Available with Business Analyst license.
The Target Marketing workflow analyzes the composition of your trade area, and then compares this to your customers, allowing you to see the types of people you are reaching as well as people you should be targeting for expansion.
The workflow uses the market segmentation system in your Business Analyst dataset, such as Esri Tapestry Segmentation in the United States, or PRIZM in Canada. Segmentation data may or may not be included with your particular Business Analyst dataset. The Target Marketing workflow uses the segmentation data to identify areas where your business significantly over- and under-performs. The workflow is also used to identify the types of consumers that are your best customers and locate new areas with dense pockets of these potential customers.
Note:
Target marketing is not available when connected to an online data source. To perform target marketing, you must select a local dataset that contains segmentation data.
Use the Target Marketing wizard
The Target Marketing wizard walks you through a six-step process that profiles your customers, then the area where they reside, and compares the two. At the end of the wizard, your project contains:
- A Target Marketing group layer in the project contents, containing layers that display targets, market penetration, target groups, market potential, and gap analysis.
- Reports you opted to create, including a Segmentation Profile report, Developing Marketing Strategies report, Market Potential report, and Market Area and Gap Analysis report.
- Target and Base Profiles catalog items
- Target Group catalog item
To perform target marketing, do the following:
- On the Analysis tab, click Business Analysis to open the gallery, and click the Target Marketing Wizard button
 .
.The Target Marketing pane appears, displaying an outline of the wizard steps and the fields to complete for the first step.
- Create a profile that defines your customers. Under Step One: Customer Profile, define the following:
- Use the Customer Layer drop-down menu to select the layer that contains the point locations of your customers.
- Use the Target Profile drop-down menu to select a profile or create one by selecting Create new from. If you are creating a new target profile, complete the following fields:
- Select a segmentation base, either Total Households or Total Adult Population. Choose a segmentation base that corresponds with your customer type—family units or individuals.
- Optionally, select a volumetric field (such as sales) in the customer layer. This field will be used to weight the calculations.
- Name the target profile.
The customer profile is a distribution of all segments with respective counts of customers and related percent composition. It is composed of the locations of your customers and the demographic unit (segmentation base) that the base calculations are based on. Note that, in this pane, customer profile and target profile are synonymous.
- Click Next.
- Define the area where most or all of your customers are located. Under Step Two: Market Area, define the following:
- Under Market Area, define the area as the current map extent, select a polygon layer, or select a standard geography.
- Use the Base Profile drop-down menu to select a profile or create one by selecting Create new from. Optionally, if you are creating a new base profile, type a name for the base profile.
In most cases, the base profile is the geographic area from which you draw close to 100 percent of your customers.
- Click Next.
The wizard now assigns your customers to segments that represent the type of consumer they are, based on their location in the market area. The next step reveals which segments your most loyal, highest potential, highly interested, and least interested customers come from. The entire spectrum of your customers, from most loyal to least interested, is called the workflow's target group.
- Review the target group and the corresponding four-quadrant analysis. Optionally, rename, delete, or reconfigure the targets and adjust the calculations of the analysis. Under Step Three: Configure Target Group, do the following:
- Click Edit to rename a target or Delete to delete it. You can also create a target. Optionally, expand a target and right-click a segment to assign it to a different target.
In the Four Quadrant Analysis pane, you can adjust the Index and Percent Composition fields to alter the calculations.
The target group is composed of the following default targets: Core, Developmental, Niche, and Monitor. Each target appears in the workflow pane in this step, as well as in the four-quadrant analysis. For more information, see Targets and four-quadrant analysis.
- Click Next.
- Choose the layers to map and the level at which to map them. Under Step Four: Mapping, do the following:
- Use the Geography Level drop-down menu to select the geographic boundaries to map.
- Under Mapping Layers, choose which parts of the analysis to map. For more information, see Target marketing map layers.
- Click Next.
