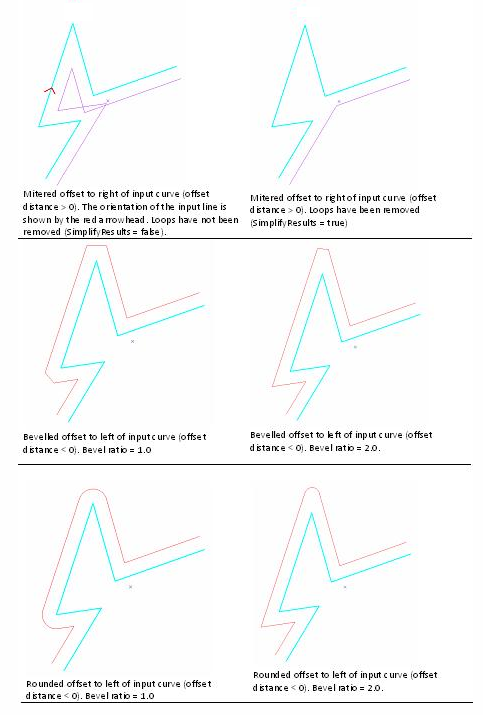
List<MapPoint> linePts = new List<MapPoint>();
linePts.Add(MapPointBuilder.CreateMapPoint(1.0, 1.0, SpatialReferences.WGS84));
linePts.Add(MapPointBuilder.CreateMapPoint(10.0, 1.0, SpatialReferences.WGS84));
Polyline polyline = PolylineBuilder.CreatePolyline(linePts);
Geometry g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polyline, 10, OffsetType.Square, 0);
Polyline gResult = g as Polyline;
// gResult.PointCount = 2
// gResult.Points[0] = (1, -9)
// gResult.Points[1] = (10, -9)
g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polyline, -10, OffsetType.Round, 0.5);
gResult = g as Polyline;
// gResult.PointCount = 2
// gResult.Points[0] = (1, -11
// gResult.Points[1] = (10, 11)
//
// elliptic arc curve
//
Coordinate2D fromPt = new Coordinate2D(2, 1);
Coordinate2D toPt = new Coordinate2D(1, 2);
Coordinate2D interiorPt = new Coordinate2D(1 + Math.Sqrt(2) / 2, 1 + Math.Sqrt(2) / 2);
EllipticArcSegment circularArc = EllipticArcBuilder.CreateEllipticArcSegment(fromPt.ToMapPoint(), toPt.ToMapPoint(), interiorPt);
polyline = PolylineBuilder.CreatePolyline(circularArc);
g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polyline, -0.25, OffsetType.Miter, 0.5);
gResult = g as Polyline;
g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polyline, 0.25, OffsetType.Bevel, 0.5);
gResult = g as Polyline;
//
// offset for a polygon
//
List<MapPoint> list = new List<MapPoint>();
list.Add(MapPointBuilder.CreateMapPoint(10.0, 10.0, SpatialReferences.WGS84));
list.Add(MapPointBuilder.CreateMapPoint(10.0, 20.0, SpatialReferences.WGS84));
list.Add(MapPointBuilder.CreateMapPoint(20.0, 20.0, SpatialReferences.WGS84));
list.Add(MapPointBuilder.CreateMapPoint(20.0, 10.0, SpatialReferences.WGS84));
Polygon polygon = PolygonBuilder.CreatePolygon(list);
g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polygon, 2, OffsetType.Square, 0);
Polygon gPolygon = g as Polygon;
g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polygon, -2, OffsetType.Round, 0.3);
gPolygon = g as Polygon;
g = GeometryEngine.Instance.Offset(polygon, -0.5, OffsetType.Miter, 0.6);
gPolygon = g as Polygon;