The Create Fishnet tool creates a feature class containing a net of rectangular cells. Creating a fishnet requires three basic sets of information: the spatial extent of the fishnet, the number of rows and columns, and the angle of rotation. There are a variety of ways to specify this information. For example, you may not know the exact number of rows and columns, but you do know that each rectangular cell must be exactly 110 meters by 63 meters and must cover the spatial extent of another feature class.
The tool has 11 parameters, and you should think of these in four distinct groups:
- The spatial extent of the fishnet
- The number of rows and columns and height and width of each cell in the fishnet
- The angle of rotation for the fishnet
- The parameters that define the output feature class name and type (polygons or lines) and an optional point dataset containing centroids of each cell
Note:
The order of the parameters on the tool dialog box is different than the order of the parameters in the Python syntax.
Sett the spatial extent
You can set the extent of the fishnet by doing any one of the following:
- Provide an existing dataset in the Template Extent parameter. The extent of this dataset will be used as the extent of the fishnet.
- Provide both the minimum and maximum x- and y-coordinates in the Template Extent parameter.
- Provide an origin and opposite corner of the fishnet using the Fishnet Origin Coordinate and Opposite corner of Fishnet parameters.
- Provide an origin, cell size, and number of rows and columns in the Fishnet Origin Coordinate, Cell Size Width, Cell Size Height, Number of Rows, and Number of Columns parameters, respectively.
Set the number of rows and columns
If you set the extent of the fishnet using one of the first three options described above, you will need to set the number of rows and columns. You can specify the number of rows and columns by doing any one of the following:
- Define the cell width and height using the Cell Size Width and Cell Size Height parameters, and leave the Number of Rows and Number of Columns parameters empty or set them to 0. When the tool runs, it calculates the number of rows and columns needed to cover the extent of the fishnet.
- Define the cell width and height as above, but also provide the number of rows and columns.
- Define the number of rows and columns using the Number of Rows and Number of Columns parameters, and leave the Cell Size Width and Cell Size Height parameters empty or set them to 0. When the tool runs, it calculates the cell size width and height based on the number of rows and columns and the value of the Opposite corner of Fishnet parameter.
- Define the number of rows and columns as above, but also provide a cell size and width. When using doing it this way, the Opposite corner of Fishnet parameter is ignored (the parameter is unavailable on the tool dialog box). The opposite corner is calculated when the tool runs.
Angle of rotation
This is the angle between the y-axis and the line connecting the Fishnet Origin Coordinate value to the Y-Axis Coordinate value.
To create a rotated fishnet, define the angle of rotation by specifying a Y-Axis Coordinate value so that the line from the origin to this point creates the desired angle with north as shown in the image below. See the Calculate a value for the y-axis coordinate section below for details.

The following example shows a rotated fishnet constructed with the following parameter values:
- Fishnet Origin Coordinate—(0, 0)
- Opposite corner of Fishnet—(6.9, 4)
- Number of Rows—3
- Number of Columns—4
- Y-Axis Coordinate—(6.9, 4)
When the tool runs, it first constructs a fishnet that is not rotated as shown in the following image:
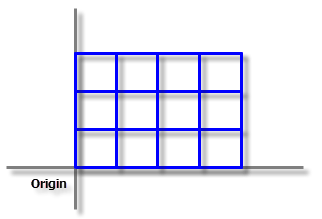
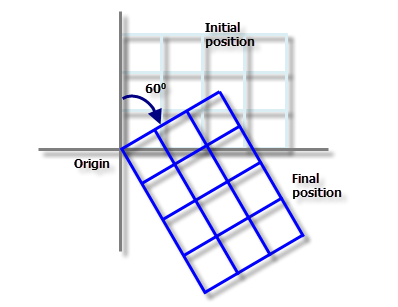
The next step is to rotate the fishnet by 60 degrees clockwise around the origin to obtain the final fishnet as shown in the following image:
Calculate a value for the y-axis coordinate
If you know the angle of rotation, you can compute a value for the Y-Axis Coordinate parameter as described below.
Assume the fishnet is to be rotated 60 degrees clockwise. From the origin of the fishnet, draw a line so that it makes an angle of 60 degrees clockwise from the vertical axis (as shown in the image below). Any point on this line can be used as the value for the Y-Axis Coordinate parameter. Use a convenient value for the y-coordinate, and calculate the x-coordinate from the relation (assuming the origin is at 0, 0):
Tangent of angle = x-coordinate / y-coordinate

For example, the angle is 60 degrees. If the y-coordinate is 10, the x-coordinate will be 17.32:
x-coordinate = tan(60) * 10Output feature class
You can create a line or a polygon feature class. If you intend to overlay the fishnet with an existing dataset using tools in the Overlay toolset, choose Polygon for the Geometry Type parameter. If you want a fishnet for display purposes, choose Polyline for the Geometry Type parameter. If you have a large number of cells, creating a fishnet using the Polygon option will be much slower than creating it with the Polyline option.
You can also create a point feature class by checking the Create Label Points parameter. The points will be located at the center of each cell. If you only want point output and nothing else, choose Polyline for the Geometry Type parameter (because it is the fastest way to construct a fishnet) and check the Create Label Points parameter. After the tool has runs, delete the output line feature class.