- Choose the reports to generate. Under Step Five:
Reporting, use the check boxes to choose from
Segmentation Profile report, Developing Marketing Strategies
report, Market Potential report, and Market Area and Gap Analysis
report.
For more information, see Target marketing reports.
- Click Next.
- Under Step Six: Summary, review the settings and options you selected in the wizard and click Finish.
The analysis creates up to five layers in the Contents pane and creates and downloads up to four reports.
Targets and four-quadrant analysis
When you use the wizard, your customers are assigned to Tapestry segments based on where they are located. Then these segments are bundled together to make targets, which are called Core, Developmental, Niche, and Monitor. Targets provide information on which types of customers to focus on for outreach and which to disregard for your current efforts. Collectively, all your targets grouped together are called your target group for the analysis.
The four targets are displayed in the wizard pane of Step Three: Configure Target Group and also in the corresponding four-quadrant analysis chart. You can adjust the calculations of the target group to put targets in different groups or define the groups with different values.
Targets
By default, Core, Developmental, Niche, and Monitor targets are included in the target group:
- Core target—Segments that contain a high percentage of your customers and above-average indexes. These are your core customers, who patronize your organization at a disproportionate rate compared to the general population in their area. These segments represent loyalty and good opportunity.
- Developmental target—Segments that contain a significant percentage of your customers but do not have an above-average index. These segments are important because they represent a significant portion of your customers, but are consuming your product or service at a lower rate than the general population in the market area. This is an indication of significant opportunity.
- Niche target—Segments that make up a small percentage of your customers but have an above-average index. They patronize your organization at a disproportionate rate compared to the general population in their area but in small numbers. Niche segments represent opportunities when exploring new market areas for expansion.
- Monitor target—Segments that do not make up a significant percentage of your customers and have below-average indexes. Segments in this target represent consumers that do not purchase your product or service.
Four-quadrant analysis chart
After you create the target and base profiles, the workflow analyzes and synthesizes the profiles using a four-quadrant analysis chart. The Four Quadrant Analysis chart analyzes the customer segmentation profile by comparing to create indexes. The chart plots the segments that represent your customers based on percent composition (x-axis) and index (y-axis) values:
- Percent Composition—The percentage of your customers assigned to each segment based on their location.
- Index—The index measures the percent of your customers assigned to a given segment against the percent of people in that segment in the market area. An index above 100 means that you are attracting customers from that segment at a higher rate than they occur in the market area. For example, if 10 percent of customers in the target profile and 5 percent of people in the base profile are assigned to Segment X, the index is 200 (10 percent / 5 percent * 100). This indicates that you are attracting customers from that segment at twice the rate they occur in the market area.
You can manually update the Index and Percent Composition values in the text boxes or click and drag the x- or y-axis, adjusting which segments fall into each of the four quadrants. Using this chart, you can identify Core, Developmental, Monitor, and Niche customers.
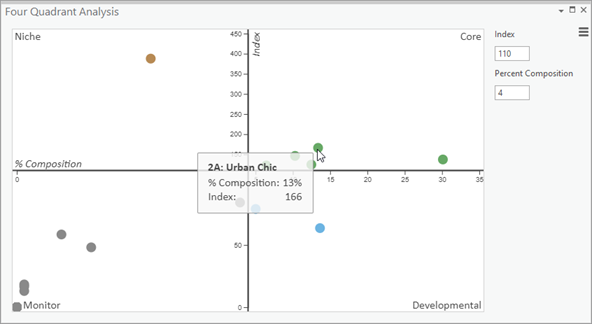
Four-quadrant analysis, using the default Index value (110) and Percent Composition value (4 percent), places segments into one of four quadrants:
- Core—Segments that make up 4 percent or more of your customers and index at 110 or greater.
- Developmental—Segments that make up 4 percent or more of your customers but have index values that are less than 110.
- Niche—Segments that make up less than 4 percent of your customers and have an index value of 110 or greater.
- Monitor—Segments that make up less than 4 percent of your customers and have index values of less than 110.
