You can search a project for items stored in the project file, such as maps and layouts, and for items available through connections that you add to the project.
Items can appear in search results only if they exist in locations that are indexed by ArcGIS Pro. For example, you can find items stored in a folder on your C:\ drive but not items stored on a server that has been added to the project. You can also index the contents of folders that have not been added to a project, or use index files created and managed by others.
Searches are performed in catalog views, the Catalog pane, and browse dialog boxes by typing a keyword or keywords in the search box and pressing the Enter key. Items, including folders, are returned if the search keyword is found in the item's name or item description metadata.
If a search result is a container of other items, you can browse into it. For example, you can browse into a file geodatabase or a folder to access its contents.
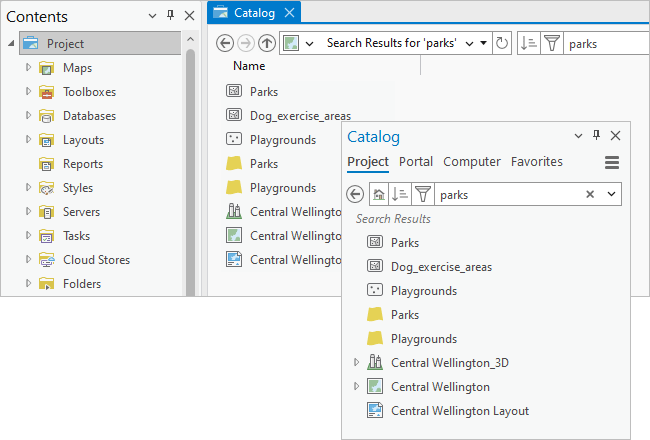
In the Catalog pane, click the Project tab to search the project. In the Contents pane of a catalog view, or in a browse dialog box, click Project  to search the project.
to search the project.
Note:
In most cases, searches do not return items that are not used by ArcGIS Pro or that cannot be added to a project. For example, searches do not return Microsoft Word documents or ArcGIS Pro projects. Searches also do not return the contents of style files. To search for style items, such as symbols or color schemes, you must manage the style in a catalog view.
Search an item container
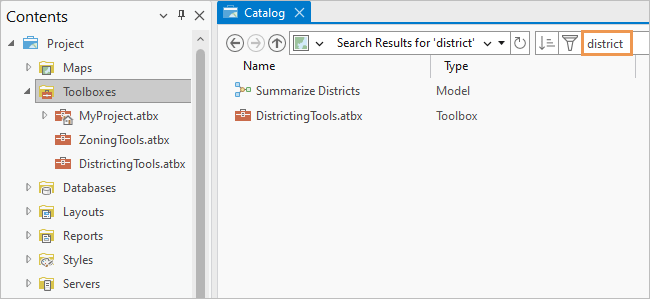
In a catalog view or browse dialog box, you can restrict the search to a specific item container by selecting it. For example, if you select the Toolboxes container  in the Contents pane of a catalog view and perform a search, results are returned only for project toolboxes and their contents.
in the Contents pane of a catalog view and perform a search, results are returned only for project toolboxes and their contents.
Search by keyword
To search for items, enter a keyword or keywords in the search box. Add more keywords to refine the search. For example, a search for city park returns only items that are indexed on both keywords.
Keyword order does not affect search results. A search for city park returns the same items as a search for park city.
Keywords are not case sensitive. Underscores and hyphens are treated like spaces. For example, a search for flow finds items named flow-direction and flow_direction.
Keywords are stemmed; that is, search results return all items that share the root form of the keyword. For example, if you search for zones, the results will include items that contain the word zone, zones, or zoning.
Note:
It is not necessary to use a wildcard character, such as an asterisk (*), to find unspecified characters at the end of a keyword. This functionality is built in to searches. For example, if you search for wind, the results will include items that contain words such as windmill, windstorm, and so on. Wildcards are not supported at the beginning or in the middle of words.
