing group, click Tools
 .
.The Geoprocessing pane appears.
- On the Toolboxes tab of the Geoprocessing pane, expand Bathymetry > BIS Management, and click Create BIS.
The Create BIS tool opens in the Geoprocessing pane.
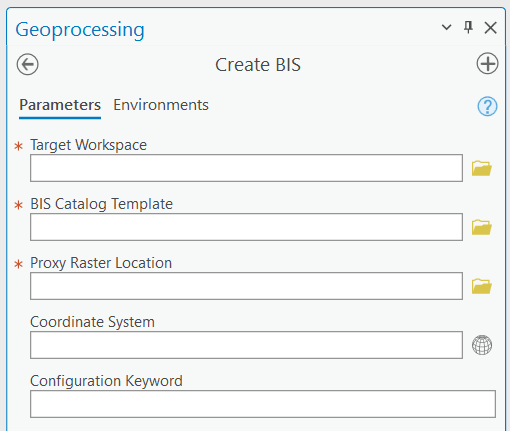
- For the Target Workspace parameter, click Browse
 and choose the file or enterprise geodatabase you want to use as the BIS.
and choose the file or enterprise geodatabase you want to use as the BIS. Hinweis:
It is recommended that you create the BIS in an empty workspace.
- For the BIS Catalog Template parameter, browse to <installation location>\ArcGIS\Pro\Resources\Bathymetry and double-click BISCatalog_schema_MGDB.geodatabase.
- Choose one of the following BIS schema templates:
- main.BisCatalog_schema—Contains the default BisCatalog metadata fields
- main.BisCatalog_bag_schema—Contains the default BisCatalog metadata and BAG fields
- main.BisCatalog_s102_schema—Contains the default BisCatalog metadata and S-102 fields
- main.BisCatalog_bag_s102_schema—Contains the default BisCatalog metadata, BAG, and S-102 fields
- Click OK to add the template.
Hinweis:
It is recommended that you copy the schema file to a new location if you want to extend or modify the default configuration.
- For the Proxy Raster Location parameter, choose the directory where you want to store the proxy raster .tif files.
Proxy rasters are automatically created when point cloud data is added to the BIS.
Hinweis:
It is important that you use a unique proxy raster folder for each BIS you create; otherwise rasters that do not match a BIS may be flagged or removed when running the Analyze BIS tool.
- Optionally, click Select coordinate system
 to choose a coordinate system to be used for the BIS.
to choose a coordinate system to be used for the BIS. If no coordinate system is chosen, WGS84 is used.
- Optionally, under Geodatabase Settings, provide a value for the Configuration Keyword parameter.
The configuration keyword determines the storage parameters of the database table; it only applies to data in an enterprise geodatabase.
- Click Run.
A BIS is created in the geodatabase that was provided as the target workspace. If the BIS was created in an enterprise geodatabase, you may want to enable editor tracking to keep track of who edits features and when the edits are made.