| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
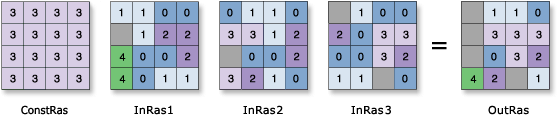
Input rank raster or constant value | The input raster that defines the rank position to be returned. A number can be used as an input; however, the cell size and extent must first be set in the environment. | Raster Layer; Constant |
Input rasters | The list of input rasters from which the cell value of the raster at the specified rank position will be obtained. For example, consider a particular location where the cell values in the three input rasters are 17, 8 and 11. The rank value for that location is defined as 3. The tool will first sort the input values. Since the rank value being requested is 3, the output value will be 17. | Raster Layer |
Process as multiband (Optional) | Specifies how the input multiband raster bands will be processed.
| Boolean |
Return Value
| Label | Explanation | Data Type | Output raster | The output raster. For each cell on the output raster, the values on the input rasters are sorted from lowest to highest, and the input rank raster's value is used to select which will be the output value. | Raster |