Sort results
The default order of search results puts the most relevant results at the top. Relevance is determined by factors such as whether the keyword is part of the item name or title and how often it appears in the item description.
In the Catalog pane, catalog views, and browse dialog boxes, you can click the Sort button  to change the sort order. In catalog views and browse dialog boxes, you can sort on different item properties depending on your catalog location. For example, in a catalog view, a search of the Databases container
to change the sort order. In catalog views and browse dialog boxes, you can sort on different item properties depending on your catalog location. For example, in a catalog view, a search of the Databases container  provides different sort options than a search of the Maps container
provides different sort options than a search of the Maps container  . In the Catalog pane, sorting is limited to the relevance and name properties. You can return to the relevance sort order at any time.
. In the Catalog pane, sorting is limited to the relevance and name properties. You can return to the relevance sort order at any time.
You can also sort items by doing the following:
- In a catalog view or browse dialog box, click a column heading in the search results. Click again to reverse the sort order.
- On the ribbon, when a catalog view is active, click the Catalog tab. In the Organize group, click Sort
 and choose a sort option.
and choose a sort option.
Filter results
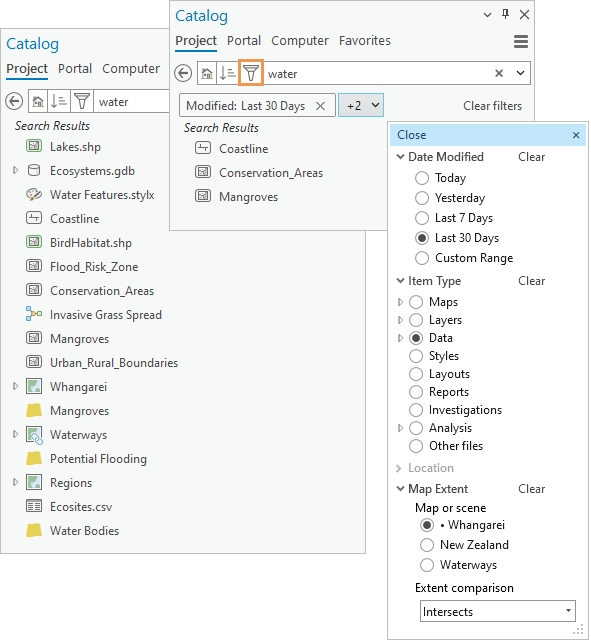
You can refine search results by applying filters. Filters can also be used without a search to limit the display of items.
Filters are available in the following contexts:
- In the Catalog pane, all filters are available.
- In catalog views, all filters are available when you search the project
 or when you search the Folders container
or when you search the Folders container  or a specific folder.
or a specific folder. - If you search an item container (other than the Folders container), the Item Type filter is not available. In some item containers, no filters are available. In those cases, the Filter button
 does not appear.
does not appear. - In browse dialog boxes, the Item Type filter is not available because browse dialog boxes already have an item filter drop-down list.
Apply and clear filters
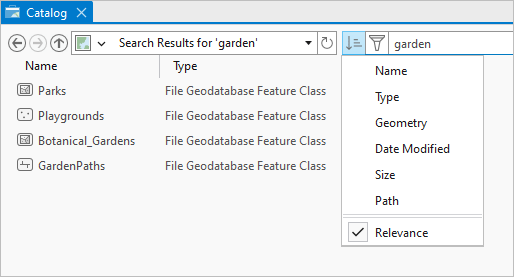
To apply a filter, click Filter  next to the search box. In the drop-down list that appears, expand a filter type, and click an option.
next to the search box. In the drop-down list that appears, expand a filter type, and click an option.
You can apply multiple filters. For example, you can filter search results by item type and modification date. Options within a filter are mutually exclusive. For example, if you filter by item type, you can choose maps or layouts but not both. An option may have further options. For example, if you filter by item type and choose Data, you can further narrow the filter by choosing a specific data option such as Raster and imagery data.
