When specifying a geoprocessing tool's input feature data, you have the following options:
- Select a feature layer from the map.
- Browse to a feature class.
- Use interactive input: add a new layer and interactively create features.

Note:
Not all geoprocessing tools support interactive feature input.
Create features
To use interactive feature input with a tool, click the interactive input button  , and select a feature type from the menu. The feature type menu includes points, lines, polygons, and multipatches. Some of these types may not be available based on the feature types that are supported by the tool. After choosing a feature type, the following occur:
, and select a feature type from the menu. The feature type menu includes points, lines, polygons, and multipatches. Some of these types may not be available based on the feature types that are supported by the tool. After choosing a feature type, the following occur:
- A
new layer is added to the map Contents pane, named according to
the tool name, parameter name, and feature type: <Tool>
<Parameter> (<Type>). This layer name automatically populates the input parameter, indicating the tool will use this
new layer as input. This layer represents a new feature class created in the project geodatabase.
Note:
The feature class name may not match the new layer name. Refer to the layer Source property to determine the feature class name and location.
- An editing template appears below the parameter that
shows the symbol and layer name for the newly drawn feature, with a palette of
tools you can use to create features. A default tool is selected so you can
immediately begin creating features on the map.
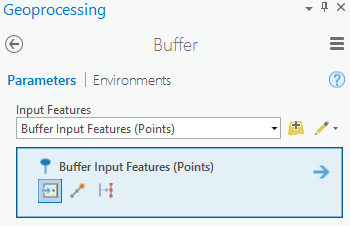
Create new input features to buffer using the Point tool. Learn more about the tools used to create points, lines, polygons, and multipatches.
Note:
Interactive feature input uses the editing system to create data in a feature class. It is fundamentally the same as if you are creating data using the Create Features pane. However, your edits are automatically saved when using geoprocessing interactive feature input, as long as you do not have an existing active editing session. Automatically saving your edits ensures that the workspace will be clear of any locks, and that the tool will run in the dedicated geoprocessing thread so you can perform other tasks while the tool is running.
Note:
The last feature you create may be selected, and since most geoprocessing tools only process selected features, you may want to clear the selection by clicking Map > Selection > Clear before running the tool.
Enter attributes for the features
Some geoprocessing tools use feature attributes as part of processing. For example, the Buffer tool has a Distance Field parameter that you can use to specify a field that contains buffer distances, so that different sized buffers can be created for each feature in the input. When using interactive feature input, there are a number of generic attribute fields available for you to enter values into along with the features you create, including text, numeric, and date fields.
Do one of the following to enter attributes for the features you create:
- Right-click the layer in the Contents pane and select Attribute Table. After creating a feature, enter its attributes in the attribute table view.
- Open the Active Template pane by clicking the forward arrow
 ; then, enter attributes for the
features you are about to create on the map. Each feature you create will have
the attributes that are currently set in the Active Template pane.
; then, enter attributes for the
features you are about to create on the map. Each feature you create will have
the attributes that are currently set in the Active Template pane. Note:
If you enter attributes using the Active Template pane, you need to switch back to the Geoprocessing pane to continue entering parameters and run the tool.
Configure interactive input using feature sets
You can add the interactive feature input capability to a custom model tool or script tool using the parameter data type feature set. You can configure the interactive input feature type, symbology, attribute fields, editing templates, feature creation tools, and other properties using a layer file template associated with the feature set parameter.
When you open a custom tool with a feature set parameter, click the interactive input button  next to the feature set parameter. Click the button to add a new layer to the active map based on the layer file you previously saved. The new layer will be empty, with no features. The editing tools, attribute fields, and symbology of the new layer will match the configured layer file. Use the feature creation tools to draw new features on the map to use as input to the custom tool.
next to the feature set parameter. Click the button to add a new layer to the active map based on the layer file you previously saved. The new layer will be empty, with no features. The editing tools, attribute fields, and symbology of the new layer will match the configured layer file. Use the feature creation tools to draw new features on the map to use as input to the custom tool.