Target marketing map layers
The Target Marketing wizard includes five mapping options, each powered by a geoprocessing tool from the Target Marketing toolset.
Target layer (segment name)
A layer that indicates whether the dominant segment for each polygon in the selected geography level falls inside or outside the set of segments that make up the target. In the wizard, the input must be an existing target, such as Core customers. If run from the geoprocessing tool, an existing target or a selected set of segments may be used as the input.
Geoprocessing tool: Generate Target Layer
Target penetration layer
A layer indicating the percent of the people in the market area that are assigned to one of the segments in the input target. The options are defined by the segmentation base in use. Common options for the segmentation base are Households or Adult Population.
If creating this type of output in the wizard, an existing target must be used as the input. If accessed from the geoprocessing tool, an existing target or custom set of segments can be used.
Geoprocessing tool: Generate Target Penetration Layer
Target group layer
A layer displaying color-coded classes for each target in the target group. Polygons in the selected geography level receive the target's shading if the dominant segment is one of the segments in the target. Using the default output target group from the wizard creates a layer with four thematically shaded classes: Core, Developmental, Niche, and Monitor.
Geoprocessing tool: Generate Target Group Layer
Market potential layer
A layer that displays expected customers at a selected geography level. Also included in the output layer is the index. If your profiles contain volume information—for example, dollars spent—expected volumes are also calculated.
Geoprocessing tool: Analyze Market Potential
Market area and gap analysis layer
A layer that displays the gap between expected customers and actual customers at a selected geography level. Use this layer to analyze where you are exceeding or falling short of expectations for market penetration. A target group that identifies your Core and Developmental targets is required for the market area and gap analysis layer.
Geoprocessing tool: Analyze Market Area Gap
Target marketing reports
You can create target marketing reports within the wizard or from their individual geoprocessing tools:
- Customer Tapestry Profile report—This report helps identify your target customers. It shows the Tapestry segments and summary groups that most accurately reflect your customers and compares your customer profile to the base profile of your study area using Tapestry segmentation.
Geoprocessing tool: Generate Segmentation Profile Report
- Developing Marketing Strategies report—This report provides an overview of the media that your target customers read, listen to, and watch. It helps guide decisions about how to reach your target segment groups based on the media they consume. The target marketing wizard uses the Generate Survey Report for Targets tool to create a Developing Marketing Strategies report for your customers. You can also use the Generate Survey Report for Profiles tool to create a Developing Marketing Strategies report for the general market area.
Geoprocessing tools: Generate Survey Report for Targets and Generate Survey Report for Profile
- Market Potential report—This report builds on information included in the Market Potential map layer. It calculates expected customers, as well as the expected market penetration rate. The report allows you to see where you are over- and under-performing. Based on the optional volumetric parameter set in Step One: Customer Profile of the wizard, this report can also be generated as a Market Potential Volume report.
Geoprocessing tool: Analyze Market Potential
- Market Area and Gap Analysis report—This report builds on information included in the Market Area and Gap Analysis map layer. It uses the Customer Tapestry Profile you created, calculating an expected number of customers based on the number of households in a geographic unit and their Tapestry composition. The report details the gap, or the difference, between actual customers and expected customers.
Geoprocessing tool: Analyze Market Area Gap
Geoprocessing tools
The Target Marketing wizard uses the Target Marketing toolset, including the following tools:
- Analyze Market Area Gap
- Analyze Market Potential
- Create Target Group
- Export Segmentation Profile
- Generate Customer Segmentation Profile
- Generate Market Area Segmentation Profile
- Generate Segmentation Profile Report
- Generate Survey Report For Profile
- Generate Survey Report For Targets
- Generate Target Group Layer
- Generate Target Layer
- Generate Target Penetration Layer
- Import Segmentation Profile
- Import Survey Profiles
You can use these geoprocessing tools directly to perform the same analysis and build and run queries through a Python script or a model.