| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Input Features | A list of the input feature classes or layers. When the distance between features is less than the cluster tolerance, the features with the lower rank will snap to the feature with the higher rank. The highest rank is 1. | Value Table |
Output Feature Class | The output feature class. | Feature Class |
Attributes To Join (Optional) | Specifies the attributes from the input features that will be transferred to the output feature class.
| String |
XY Tolerance (Optional) | The minimum distance separating all feature coordinates (nodes and vertices) as well as the distance a coordinate can move in x or y (or both). Caution:Changing this parameter's value may cause failure or unexpected results. It is recommended that you do not modify this parameter. It has been removed from view on the tool dialog box. By default, the input feature class's spatial reference x,y tolerance property is used. | Linear Unit |
Output Type (Optional) | Specifies the type of intersections that will be returned.
| String |
Summary
Computes a geometric intersection of the input features. Features or portions of features that overlap in all layers or feature classes will be written to the output feature class.
An alternate tool is available for intersect operations. See the Pairwise Intersect tool documentation for details.
The Pairwise Intersect tool is similar to this tool in that geometric intersections are computed, but it is different in that intersections are computed on pairs of features rather than all combinations of features.
Illustration
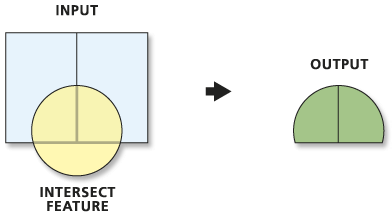
Usage
The input must be simple features, such as point, multipoint, line, or polygon features. You cannot use complex features such as annotation features, dimension features, or network features.
If the inputs have different geometry types, the output geometry type will default to the lowest dimension of the inputs.
- If an input is point features, the default output will be point features.
- If an input is line features, and there are no inputs with point features, the default output will be line features.
- If all inputs are polygon features, the default output will be polygon features.
The Output Type parameter value can be that of the Input Features parameter value with the lowest dimension geometry or lower. For example, if all the inputs are polygons, the output can be polygon, line, or point. If one of the inputs is of type line and none are points, the output can be line or point. If any of the inputs are point, the Output Type value can only be point.
Attribute values from the input feature classes will be copied to the output feature class. However, if the input is a layer or layers created by the Make Feature Layer tool and a field's Use Ratio Policy is checked, then a ratio of the input attribute value is calculated for the output attribute value. When Use Ratio Policy is enabled, whenever a feature in an overlay operation is split, the attributes of the resulting features are a ratio of the attribute value of the input feature. The output value is based on the ratio in which the input feature geometry was divided. For example, if the input geometry was divided equally, each new feature's attribute value is assigned one-half of the value of the input feature's attribute value. Use Ratio Policy only applies to numeric field types.
Caution:
Geoprocessing tools do not honor geodatabase feature class or table field split policies.
For better performance and scalability, this tool uses a tiling process to handle very large datasets. For details, see Tiled processing of large datasets.
License:
With ArcGIS Desktop Basic and Desktop Standard licenses, the number of input feature classes or layers is limited to two.
Parameters
arcpy.analysis.Intersect(in_features, out_feature_class, {join_attributes}, {cluster_tolerance}, {output_type})| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features [[in_features, {Rank}],...] | A list of the input feature classes or layers. When the distance between features is less than the cluster tolerance, the features with the lower rank will snap to the feature with the higher rank. The highest rank is 1. For more information, see Priority ranks and geoprocessing tools. | Value Table |
out_feature_class | The output feature class. | Feature Class |
join_attributes (Optional) | Specifies the attributes from the input features that will be transferred to the output feature class.
| String |
cluster_tolerance (Optional) | The minimum distance separating all feature coordinates (nodes and vertices) as well as the distance a coordinate can move in x or y (or both). Caution:Changing this parameter's value may cause failure or unexpected results. It is recommended that you do not modify this parameter. It has been removed from view on the tool dialog box. By default, the input feature class's spatial reference x,y tolerance property is used. | Linear Unit |
output_type (Optional) | Specifies the type of intersections that will be returned.
| String |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the Intersect function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/RedRiver_basin.gdb"
arcpy.analysis.Intersect(["vegetation_stands", "road_buffer200m", "water_buffer100"], "mysites", "ALL")
arcpy.analysis.Intersect([["vegetation_stands", 2], ["road_buffer200m", 1], ["water_buffer100", 2]],
"mysites_ranked", "ALL")The following stand-alone script uses the Intersect function as part of a workflow with other analysis tools to determine the type of vegetation within 100 meters of all stream crossings.
#Name: VegRoadIntersect.py
# Purpose: Determine the type of vegetation within 100 meters of all stream
# crossings
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Set the workspace (to avoid having to type in the full path to the data every
# time)
arcpy.env.workspace = "c:/data/data.gdb"
# Process: Find all stream crossings (points)
inFeatures = ["roads", "streams"]
intersectOutput = "stream_crossings"
arcpy.analysis.Intersect(inFeatures, intersectOutput, "", "", "point")
# Process: Buffer all stream crossings by 100 meters
bufferOutput = "stream_crossings_100m"
bufferDist = "100 meters"
arcpy.analysis.Buffer(intersectOutput, bufferOutput, bufferDist)
# Process: Clip the vegetation feature class to stream_crossing_100m
clipInput = "vegetation"
clipOutput = "veg_within_100m_of_crossings"
arcpy.analysis.Clip(clipInput, bufferOutput, clipOutput)
# Process: Summarize how much (area) of each type of vegetation is found
# within 100 meters of the stream crossings
statsOutput = "veg_within_100m_of_crossings_stats"
statsFields = [["shape_area", "sum"]]
caseField = "veg_type"
arcpy.analysis.Statistics(clipOutput, statsOutput, statsFields, caseField)Environments
Special cases
- Parallel Processing Factor
This tool honors the Parallel Processing Factor environment. If the environment is not set (the default) or is set to 0, parallel processing will be disabled; parallel processing will not be used and processing will be done sequentially. Setting the environment to 100 will enable parallel processing; parallel processing will be used and processing will be done in parallel. Up to 10 cores will be used when parallel processing is enabled.
Parallel processing is currently supported for polygon-on-polygon, line-on-polygon, and point-on-polygon overlay operations.
Licensing information
- Basic: Limited
- Standard: Limited
- Advanced: Yes