Follow the steps below to configure a feature set parameter for model and script tools.
Configure input for a model tool
To configure interactive feature input for a custom model tool, complete the following steps:
- Create a layer with the necessary attributes, symbology, and editing templates.
- Save the layer as a layer file.
- Create a model tool in a toolbox.
- On the ribbon, click ModelBuilder > Insert > Variable to add a new variable to the model.
- On the Variable Data Type dialog box, select Feature Set, and click OK.
- Double-click the feature set variable to open the Feature Set dialog box.
- On the Properties tab, for the Template property, click the browse button
 to browse to and select the layer file you saved. Alternatively, you can select a layer from the list of layers in the last active map, and it will automatically create and set the feature set template.
to browse to and select the layer file you saved. Alternatively, you can select a layer from the list of layers in the last active map, and it will automatically create and set the feature set template. - Click OK
This feature set variable can now be connected to and used with any geoprocessing tool in the model that accepts feature layers as input.
- Right-click the feature set variable and select Parameter to make it a model parameter.
- Save the model.
Configure input for a script tool
To configure interactive feature input for a custom script tool, complete the following steps:
- Create a layer with the necessary attributes, symbology, and editing templates.
- Save the layer as a layer file.
- Create a script tool in a toolbox.
- On the Parameters tab of the Properties dialog box of the new script tool, enter a new parameter, and set the parameter data type as Feature Set.
- Click the cell for the feature set parameter's Default property, and click the browse button
 .
. - Browse to and select the layer file you previously saved, and click OK.
- Finish creating the tool.
Note:
When a layer file is specified, the path to the layer file is internalized, and if the Properties dialog box is reopened, an embedded label appears in the cell.
Interactive tables
Interactive tables are also supported as input to geoprocessing tools.
To use an interactive table, the geoprocessing tool parameter must be a record set data type. The use of this interactive table is the same as described above for interactive feature input. However, you do not use editing controls embedded in the geoprocessing tool. Instead, table data entry is done in the attribute table. Record sets can be configured using the same steps as feature sets described above.
Web tools and geoprocessing services
Interactive feature input is available for any web tool or geoprocessing service published with an Input Mode value of User defined value.
If the tool parameter does not have a layer file configured, click the Configure Tool Properties button  in the Share As Web Tool pane. The properties show the default schema—including symbology, table attributes, geometry type, and spatial reference—that are used for the parameter when running the tool before it is published. When using the tool, you can click the drop-down list next to the Interactive Input button
in the Share As Web Tool pane. The properties show the default schema—including symbology, table attributes, geometry type, and spatial reference—that are used for the parameter when running the tool before it is published. When using the tool, you can click the drop-down list next to the Interactive Input button  and select one of the geometry types (point, line, polygon, or multipatch).
and select one of the geometry types (point, line, polygon, or multipatch).
If the tool parameter has a layer file configured, click the Configure Tool Properties button  in the Share As Web Tool pane. The properties only show the default table attributes, geometry type, and spatial reference that are used for the parameter when running the tool before it is published. The symbology is rendered by the layer file. The drop-down list next to the Interactive Input button
in the Share As Web Tool pane. The properties only show the default table attributes, geometry type, and spatial reference that are used for the parameter when running the tool before it is published. The symbology is rendered by the layer file. The drop-down list next to the Interactive Input button  of a web tool or geoprocessing service shows all four feature types. The schema of each feature type, including symbology, uses generic schema when there is no layer file configured for the parameter.
of a web tool or geoprocessing service shows all four feature types. The schema of each feature type, including symbology, uses generic schema when there is no layer file configured for the parameter.
Regardless of whether the parameter of the tool has a layer file configured or if you filter the feature types of the parameter in the tool before it is published, only the filtered feature types appear in the drop-down list of the web tool or geoprocessing service parameter's Interactive Input button.