Disponible avec une licence Spatial Analyst.
Disponible avec une licence Image Analyst.
Résumé
Raises the cell values in a raster to the power of the values found in another raster.
Illustration
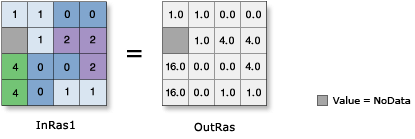
Discussion
Lorsque vous utilisez un opérateur avec un raster en entrée, le résultat est un raster. En revanche, si toutes les entrées sont des nombres, le résultat est un nombre.
Si plusieurs opérateurs sont utilisés dans une expression, ils ne sont pas nécessairement exécutés de gauche à droite. L'opérateur doté de la valeur de priorité la plus élevée est exécuté en premier. Pour plus d'informations sur la priorité des opérateurs, consultez la rubrique Table de priorité des opérateurs. Vous pouvez utiliser des parenthèses pour contrôler l'ordre d'exécution.
Output values are always floating point, regardless of the input value type.
Another way to perform the power operation is a **= b, which is an alternative way to write a = a ** b.
Si les deux entrées correspondent à des rasters monocanaux ou que l’une des entrées est une constante, la sortie correspond à un raster monocanal.
Si les deux entrées correspondent à des rasters multicanaux ou que l’une des entrées est une constante, la sortie correspond à un raster multicanal. Le nombre de canaux de chaque entrée multicanal doit être identique.
L’opérateur effectue l’opération sur chaque canal d’une entrée par rapport au canal correspondant de l’autre entrée. Si l’une des entrées correspond à un raster multicanal et que l’autre entrée est une constante, l’opérateur effectue l’opération par rapport à la valeur constante de chaque canal de l’entrée multicanal.
Syntaxe
in_raster_or_constant1 ** in_raster_or_constant2
| Opérande | Explication | Type de données |
in_raster_or_constant1 | The input values to be raised to the power defined by the second input. If the first input is a raster and the second is a scalar, an output raster is created with each input raster value being raised to the power of the scalar value. | Raster Layer | Constant |
in_raster_or_constant2 | The input that determines the power to which the values in the first input will be raised. If the first input is a scalar and the second is a raster, an output raster is created with the scalar value being raised to the power of each input raster value. | Raster Layer | Constant |
Valeur renvoyée
| Nom | Explication | Type de données |
| out_raster | Objet raster en sortie. The cell values are the result of raising the values in the first input to the power of the values in the second input. | Raster |
Exemple de code
This sample uses the values in the second input raster as the power by which to raise the values in the first input raster.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outPower = Raster("degs") ** Raster("cost")
outPower.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outpower.img")This sample uses the values in the second input raster as the power by which to raise the values in the first input raster.
# Name: Op_Power_Ex_02.py
# Description: Raises the cells in a raster to the power of the values
# found in another raster
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster1 = Raster("degs")
inRaster2 = Raster("cost")
# Execute Power
outPower = inRaster1 ** inRaster2
# Save the output
outPower.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outpower")Environnements
Rubriques connexes
Vous avez un commentaire à formuler concernant cette rubrique ?