Synthèse
An extent is a rectangle specified by providing the coordinate of the lower left corner and the coordinate of the upper right corner in map units.
Discussion
The Extent object supports equal (==) and not equal (!=) operators for comparing extents.
Remarque :
When used as input to Extension ArcGIS Spatial Analyst tools—Create Constant Raster, Create Normal Raster, Create Random Raster, Extract By Rectangle, Extract by Mask, and Topo To Raster—only the XMin, YMin, XMax, and YMax values are used by these tools.
Syntaxe
Extent ({XMin}, {YMin}, {XMax}, {YMax}, {ZMin}, {ZMax}, {MMin}, {MMax}, {spatial_reference})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
XMin | The extent XMin value. | Double |
YMin | The extent YMin value. | Double |
XMax | The extent XMax value. | Double |
YMax | The extent YMax value. | Double |
ZMin | The extent ZMin value. None if no z-value. | Double |
ZMax | The extent ZMax value. None if no z-value. | Double |
MMin | The extent MMin value. None if no m-value. | Double |
MMax | The extent MMax value. None if no m-value. | Double |
spatial_reference | The spatial reference of the extent. | SpatialReference |
Propriétés
| Propriété | Explication | Type de données |
| JSON (Lecture seule) | Returns a JSON representation of the extent as a string. Conseil :The returned string can be converted to a dictionary using the json module's loads function. | String |
| MMax (Lecture seule) | The extent MMax value. None if no m-value. | Double |
| MMin (Lecture seule) | The extent MMin value. None if no m-value. | Double |
| XMax (Lecture seule) | The extent XMax value. | Double |
| XMin (Lecture seule) | The extent XMin value. | Double |
| YMax (Lecture seule) | The extent YMax value. | Double |
| YMin (Lecture seule) | The extent YMin value. | Double |
| ZMax (Lecture seule) | The extent ZMax value. None if no z-value. | Double |
| ZMin (Lecture seule) | The extent ZMin value. None if no z-value. | Double |
| depth (Lecture seule) | The extent depth value. None if no depth. | Double |
| geohash (Lecture seule) | A geohash string of the extent is returned. | String |
| geohashCovers (Lecture seule) | Returns a list of up to the four longest geohash strings that fit within the extent. | String |
| geohashNeighbors (Lecture seule) | A list of the geohash neighbor strings for the extent is returned. | String |
| height (Lecture seule) | The extent height value. | Double |
| lowerLeft (Lecture seule) | The lower left property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| lowerRight (Lecture seule) | The lower right property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| polygon (Lecture seule) | Returns the extent as a polygon object. | Polygon |
| spatialReference (Lecture seule) | The spatial reference of the extent. | SpatialReference |
| upperLeft (Lecture seule) | The upper left property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| upperRight (Lecture seule) | The upper right property: A point object is returned. | Point |
| width (Lecture seule) | The extent width value. | Double |
Vue d’ensemble des méthodes
| Méthode | Explication |
| contains (second_geometry, {relation}) | Indicates if the base geometry contains the comparison geometry. contains is the opposite of within. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 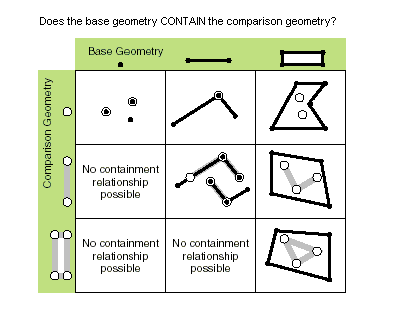 |
| crosses (second_geometry) | Indique si les deux géométries s'intersectent dans une géométrie de type de forme inférieure. Deux polylignes se croisent si elles partagent uniquement des points, dont au moins un n'est pas une extrémité. Une polyligne et un polygone se croisent s'ils partagent une polyligne ou un point (pour une ligne verticale) à l'intérieur du polygone qui n'est pas équivalent à la polyligne entière. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 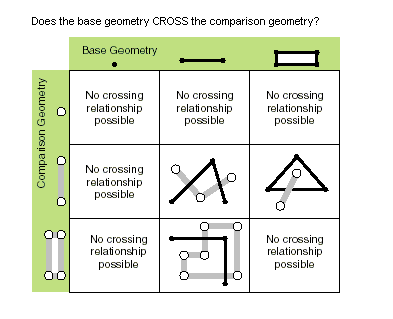 |
| disjoint (second_geometry) | Indique si la géométrie de base et la géométrie de comparaison n'ont aucun point en commun. Deux géométries s'intersectent si la propriété disjoint renvoie False. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 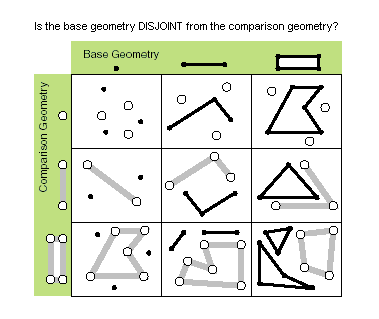 |
| equals (second_geometry) | Indicates if the base and comparison geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. This is a 2D comparison only; M and Z values are ignored. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 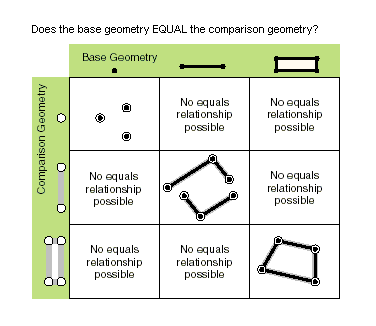 |
| overlaps (second_geometry) | Indique si l'intersection des deux géométries possède le même type de forme que l'une des géométries en entrée et qu'elle n'est pas équivalente à l'une des géométries en entrée. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.  |
