Zusammenfassung
An extent is a rectangle specified by providing the coordinate of the lower left corner and the coordinate of the upper right corner in map units.
Diskussion
The Extent object supports equal (==) and not equal (!=) operators for comparing extents.
Hinweis:
When used as input to Erweiterung "ArcGIS Spatial Analyst" tools—Create Constant Raster, Create Normal Raster, Create Random Raster, Extract By Rectangle, Extract by Mask, and Topo To Raster—only the XMin, YMin, XMax, and YMax values are used by these tools.
Syntax
Extent ({XMin}, {YMin}, {XMax}, {YMax}, {ZMin}, {ZMax}, {MMin}, {MMax}, {spatial_reference})| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
XMin | The extent XMin value. | Double |
YMin | The extent YMin value. | Double |
XMax | The extent XMax value. | Double |
YMax | The extent YMax value. | Double |
ZMin | The extent ZMin value. The value is None if there is no z-value. | Double |
ZMax | The extent ZMax value. The value is None if there is no z-value. | Double |
MMin | The extent MMin value. The value is None if there is no m-value. | Double |
MMax | The extent MMax value. The value is None if there is no m-value. | Double |
spatial_reference | The spatial reference of the extent. | SpatialReference |
Eigenschaften
| Eigenschaft | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
| JSON (Schreibgeschützt) | A JSON representation of the extent as a string. Tipp:The returned string can be converted to a dictionary using the json module's loads function. | String |
| MMax (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent MMax value. The value is None if there is no m-value. | Double |
| MMin (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent MMin value. The value is None if there is no m-value. | Double |
| XMax (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent XMax value. | Double |
| XMin (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent XMin value. | Double |
| YMax (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent YMax value. | Double |
| YMin (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent YMin value. | Double |
| ZMax (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent ZMax value. The value is None if there is no z-value. | Double |
| ZMin (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent ZMin value. The value is None if there is no z-value. | Double |
| depth (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent depth value. The value is None if there is no depth value. | Double |
| geohash (Schreibgeschützt) | A geohash string of the extent. | String |
| geohashCovers (Schreibgeschützt) | A list of up to the four longest geohash strings that fit within the extent. | String |
| geohashNeighbors (Schreibgeschützt) | A list of the geohash neighbor strings for the extent. | String |
| height (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent height value. | Double |
| lowerLeft (Schreibgeschützt) | The lower left property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| lowerRight (Schreibgeschützt) | The lower right property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| polygon (Schreibgeschützt) | Returns the extent as a polygon object. | Polygon |
| spatialReference (Schreibgeschützt) | The spatial reference of the extent. | SpatialReference |
| upperLeft (Schreibgeschützt) | The upper left property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| upperRight (Schreibgeschützt) | The upper right property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| width (Schreibgeschützt) | The extent width. | Double |
Methodenübersicht
| Methode | Erläuterung |
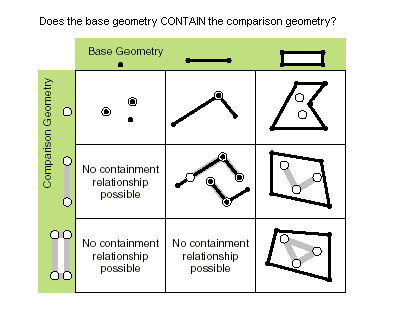
| contains (second_geometry, {relation}) | Specifies whether the base geometry contains the comparison geometry. The contains method is the opposite of the within method. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
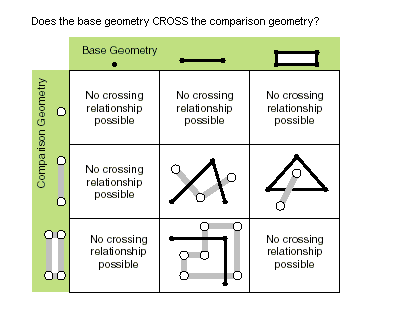
| crosses (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the two geometries intersect in a geometry of a lesser shape type. Two polylines cross if they share only points in common, at least one of which is not an endpoint. A polyline and a polygon cross if they share a polyline or a point (for a vertical line) in common on the interior of the polygon that is not equivalent to the entire polyline. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
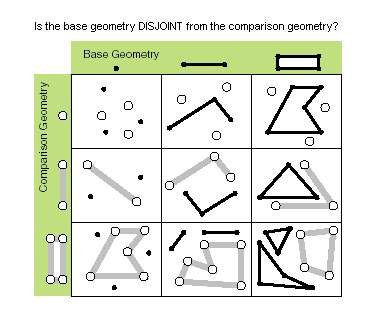
| disjoint (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the base and comparison geometries have points in common. Two geometries intersect when this method returns False. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
| equals (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the base and comparison geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. This is a 2D comparison only; m- and z-values are ignored. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
