Overview
The Aspect-Slope function creates a raster layer that simultaneously displays the aspect and slope of a surface.
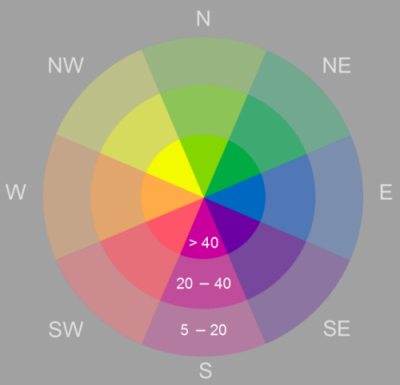
Aspect identifies the downslope direction of the maximum rate of change in value from each pixel to its neighbors. Aspect can be thought of as the slope direction. The values of the output raster will be the compass direction of the aspect, represented by a hue (color).
Slope represents the rate of change of elevation for each digital elevation model (DEM) pixel, measured in degrees. Slope represents the steepness of the surface and is symbolized into three classes that are shown using color saturation (brightness).
Notes
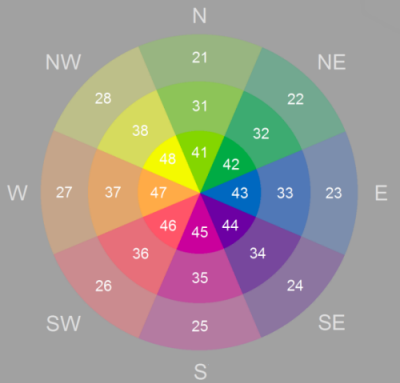
The pixel values in the output aspect-slope raster reflect a combination of aspect and slope. Pixels with values below 20 are considered flat and are shown in gray. Aspect-slope values of 21 and above will be displayed with varying saturations as follows:
- 21 to 30—Low slope saturation
- 31 to 40—Moderate slope saturation
- 41 and above—High slope saturation
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Raster | The input DEM. |
| Z Factor | A scaling factor used to convert the elevation values for the following two purposes:
|