Synthèse
A representation of an x,y pair, optionally with measure, height, and ID attributes.
Discussion
A Point object does not include spatial reference information and is frequently used to construct other geometry objects, including PointGeometry, Polyline, Polygon, and Multipoint objects. In the example below, a Point object is used to create a PointGeometry object.pt = arcpy.Point(-12683890.6, 5811151.5)
pt_geometry = arcpy.PointGeometry(pt, spatial_reference=arcpy.SpatialReference(3857))
Syntaxe
Point ({X}, {Y}, {Z}, {M}, {ID})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
X | The x-coordinate of the point. (La valeur par défaut est 0.0) | Double |
Y | The y-coordinate of the point. (La valeur par défaut est 0.0) | Double |
Z | The z-coordinate of the point. (La valeur par défaut est None) | Double |
M | The m-value of the point. (La valeur par défaut est None) | Double |
ID | The shape ID of the point. (La valeur par défaut est 0) | Integer |
Propriétés
| Propriété | Explication | Type de données |
| ID (Lecture et écriture) | An integer used to uniquely identify the point. | Integer |
| M (Lecture et écriture) | The measure value of the point. | Double |
| X (Lecture et écriture) | The horizontal coordinate of the point. | Double |
| Y (Lecture et écriture) | The vertical coordinate of the point. | Double |
| Z (Lecture et écriture) | The elevation value of the point. | Double |
Vue d’ensemble des méthodes
| Méthode | Explication |
| clone (point_object) | Clone the Point object. |
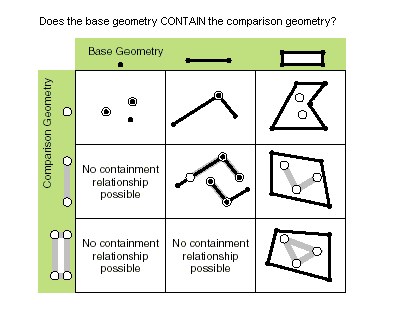
| contains (second_geometry, {relation}) | Specifies whether the base geometry contains the comparison geometry. The contains method is the opposite of the within method. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
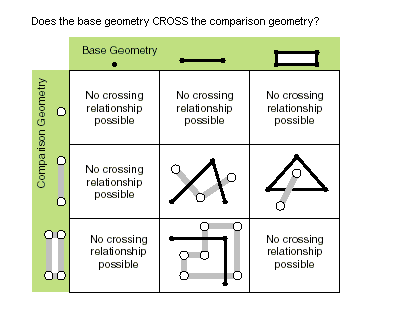
| crosses (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the two geometries intersect in a geometry of a lesser shape type. Two polylines cross if they share only points in common, at least one of which is not an endpoint. A polyline and a polygon cross if they share a polyline or a point (for a vertical line) in common on the interior of the polygon that is not equivalent to the entire polyline. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
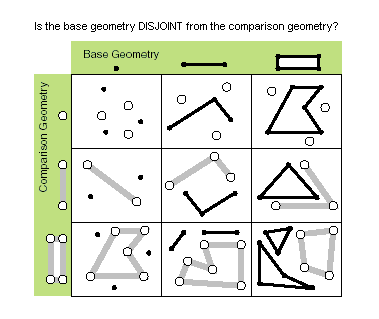
| disjoint (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the base and comparison geometries have points in common. Two geometries intersect when this method returns False. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
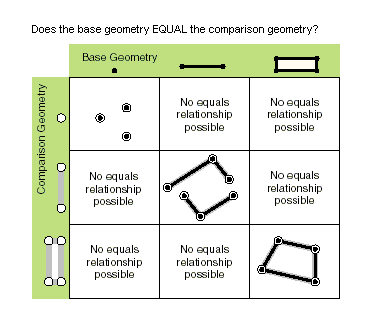
| equals (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the base and comparison geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. This is a 2D comparison only; m- and z-values are ignored. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
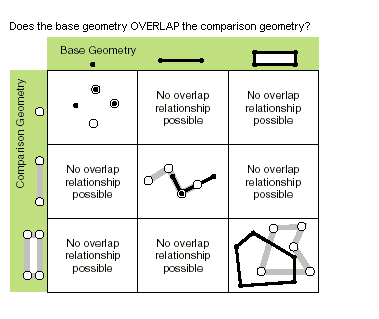
| overlaps (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the intersection of the two geometries has the same shape type as one of the input geometries and is not equivalent to either of the input geometries. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
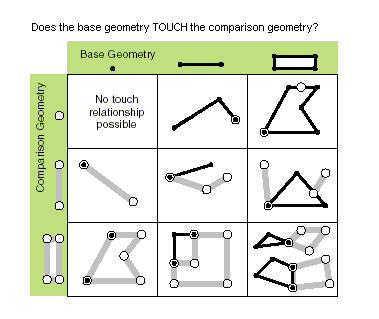
| touches (second_geometry) | Specifies whether the boundaries of the geometries intersect. Two geometries touch when the intersection of the geometries is not empty, but the intersection of their interiors is empty. For example, a point touches a polyline only if the point is coincident with one of the polyline end points. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
|
| within (second_geometry, {relation}) | Specifies whether the base geometry is within the comparison geometry. The within method is the opposite operator of the contains method. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.
The base geometry is within the comparison geometry if the base geometry is the intersection of the geometries, and the intersection of their interiors is not empty. The within method is a Clementini operator, except in the case of an empty base geometry. |
Méthodes
clone (point_object)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
point_object | A Point object. | Point |
contains (second_geometry, {relation})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | Specifies the spatial relationship type that will be used.
(La valeur par défaut est None) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean |
Returns whether this geometry contains the second geometry. |
crosses (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Returns whether the two geometries intersect in a geometry of a lesser shape type. |
disjoint (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Returns whether the two geometries have points in common. |
equals (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean |
Returns whether the two geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. |
overlaps (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Returns whether the intersection of the two geometries has the same dimension as one of the input geometries. |
touches (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Returns whether the boundaries of the geometries intersect. |
within (second_geometry, {relation})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | Specifies the spatial relationship type that will be used.
(La valeur par défaut est None) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Returns whether the base geometry is within the comparison geometry. |
Exemple de code
Create a Point object and print some of its properties.
import arcpy
# Create point object
point = arcpy.Point(2000, 2500)
# Print point properties
print("Point properties:")
print(" X: {0}".format(point.X))
print(" Y: {0}".format(point.Y))Examine Point objects returned from a Polygon object.
import arcpy
# Create cursor to retrieve Hawaii shape
feature_class = "c:/data/Hawaii.shp"
cursor = arcpy.da.SearchCursor(feature_class, ["SHAPE@"])
for row in cursor:
# Get the geometry object from the shape field
print("Number of Hawaiian islands: {0}".format(row[0].partCount))
# GetPart returns an array of point objects for each part.
for island in row[0].getPart():
print("Vertices in island: {0}".format(island.count))
for point in island:
print("X: {0}, Y: {1})".format(point.X, point.Y))Rubriques connexes
Vous avez un commentaire à formuler concernant cette rubrique ?