Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Available with Image Analyst license.
Available with 3D Analyst license.
Summary
Converts each cell value of a raster to an integer by truncation.
Illustration
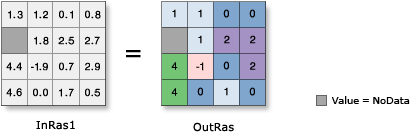
Usage
The input values can be either positive or negative.
If rounding is preferred to truncating, add a 0.5 input raster prior to performing the operation.
There is a difference between the Int tool and the Round Down tool. For example, given the following two values, Int always truncates the number:
- 1.5 becomes 1
- -1.5 becomes -1
For the same two values, Round Down returns the following:
- 1.5 becomes 1.0
- -1.5 becomes -2.0
Another difference is that Round Down outputs floating-point values, while Int only outputs integer values.
The maximum supported range of integer raster values is -2,147,483,648 (minimum size determined by -231) to 2,147,483,647 (maximum size determined by 231 – 1). If Int is used on a floating-point raster which has cells with values outside this range, those cells will be NoData in the output raster.
Storing categorical (discrete) data as an integer raster will use significantly less disk space than the same information stored as a floating-point raster. Whenever possible, it is recommended to convert floating-point rasters to integer with this tool.
If the input is a multiband raster, the output will be a multiband raster. The tool will perform the operation on each band in the input.
See Analysis environments and Spatial Analyst for additional details on the geoprocessing environments that apply to this tool.
Syntax
Int(in_raster_or_constant)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster_or_constant | The input raster to be converted to integer. To use a number as an input for this parameter, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster. The cell values are the input values converted to integers by truncation. | Raster |
Code sample
This example converts the input values to integer by truncation.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outInt = Int("gwhead")
outInt.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outint2")This example converts the input values to integer by truncation.
# Name: Int_Ex_02.py
# Description: Converts each cell value of a raster to an integer by truncation
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster = "gwhead"
# Execute Int
outInt = Int(inRaster)
# Save the output
outInt.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outint")Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Requires Spatial Analyst or Image Analyst or 3D Analyst
- Standard: Requires Spatial Analyst or Image Analyst or 3D Analyst
- Advanced: Requires Spatial Analyst or Image Analyst or 3D Analyst