This geoprocessing tool is available with ArcGIS Enterprise 10.9 or later.
The result of Calculate Motion Statistics is a copy of the input points with a new field for each calculated statistic.
You can specify one or more fields to identify unique entities, also known as tracks. Tracks are represented by the unique combination of one or more track fields. For example, if the flightID and Destination fields are used as track identifiers, the ID007, Solden, ID007, and Tokoyo features would be in two separate tracks, since they have different Destination field values.
By default, all supported statistics will be calculated for each input point if possible. Alternatively, you can choose one or more groups of statistics to calculate using the Motion Statistics parameter.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Distance group:
- Distance—Distance traveled from the previous observation to the current.
- TotDistance—Sum of distances traveled between observations in the track history window.
- MinDistance—Minimum of distances traveled between observations in the track history window.
- MaxDistance—Maximum of distances traveled between observations in the track history window.
- AvgDistance—Average of distances traveled between observations in the track history window.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Speed group:
- Speed—Speed of travel from the previous observation to the current.
- MinSpeed—Minimum speed between observations in the track history window.
- MaxSpeed—Maximum speed between observations in the track history window.
- AvgSpeed—Sum of distances between observations in the track history window divided by the sum of durations between observations in the track history window.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Acceleration group:
- Acceleration—Difference between the current speed and previous speed divided by the current duration.
- MinAcceleration—Minimum acceleration calculated in the track history window.
- MaxAcceleration—Maximum acceleration calculated in the track history window.
- AvgAcceleration—Difference between the current and first speeds in the track history window divided by the sum of durations between observations in the track history window.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Duration group:
- Duration—Elapsed time since the previous observation.
- TotDuration—Sum of durations in the track history window.
- MinDuration—Minimum duration in the track history window.
- MaxDuration—Maximum duration in the track history window.
- AvgDuration—Sum of durations in the track history window divided by the number of durations calculated in the track history window.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Elevation group:
- Elevation—Current elevation of the observation.
- ElevChange—Difference between the current elevation and the previous elevation.
- TotElevChange—Sum of elevation changes between points in the track history window.
This can be a negative value.
- MinElevation—Minimum elevation in the track history window.
- MaxElevation—Maximum elevation in the track history window.
- AvgElevation—Sum of elevations in the track history window divided by the number of observations in the track history window.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Slope group:
- Slope—Ratio of elevation change to distance between the current and previous observations.
- MinSlope—Minimum slope in the track history window.
- MaxSlope—Maximum slope in the track history window.
- AvgSlope—Sum of slopes in the track history window divided by the number of slopes calculated in the track history window.
The following statistics fields will be calculated for the Idle group:
- Idling—True if the distance between the current observation and the previous is less than the Idle Distance Tolerance parameter value, and the duration between the current observation and the previous is greater than the Idle Time Tolerance parameter value. False if one or both of these conditions are not met.
- TotIdleTime—Sum of durations in the track history window that meet idling criteria.
- PctIdleTime—Percentage of time for which idling was detected.
The following statistics field will be calculated for the Bearing group:
- Bearing—Angle of travel from the previous observation to the current observation.
Statistics starting with Min, Max, Avg, or Tot will be calculated using the current observation and a number of previous observations defined by the Track History Window parameter. Other statistics are always calculated using only the current and previous observation and do not consider the Track History Window values. For example, if you set a Track History Window value of 5 and request the Speed statistic group, the current observation and the previous 4 observations will be used to calculate the MinSpeed, MaxSpeed, and AvgSpeed fields at each observation, while the Speed field will be calculated using only the current and previous observations at each point. The Track History Window parameter value must be greater than 1. The default is 3.
The diagram below shows a track with six point features. The statistics are calculated based on each feature's elevation, distance, and time.
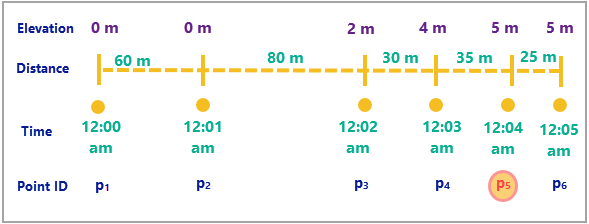
The following table summarizes the statistics calculations for the diagram above. All calculations are evaluated at point 5 and the track history window is 3. An observation is considered idling if it has moved less than 32 meters in 1 minute.
| Statistic | Formula | Example |
|---|
Distance | | 35 m |
Total Distance | | 80 + 30 + 35 = 145 m |
Speed | Distance / Duration | 35 / 60 = 0.58 m/s |
Average Speed | Total Distance / Total Duration | 145 / 180 m/s |
Acceleration | | (0.58 – 0.5) / 60 = 0.001 m/s2 |
Average Acceleration | (Speed (last) – Speed (first)) / (Total Duration) | (0.58 – 1.33) / 60 = -0.01 m/s2 |
Duration | | 60 s |
Total Duration | | 60 + 60 + 60 = 180 s |
Elevation | | 5 m |
Elevation Change | | 5 – 4 = 1 m |
Total Elevation Change | | 5 – 0 = 5 m |
Slope | Elevation Change / Distance | 1 / 35 |
Average Slope | Total Elevation Change / Total Distance | 5 / 145 |
Idling | | False |
Total Idle Time | | 60 s |
Percentage Idle Time | | 1 / 3 |
Bearing | | 0 |
If there are fewer observations in a track's history than the Track History Window parameter value, statistics starting with Min, Max, Avg, or Tot will be calculated using all observations in the track history.
Statistics will not be calculated for the first feature in each track. Statistics in the Acceleration group will not be calculated for the first two features in each track.
The result values will be in the units specified by the Distance Unit, Duration Unit, Speed Unit, Acceleration Unit, and Elevation Unit parameters.
When calculating statistics on large tracks, you can use the Time Boundary Split parameter to split the large tracks into smaller tracks to improve performance.
This geoprocessing tool is powered by ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server. Analysis is completed on GeoAnalytics Server, and results are stored in your content in ArcGIS Enterprise.
When running GeoAnalytics Server tools, the analysis is completed on GeoAnalytics Server. For optimal performance, make data available to GeoAnalytics Server through feature layers hosted on your ArcGIS Enterprise portal or through big data file shares. Data that is not local to GeoAnalytics Server will be moved to GeoAnalytics Server before analysis begins. This means that it will take longer to run a tool and, in some cases, moving the data from ArcGIS Pro to GeoAnalytics Server may fail. The threshold for failure depends on your network speeds, as well as the size and complexity of the data. It is recommended that you always share your data or create a big data file share.
Learn more about sharing data to your portal
Learn more about creating a big data file share through Server Manager
You can improve the performance of the Calculate Motion Statistics tool by doing any or all of the following:
- Set the extent environment so you only analyze data of interest.
- Decrease the Track History Window parameter value.
- Use the Time Boundary Split parameter to break up large tracks at a defined time interval.
- Use data that is local to where the analysis is being run.

