Available with Image Analyst license.
You can use
Pixel Editor to edit multispectral and panchromatic imagery. The operations that can be applied are mainly related to obscuring the pixels: Blur 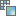 , Pixelate
, Pixelate 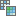 , Redact
, Redact 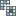 , and Set NoData
, and Set NoData 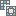 .
.
The Capture group contains Copy Region  and Replace Region
and Replace Region  . These tools copy or replace pixels from the same dataset or from a different dataset in the map. If using another dataset within the map, use the Source Layer drop-down list to set the correct map layer to use; this layer must have the same bit depth as the raster being edited. The target layer is always the raster dataset that you are editing.
. These tools copy or replace pixels from the same dataset or from a different dataset in the map. If using another dataset within the map, use the Source Layer drop-down list to set the correct map layer to use; this layer must have the same bit depth as the raster being edited. The target layer is always the raster dataset that you are editing.
Use the Region and Region Mode tools to create a region, or edit an existing region. Then choose the operation you want to perform on your selected region. For an example of how to create a region and perform an operation, see Pixelate a confidential region.
The Edit group has an interactive Redact tool  and an Operations drop-down gallery. The Redact tool allows you to draw a polygon on the image, and it will black out your region. Each of the Operations will open the Pixel Editor Operations pane, and the operation will only be performed on the selected region. The Pixel Editor Operations pane shows you the parameters available for the edit operation.
and an Operations drop-down gallery. The Redact tool allows you to draw a polygon on the image, and it will black out your region. Each of the Operations will open the Pixel Editor Operations pane, and the operation will only be performed on the selected region. The Pixel Editor Operations pane shows you the parameters available for the edit operation.
Note:
Only raster datasets can be edited using Pixel Editor. Raster products, mosaic datasets, and image services are not supported.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
Blur
| Obscure the selected region with a blurred effect. Blur can also be used to smooth a noisy area. The Factor option allows you to set the level of blurring to perform, in which higher values result in more blurring. Check the Sharpen check box to sharpen the image that has been obscured. This will make the region less noticeably obscured. When the Exclude Region Intersections check box is checked, any regions that intersect the active region are excluded from this operation. |
Custom Processing
| Apply a raster processing template (.rft.xml) to the selected region. The following two factors must be true for the operation to be successful:
|
Pixelate
| Obscure the region by resampling the region to an exaggerated pixel size. The Factor option allows you to set the level of resampling to perform, in which higher values create more pixelation. Check the Sharpen check box to sharpen the image that has been obscured. This will make the region less noticeably obscured. When the Exclude Region Intersections check box is checked, any regions that intersect the active region are excluded from this operation. |
Redact
| Black out the selected region. When the Exclude Region Intersections check box is checked, any regions that intersect the active region are excluded from this operation. |
Set NoData
| Set the pixels in the selected region as NoData pixels for each band. When the Exclude Region Intersections check box is checked, any regions that intersect the active region are excluded from this operation. |
You can use the Undo button  to reverse the last action that was performed by the tools on the Pixel Editor tab. The undo action can also be performed by pressing Ctrl+Z; this shortcut can also be used to undo actions that were performed in the Pixel Editor Operations pane. You can use the Redo button
to reverse the last action that was performed by the tools on the Pixel Editor tab. The undo action can also be performed by pressing Ctrl+Z; this shortcut can also be used to undo actions that were performed in the Pixel Editor Operations pane. You can use the Redo button 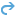 to reverse the undo action that was performed by the tools on the Pixel Editor tab. The redo action can also be performed by pressing Ctrl+Y; this shortcut can also be used to redo actions that were performed in the Pixel Editor Operations pane.
to reverse the undo action that was performed by the tools on the Pixel Editor tab. The redo action can also be performed by pressing Ctrl+Y; this shortcut can also be used to redo actions that were performed in the Pixel Editor Operations pane.