Active filters are displayed by name on chips in the Catalog pane, catalog views, and browse dialog boxes. If there isn't enough space to show the name, the number of additional active filters is shown instead. The filter name or names can be displayed in a drop-down list.
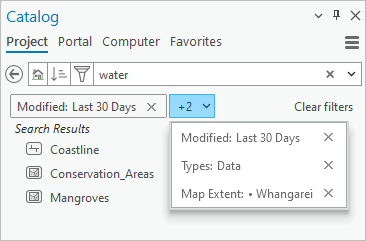
You can change the search results by applying more filters, choosing different filter options, or clearing filters. The list of search results updates automatically. (However, if you apply a map extent filter and subsequently change the map extent, you must refresh the display to update the results.) If you change search terms, active filters stay in place.
To clear a filter, click Filter  and click Clear next to the filter name in the drop-down list that appears. Alternatively, click the close button
and click Clear next to the filter name in the drop-down list that appears. Alternatively, click the close button  on the filter chip. Click Clear filters to remove all active filters.
on the filter chip. Click Clear filters to remove all active filters.
Date Modified filter
You can filter search results by their modification date using predefined options, such as Last 30 Days, or a date range that you specify. Items stored in the project file, such as maps and layouts, don't have modification dates. Neither do items stored in a mobile geodatabase or OGC GeoPackage. Filtering by modification date removes these items from the search results.
Item Type filter
You can filter search results by a variety of item types, such as maps, layers, data, and analysis. Some item types have additional options. For example, you can filter by the Data item type, which returns all data items, or by one of its options, such as raster and imagery data.
Location filter
You can filter search results by typing a geographic location or latitude-longitude coordinates expressed in DD, DMS, or DDM. Items are returned if their spatial extent intersects the location. The ArcGIS World Geocoding Service is used to find locations.
When a location filter is applied, search results are commonly limited to spatial datasets such as geodatabase feature classes and shapefiles. Spatial datasets always have a geographic extent that can be read either from the item metadata or from the item properties if metadata does not exist. Items that are not inherently spatial, such as geoprocessing models and .csv files, can be included in the search results if spatial coordinates are added to their metadata. Similarly, items stored in the project file (.aprx), such as maps, layers, and layouts, are not returned unless spatial coordinates have been added to their metadata.
The Location and Map Extent filters cannot be used together.
Map Extent filter
You can filter search results by the extent of a map or scene in a project. Maps and scenes are available as filters if they are open in the project and have been made active in the current session. (If a map or scene is open but has not been made active, it appears dimmed in the Filter drop-down list.) A map that is currently the active view has a dot next to its name. Multiple views of the same map are numerically distinguished in parentheses (for example, Europe (1/2) and Europe (2/2)). On a browse dialog box, only the currently active map or scene can be used as a filter.
The map extent filter has two comparison options: Intersects (the default) and Within. An item intersects the map extent if any part of its spatial boundary overlaps the map extent. An item is within the map extent if its spatial boundary is entirely contained by the map extent.
Note:
These extent comparison options do not appear when you filter portal items by map extent. For portal items, intersection is the only option.
As with the location filter, search results are commonly limited to spatial datasets. No other items are returned unless coordinates are added to their metadata.
The Map Extent and Location filters cannot be used together.
