Description
Gnomonic is an azimuthal projection that uses the center of the earth as its perspective point. It projects great circles as straight lines, regardless of the aspect. The projection is not conformal nor is it equal-area. This is a useful projection for navigation because great circles highlight routes with the shortest distance.
The gnomonic projection is available in ArcGIS Pro 1.0 and later and in ArcGIS Desktop 8.1.1 and later.
Projection properties
The subsections below describe the gnomonic projection properties.
Graticule
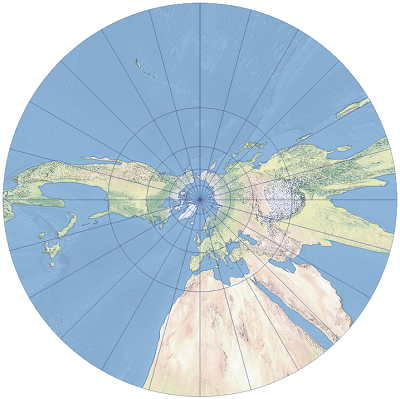
Gnomonic is an azimuthal projection.
In the polar aspect, the meridians project as straight lines originating at the pole. Angles between the meridians are true. The parallels are unequally distributed concentric circles. Their spacing rapidly increases from the pole. The equator cannot be shown in a polar aspect.
In the equatorial aspect, the meridians project as straight vertical lines. Their spacing increases away from the central meridian. The equator is shown as a straight line, perpendicular to the meridians. Other parallels are convex curves that bend away from the equator. Neither pole can be shown.
Regardless of the aspect, all great circles project as straight lines.
Distortion
The gnomonic projection is neither conformal nor equal-area. Shape, area, and distance distortions increase with distance from the center. There is moderate distortion within a 30-degree radius of the center. Directions and angles are accurate only at the center of the projection.
Usage
The gnomonic projection is appropriate for navigational maps at large scales, displaying less than one-sixth of the planet. It has been used for creating world globes using polyhedral mapping.
Variants
There are three variants available in ArcGIS. All three variants correctly support the sphere-based Earth models.
- The gnomonic variant is available in ArcGIS Pro 1.0 and later and in ArcGIS Desktop 9.3 and later. The semimajor axis is used for the radius.
- The gnomonic auxiliary sphere variant is available in ArcGIS Pro 1.0 and later and in ArcGIS Desktop 9.3 and later. This variant uses a sphere specified by the Auxiliary Sphere Type parameter.
- The gnomonic ellipsoidal variant is available in ArcGIS Pro 1.2 and later and in ArcGIS Desktop 10.4 and later. This is the only variant of the three that correctly supports projection of ellipsoids.
Limitations
The gnomonic projection is limited by its perspective point and cannot project a line that is 90 degrees or more from the center point. This means that the equatorial aspect cannot project the poles, and the polar aspects cannot project the equator. This projection should not be used to map more than one-third of the planet.
Parameters
Gnomonic parameters are as follows:
- False Easting
- False Northing
- Longitude of Center
- Latitude of Center
Gnomonic auxiliary sphere parameters are as follows:
- False Easting
- False Northing
- Longitude of Center
- Latitude of Center
- Auxiliary Sphere Type, with values as follows:
- 0 = Use semimajor axis of the geographic coordinate system
- 1 = Use semiminor axis
- 2 = Calculate and use authalic radius
- 3 = Use authalic radius and convert geodetic latitudes to authalic latitudes
Note:
If the geographic coordinate system uses a sphere, the Auxiliary Sphere Type uses the radius of the sphere in all four cases.
Gnomonic ellipsoidal parameters are as follows:
- False Easting
- False Northing
- Longitude of Center
- Latitude of Center
Sources
Snyder, J. P. (1987). Map Projections: A Working Manual. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1395. Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office.
Snyder, J. P. and Voxland, P. M. (1989). An Album of Map Projections. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1453. Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office.