| projectAs (spatial_reference, {transformation_name}) | Projects a geometry from one spatial reference to another. When the geometry object and the destination spatial reference do not have a common datum, specify a transformation_name parameter value. For more information, see Geographic datum transformations and ListTransformations. A vertical transformation will be performed when the following criteria are met:
When the transformation_name parameter value is a vertical transformation, and neither the geometry object nor the destination spatial reference have a vertical coordinate system, the function will fail with a ValueError exception. If either the geometry object or the spatial_reference parameter value have an unknown spatial reference, the output geometry's spatial reference will be that of the spatial_reference parameter value. Use of unknown spatial reference is not recommended for analysis. The projectAs method will not modify m-values, if present. |
| touches (second_geometry) | Indicates if the boundaries of the geometries intersect. Two geometries touch when the intersection of the geometries is not empty, but the intersection of their interiors is empty. For example, a point touches a polyline only if the point is coincident with one of the polyline end points. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 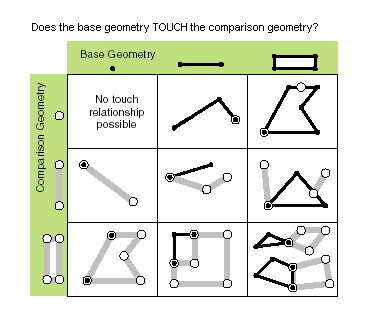 |
| within (second_geometry, {relation}) | Indicates if the base geometry is within the comparison geometry. within is the opposite operator of contains. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 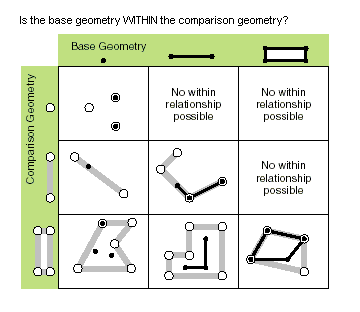 The base geometry is within the comparison geometry if the base geometry is the intersection of the geometries and the intersection of their interiors is not empty. within is a Clementini operator, except in the case of an empty base geometry. |
Méthodes
contains (second_geometry, {relation})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | The spatial relationship type.
(La valeur par défaut est None) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean |
A return Boolean value of True indicates this geometry contains the second geometry. |
crosses (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Une valeur booléenne renvoyée True indique que les deux géométries s'intersectent dans une géométrie de type de forme inférieure. |
disjoint (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Une valeur booléenne renvoyée True indique que les deux géométries n'ont aucun point en commun. |
equals (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean |
A return Boolean value of True indicates that the two geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. |
overlaps (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Une valeur booléenne renvoyée True indique que l'intersection des deux géométries a la même dimension que l'une des géométries en entrée. |
projectAs (spatial_reference, {transformation_name})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
spatial_reference | The spatial reference to which the geometry will be projected. The value can be a SpatialReference object or the coordinate system name. | SpatialReference |
transformation_name | The geotransformation name. With ArcGIS Pro, if you do not specify a transformation, none will be applied. With ArcGIS Server, if you do not specify a transformation, a fallback transformation will be applied. | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | The projected geometry. |
touches (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | A return Boolean value of True indicates the boundaries of the geometries intersect. |
within (second_geometry, {relation})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | The spatial relationship type.
(La valeur par défaut est None) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | A return Boolean value of True indicates this geometry is contained within the second geometry. |
Exemple de code
Display extent object properties for features.
import arcpy
feature_class = 'c:/Data/Florida.gdb/airports'
# Fetch each feature from the cursor and examine the extent properties
for row in arcpy.da.SearchCursor(feature_class, ['SHAPE@', 'CNTY_NAME']):
extent = row[0].extent
print('Extent of county {}:'.format(row[1]))
print('XMin: {}, YMin: {}'.format(extent.XMin, extent.YMin))
print('XMax: {}, YMax: {}'.format(extent.XMax, extent.YMax))Rubriques connexes
Vous avez un commentaire à formuler concernant cette rubrique ?