Use Boolean operators
You can narrow or widen a search using the Boolean operators AND, OR, and NOT. Boolean operators must be entered in capital letters. The Boolean operators are described in the following table:
Boolean operators
| Boolean operator | Description |
|---|---|
AND | This operator is used between keywords. Items are returned if they are indexed on all the keywords connected by AND. This operator is usually unnecessary because typing two keywords without AND has the same effect. The search parks AND urban returns items indexed both on the word parks and on the word urban. (The search parks urban returns the same results.) |
OR | This operator is used between keywords. Items are returned if they are indexed on any of the words connected by OR. The search parks OR urban returns items indexed on the word parks, items indexed on the word urban, and items indexed on both words. |
NOT | This operator is used before keywords. Items are not returned if they are indexed on a word that follows NOT. The search parks NOT urban returns items indexed on the keyword parks that are not indexed on the keyword urban. |
You can combine operators to add complexity to a search. Use parentheses or repeat the operator to make the logic clear. The following are examples:
- The search historic AND (buildings OR districts) returns these items:
- Items indexed on the word historic and the word buildings
- Items indexed on the word historic and the word districts
- The search (historic AND buildings) OR districts returns these items:
- Items indexed on the word historic and the word buildings
- Items indexed on the word districts
- The search historic NOT buildings NOT districts returns items indexed on the word historic and not indexed on the word buildings and not indexed on the word districts.
Tip:
A hyphen (-) placed before a word (with no space in between) has the same effect as the NOT operator.
Use quotation marks
Use quotation marks to find items that contain an exact phrase. For example, a search for “open water” returns items only if these two words are indexed next to each other and in this order.
Use item fields
Indexes are built from item descriptions. You can limit searches to specific elements of the item description with item field names. The syntax for an item field name search is item field name:keyword. The following table lists item field names and usage examples:
Item field names
| Item field name | Description |
|---|---|
title | The Title field of the item description. By default, the title matches the item's file name, but it can be changed. The search title:birds returns items with the word birds in the title. (It also returns items with birds in the item name.) |
type | The data type of an item. This property is set by the software. The search type:"geodatabase feature class" returns geodatabase feature classes. The search type:shapefile returns shapefiles. To get the best results, use quotation marks around the item type if it contains more than one word. Items of a specific data type are also returned if the search keyword specifies the data type without an item field name. For example, a search for shapefile returns shapefiles as well as items indexed on the word shapefile. |
tags | The Tags field of the item description. The search tags:agriculture returns items only if the word agriculture is a tag. |
snippet | The Summary field of the item description. The search snippet:boundary returns items only if the word boundary appears in the summary. |
description | The Description field of the item description. The search description:satellite returns items only if the word satellite appears in the description. |
credits | The Credits field of the item description. The search credits:Esri returns items only if the name Esri appears in the credits. |
accessinformation | The Use Limitations field of the item description. The search accessinformation:attribution returns items only if the word attribution appears in the use limitations. |
Manage search results
You can manage search results in the search box by doing the following:
- To clear a search, click the Delete button
 in the search box.
in the search box. - To repeat a recent search, click the search box drop-down arrow and click one of the listed searches.
- To clear the search history, click the search box drop-down arrow and click Clear History.
Incomplete search results
When a project is indexed for the first time, or if a scheduled indexing task is in progress, a message appears indicating that indexing is in progress. Search results may be incomplete until the indexing task finishes.
If a search does not return expected results, possible reasons include the following:
- The search term may be misspelled.
- You may be searching an item container instead of the entire project.
- An indexing task may have failed to complete.
- Indexing may be turned off for one or more locations such as local disks, network disks, or enterprise geodatabases.
- Indexing may be turned off for the ArcGIS Pro application.
Differences in search experiences
The Catalog pane, catalog views, and browse dialog boxes provide similar, but not identical, search experiences. Keep the following in mind when performing a search:
- Search results can be sorted on more properties in a catalog view or browse dialog box than in the Catalog pane.
- A search performed in the Catalog pane searches all items in the project. In a catalog view or browse dialog box, you can restrict a search to an item container, such as Databases
 or Toolboxes
or Toolboxes  .
. - In a catalog view, if a map is returned as a search result, you can double-click it to see its layers. In the Catalog pane, double-clicking a map that is a search result opens the map.
- In the Catalog pane, you can hover over search results to see their item pop-ups. Item pop-ups aren't available in catalog views or browse dialog boxes.
- In a catalog view, the number of search results is shown at the bottom of the view. In the Catalog pane and browse dialog boxes, the number of search results is not shown.