| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Input Features | The input features, which can be line, polygon, or both. | Feature Layer |
Output Feature Class | The output polygon feature class. | Feature Class |
XY Tolerance (Optional) | The minimum distance separating all feature coordinates, and the distance a coordinate can move in X, Y, or both during spatial computation. The default XY tolerance is set to 0.001 meter or its equivalent in feature units. Caution:Changing this parameter's value may cause failure or unexpected results. It is recommended that you do not modify this parameter. It has been removed from view on the tool dialog box. By default, the input feature class's spatial reference x,y tolerance property is used. | Linear Unit |
Preserve attributes (Optional) | Note:This parameter is no longer supported. The parameter remains for backward compatibility of scripts and models. See the Usage section for more information. | Boolean |
Label Features (Optional) | The optional input point features that contain the attributes to be transferred to the output polygon features. | Feature Layer |
Summary
Creates a feature class containing polygons generated from areas enclosed by input line or polygon features.
Illustration
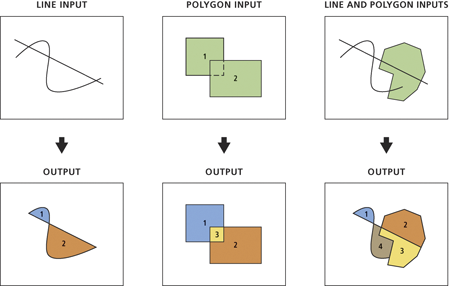
Usage
Where one or more input features form a closed area, a new polygon feature will be constructed and written to the output feature class. The output attributes will vary depending on the Preserve attributes parameter value and the Label Features parameter value.
When multiple feature classes or layers are specified in the list of input features, the order of the entries in the list does not affect the output feature type, but the spatial reference of the top entry on the tool dialog box (the first entry in Python) in the list will be used during processing and set to the output.
Parametric (true) curves in the input features will remain true curves in the output polygons, even if they are split. This does not apply to shapefile data.
Note:
It is recommended that you do not use the Preserve attributes parameter, as it is no longer supported and does not work. It will remain, however, for backward compatibility of scripts and models. While the output attribute schema and field values for certain input combinations may be produced as described below, most of them are unintended.
If the Preserve attributes parameter is checked, the output attribute schema and field values will depend on whether the label features (points) are provided in the following ways:
- If no Label Features parameter values are provided, the attribute schema (field names and properties, not field values) from each input entry will be maintained in the output in the order they appear in the input list. A new field, FID_xxx, in which xxx is the source feature class name of a particular input entry, will be added to the output for each input entry and set to the value of -1. All other fields will have zero or null values.
- If a Label Features parameter value is provided, no input attribute schemas will be maintained in the output feature class; only the attributes of the label features will be included in the output feature class. If an output polygon contains a label feature, it will have field values from that label feature. If an output polygon contains more than one label feature, it will have field values from one of them; otherwise, it will have zero or null field values.
If the Preserve attributes parameter is unchecked, the input attribute schemas will be written to the output; however, the attribute values will be empty. If you do not want attributes in the output polygon feature class, supply a point feature class that has no attributes for the Label Features parameter.
When input polygon features are broken into smaller output polygon features, you can use the Identity tool to transfer attributes from the input polygon features to the resulting polygon features.
For better performance and scalability, this tool uses a tiling process to handle very large datasets. For details, see Tiled processing of large datasets.
Parameters
arcpy.management.FeatureToPolygon(in_features, out_feature_class, {cluster_tolerance}, {attributes}, {label_features})| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features [in_features,...] | The input features, which can be line, polygon, or both. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The output polygon feature class. | Feature Class |
cluster_tolerance (Optional) | The minimum distance separating all feature coordinates, and the distance a coordinate can move in X, Y, or both during spatial computation. The default XY tolerance is set to 0.001 meter or its equivalent in feature units. Caution:Changing this parameter's value may cause failure or unexpected results. It is recommended that you do not modify this parameter. It has been removed from view on the tool dialog box. By default, the input feature class's spatial reference x,y tolerance property is used. | Linear Unit |
attributes (Optional) | Note:This parameter is no longer supported. The parameter remains for backward compatibility of scripts and models. See the Usage section for more information. | Boolean |
label_features (Optional) | The optional input point features that contain the attributes to be transferred to the output polygon features. | Feature Layer |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the FeatureToPolygon function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.management.FeatureToPolygon(["mainroads.shp","streets.shp"],
"c:/output/output.gdb/streetblocks",
"", "NO_ATTRIBUTES")The following stand-alone script is a simple example of how to apply the FeatureToPolygon function in a scripting environment.
# Name: FeatureToPolygon_Example2.py
# Description: Use FeatureToPolygon function to construct habitat areas
# from park boundaries and rivers.
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Set environment settings
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/parks_analysis.gdb"
# Set local parameters
inFeatures = ["park_boundaries", "rivers"]
outFeatureClass = "c:/output/output.gdb/habitat_areas"
clusTol = "0.05 Meters"
# Use the FeatureToPolygon function to form new areas
arcpy.management.FeatureToPolygon(inFeatures, outFeatureClass, clusTol,
"NO_ATTRIBUTES")Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: No
- Standard: Yes
- Advanced: Yes