Available with Standard or Advanced license.
Available for an ArcGIS organization with the ArcGIS Reality license.
Gaussian splats is a photo realistic 3D model created using high density points with an elliptical Gaussian distribution—called splats—instead of triangulated meshes used in 3D mesh generation. The splats are used with machine learning techniques to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D scenes that captures fine details like thin structures. For best results, create Gaussian Splats from multi-angle aerial or drone imagery. Satellite imagery is not supported for this layer. Gaussian splats are provided in 3D tile format and can be viewed using the ArcGIS Pro scene viewer. The Gaussian splats product generation wizard simplifies the workflow with predefined, sensor-based parameters for high-quality layer generation.
Before you begin the workflow, ensure that your computer meets the minimum software and hardware requirements listed below for Gaussian Splats generation.
- A current CPU with minimum 64 GB of RAM and a Nvidia GPU with minimum 8 GB VRAM and a compute capability of 7.5 or higher. Check your computer’s compute capability.
- Installed ArcGIS Pro Deep Learning Libraries associated with your ArcGIS Pro version.
- Create a digital aerial or drone Reality mapping workspace, and complete the block adjustment process. Images previously adjusted does not require re-adjustment.
Gaussian splats generation is recommended from oblique imagery or a combination of oblique and nadir imagery with high overlap. Complete the following steps to download the ArcGIS Pro Deep Learning Libraries:
- Download the ArcGIS Pro Deep Learning Libraries associated with your ArcGIS Pro version to a known location on disk.
This requires 10 GB of space on your computer.
- If compressed, unzip the downloaded installer.
- Expand the folder containing the installer and double-click the ProDeepLearning.msi file to initiate installation.
- Follow the installer instructions.
- Click Finish when the installation is complete.
The deep learning libraries will be installed and available for use when generating the Gaussian splat product. Once installed, an entry similar to the following graphic can be seen in your installed software list when you click Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features > Uninstall or Change a Program.

Generate a Gaussian splats product
To generate Gaussian splats using the ArcGIS Reality for ArcGIS Pro product wizard, complete the following steps.
- On the Reality Mapping tab, click the Gaussian Splats button
 in the Product group.
in the Product group.If the Gaussian Splats button is unavailable but other Reality mapping products are available, either or both of the following is a possible cause:
- The required Deep Learning Libraries package is not installed.
- Your computer system does not meet the minimum hardware requirements.
See the workflow Prerequisite section above for additional information.
The Reality Mapping Products Wizard window appears.
- Click Shared Advanced Settings.
The Advanced Products Settings dialog box appears, where you can define parameters that will determine all Reality mapping products to be generated. For a detailed description of the advanced product settings options, click the Learn more about advanced product settings link at the bottom of the dialog box.
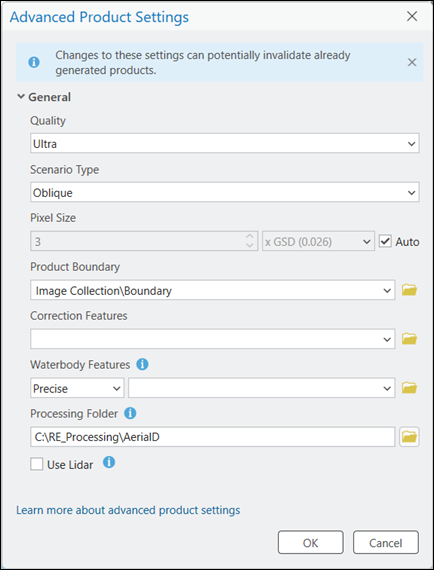
The Quality and Scenario Type settings are automatically set by the application and should not be changed to ensure optimum performance and product quality. However, if you want to generate a reduced resolution product, you can lower the Quality setting. See Shared Advanced Settings above for more information about the impact of the various Quality options on product generation.
- For Product Boundary, select a feature class identifying the output product extent from the drop-down list or click the Browse button
 and browse to one.
and browse to one. It is recommended that you specify a project boundary for the following reasons:
- Define the proper output extent—When you do not define a product boundary, the application automatically defines an extent based on various dataset parameters that may not match the project extent.
- Reduce processing time—If the required product extent is smaller than the image collection extent, defining a product boundary reduces the processing duration and automatically clips the output to the boundary extent.
- To specify a water body feature layer, click the Browse button
 next to Waterbody Features.
next to Waterbody Features.Note:
If water body features, such as lakes and rivers, exist within the project area, it is recommended that you add a pre-created 3D feature class identifying those areas, using the Waterbody Features setting to hydrologically enforce those features in the output product. Use the stereoscopic compilation in ArcGIS Image Analyst to generate the 3D feature layer that identifies water body features. This ensures that there will be no image stretching around hydrological feature boundaries in the output due to differences in elevation between the derived digital surface model (DSM) height and the feature class height values.
There are two Waterbody Features options: Precise and Coarse. Use the Precise option when the 3D polygon being added accurately defines the shape of the hydrological features in the project area. Precise polygons can be created using the stereoscopic compilation in ArcGIS Image Analyst. A precise water body polygon can also be derived from national mapping organizations with open data policies. Additionally, it can be created using 2D heads-up digitizing from an authoritative, orthorectified imagery that is temporally similar, with the aid of a DEM.
Use the Coarse option when a generalized 3D polygon is being used as the water body feature. Generalized polygons can be created using a 2D heads-up digitizing workflow. If 2D heads-up digitizing is used to create a precise or coarse polygon, it must be converted to 3D (x,y,z) before it can be used as a water body feature. See Introduction to 2D and 3D features for additional information about converting a 2D feature to 3D. When using a coarse water body feature, the shape of the polygon must follow the shape of the water body feature for best results.

- For Processing Folder, click the browse button
 , and browse to and define the Reality Mapping temporary folder location.
, and browse to and define the Reality Mapping temporary folder location. The temporary files required for generating 2D or 3D products are stored here.
- Ensure the Use LiDAR is unchecked.Lidar integration in Gaussian Splats product generation is not supported.
Note:
Lidar captured simultaneously with the images being processed can be integrated into the Reality mapping workflow at the workspace creation stage to enhance the quality of the True Ortho, DSM, DSM Mesh, and 3D Mesh products. This option will be unavailable if the lidar point cloud and trajectory data was not previously added to the workspace.
- Leave all the other default settings and click OK.
The Advanced Product Settings dialog box closes, and you are returned to the Products Generation Settings page in the Reality Mapping Products wizard.
- Click Finish to initiate product processing.
Gaussian splats will be generated in 3D tiles, which are supported in ArcGIS Pro.
When processing is complete, the Gaussian splats product is added to the Reality Mapping container in the Gaussian Splats folder in the Catalog pane.

- To visualize the generated Gaussian Splats layer, click Meshes > Gaussian Splats to expand the folder in the Reality Mapping container. Right-click the 3D_Tiles layer, and click Add to New > Local Scene