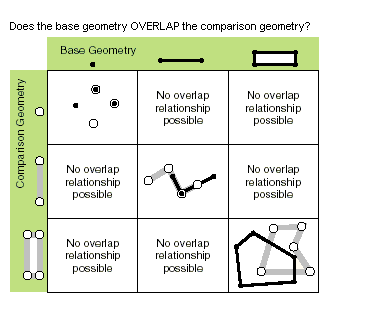
| overlaps (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the intersection of the two geometries has the same shape type as one of the input geometries and is not equivalent to either of the input geometries. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
| projectAs (spatial_reference, {transformation_name}) | Projects a geometry from one spatial reference to another. When the geometry object and the destination spatial reference do not have a common datum, specify a transformation_name parameter value. For more information, see Geographic datum transformations and ListTransformations. A vertical transformation will be performed when the following criteria are met:
When the transformation_name parameter value is a vertical transformation, and neither the geometry object nor the destination spatial reference have a vertical coordinate system, the function will fail with a ValueError exception. If either the geometry object or the spatial_reference parameter value have an unknown spatial reference, the output geometry's spatial reference will be that of the spatial_reference parameter value. Use of unknown spatial reference is not recommended for analysis. The projectAs method will not modify m-values, if present. |
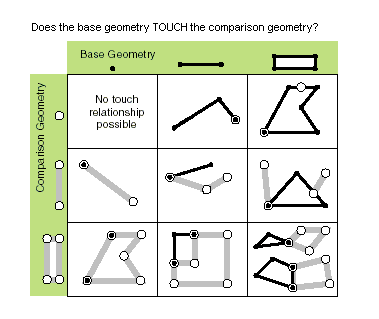
| touches (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the boundaries of the geometries intersect. Two geometries touch when the intersection of the geometries is not empty, but the intersection of their interiors is empty. For example, a point touches a polyline only if the point is coincident with one of the polyline end points. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
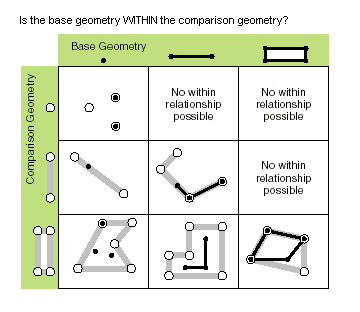
| within (second_geometry, {relation}) | Specifies whether the base geometry is within the comparison geometry. The within method is the opposite operator of the contains method. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
The base geometry is within the comparison geometry if the base geometry is the intersection of the geometries, and the intersection of their interiors is not empty. The within method is a Clementini operator, except in the case of an empty base geometry. |
Methoden
contains (second_geometry, {relation})| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | Specifies the spatial relationship type that will be used.
(Der Standardwert ist None) | String |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean |
Returns whether this geometry contains the second geometry. |
crosses (second_geometry)
| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean | Returns whether the two geometries intersect in a geometry of a lesser shape type. |
disjoint (second_geometry)
| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean | Returns whether the two geometries have points in common. |
equals (second_geometry)
| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean |
Returns whether the two geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. |
overlaps (second_geometry)
| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean | Returns whether the intersection of the two geometries has the same dimension as one of the input geometries. |
projectAs (spatial_reference, {transformation_name})| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
spatial_reference | The spatial reference to which the geometry will be projected. The value can be a SpatialReference object or the coordinate system name. | SpatialReference |
transformation_name | The geotransformation name. With ArcGIS Pro, if you do not specify a transformation, none will be applied. With ArcGIS Server, if you do not specify a transformation, a fallback transformation will be applied. | String |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Object | The projected geometry. |
touches (second_geometry)
| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean | Returns whether the boundaries of the geometries intersect. |
within (second_geometry, {relation})| Parameter | Erläuterung | Datentyp |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | Specifies the spatial relationship type that will be used.
(Der Standardwert ist None) | String |
| Datentyp | Erläuterung |
| Boolean | Returns whether the base geometry is within the comparison geometry. |
Codebeispiel
Display extent object properties for features.
import arcpy
feature_class = 'c:/Data/Florida.gdb/airports'
# Fetch each feature from the cursor and examine the extent properties
for row in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(feature_class, ['SHAPE@', 'CNTY_NAME']):
extent = row[0].extent
print('Extent of county {}:'.format(row[1]))
print('XMin: {}, YMin: {}'.format(extent.XMin, extent.YMin))
print('XMax: {}, YMax: {}'.format(extent.XMax, extent.YMax))