Available with Image Analyst license.
Image anomalies refer to pixels and objects that are spectrally distinct from the surrounding image background. The anomaly detection workflow calculates anomalies based on the image background, and extracts pixels that differ significantly from their surroundings.
The purpose of anomaly detection is to analyze an image and detect unknown targets with distinct spectral characteristics, allowing image analysts to quickly focus on areas requiring further investigation. Anomaly detection does not rely on predefined inputs, unlike target detection or feature extraction which require reference spectra or training data. Instead, it computes an average spectral background and identifies pixels that deviate significantly from this background. The Anomaly Detection Wizard combines tools and functions to guide you through the anomaly detection workflow.
The Anomaly Detection Wizard
The Anomaly Detection Wizard guides you through the entire anomaly detection and extraction workflow from start to finish. The Anomaly Detection Wizard provides a guided workflow that is composed of best practices and a simplified user experience so you can perform image anomaly detection without missing a step.
The Anomaly Detection Wizard is found in the Analysis group on the Imagery tab. Select the raster dataset to analyze in the Contents pane to display the Imagery tab, click the Spectral Analysis drop-down expander, select the Anomaly Detection Wizard, and dock it.
The wizard consists of four steps, outlined below.
Configure
The first page of the Anomaly Detection Wizard is the Configure page, where you set up your anomaly detection project. The parameters set on the Configure page determine the steps and functionality available in the subsequent wizard pages.
The configuration step allows you to set the input image, select bands, and define the extent of the analysis.
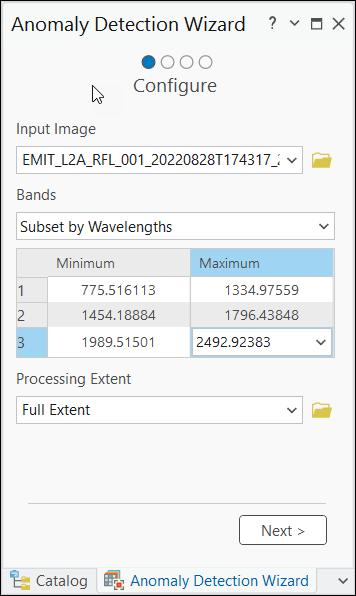
- Input Image—The input can be a multiband or hyperspectral image.
- Bands—Specify the bands you want to include in the analysis. The options include the following:
- Use All—Use all bands in the input image. This is the default.
- Subset by IDs—Select bands based on ID ranges. This is usually the band number.
- Subset by Wavelengths—Select bands based on wavelength ranges.
- Subset by Name—Select bands by band names.
When you choose to subset the image data, a dialog box appears for you to specify a band, multiple bands, range of bands, multiple ranges of bands, or a mix of individual bands and ranges of bands. Select the bands using the drop-down list. To specify a range of bands, select the minimum and maximum value of the range. Add more bands or combinations of bands by pressing Enter on the keyboard.
Note:
Only individual bands can be selected when you choose the Subset by Name option.
- Processing Extent—Specify the extent of the analysis. The options include the following:
- Full Extent—Use the extent of the entire input image.
- Current Display Extent—Use the current display extent.
- Select a layer in the map as the processing extent.
- Navigate to a saved shapefile defining the extent.
Click Next to move on to the next step in the workflow.
Anomaly Calculation
In the Anomaly Calculation pane, create an anomaly score raster using the selected method.
- Detection Method—Specify the method used to calculate anomaly scores in the output raster.
- RXD (Reed-Xiaoli Detector)—Calculates the pixels’ Mahalanobis distance to the background that is defined by the mean.
- UTD (Uniform Target Detector )—Calculates the pixels’ Mahalanobis distance to the background using a unit vector.
- KMEANS—Identifies pixels that deviate significantly from the established clusters in the data using K-means clustering algorithms.
See Detect Image Anomalies for more details about the detection methods.
- Background Region—A polygon feature class used to define a region for calculating background statistics. If not defined, whole input image will be used to calculate background.
- Recompute Statistics—Calculate statistics based on the background region. Anomaly calculation requires statistics and correlation to be calculated at base pixel level. Recompute Statistics ensures the statistics are updated corresponding to the background region. This parameter can be turned off (unchecked) only when you repeat processing with the same background calculation option.
Click Run to create the output raster comprised of anomaly scores, which is created in the AnomalyDetection folder under the current ArcGIS Pro project folder. Click Next to progress to the next step in the workflow.
Anomaly Threshold
In the Anomaly Threshold pane, select pixels in the score raster that identify the anomalies of interest. When the pane appears, a histogram of the score raster is displayed, along with controls to set a threshold for identifying anomalies. Interactively adjust the threshold using histogram controls, while the results are displayed instantly on the score raster in the map.

- Select Pixels—Filter anomalies or the background using Greater Than and Less Than options:
- Greater Than—Filters anomaly pixels in the score raster.
- Less Than—Filters background pixels in the score raster.
Histogram controls
Use the histogram controls to set the threshold for identifying anomalies in the score raster. Set the threshold value by typing a value, or by using the increase or decrease control to fine-tune the threshold value. A single click changes the threshold by 0.001; continue to press the increase and decrease controls to change by a larger increment.
You can also adjust the threshold by pressing the handle in the histogram display, and sliding it along the histogram. Zoom in and out of the histogram using the zoom controls. This allows you interactively fine-tune your threshold value.
Note:
The histogram display is optimized to enable you to interactively select threshold values. While the histogram values are correct, the shape of the histogram may be optimized to accommodate outliers while maintaining the shape of the bulk of histogram values.
As you interactively adjust the threshold on the histogram, the results are displayed as a preview on the score raster in the map. The first time you set a threshold value, click Preview to display the results in the map. Once Preview is enabled, any adjustments to the threshold values will be interactively displayed on the map.
Preview Settings
Define the display colors for the anomaly and background in the preview.
When satisfied with your results, click Next to advance to the next step in the workflow wizard.
Output Generation
Prepare the final results using the parameters and option in the Output Generation pane. Enhance the result by checking the check boxes. The enhanced result can be previewed by clicking the Preview button.
- Minimum Region Size (Pixels)—Check the check box to set a minimum region size for the anomaly. Regions of pixels smaller than the specified size will be removed from the output. This eliminates insignificant regions and salt-and-pepper effects in the final result.
- Smoothing Neighborhood—Smooth the result using one of the smoothing kernels, such as 2x2, 3x3, 4x4, and 5x5. The larger the kernel, the more the result is smoothed. This creates more contiguous regions.
Note:
It is recommended that you perform these enhancements for feature class output.Click the Preview button to create a preview layer to review the enhanced result.
- Save Result As—Specify the output type to generate the results:
- Raster Dataset—Results are saved as a raster dataset.
- Feature Class—Results are saved as a polygon feature class.
- Output Dataset—The name of the output dataset. If the output is a raster dataset, specify the file extension to generate a raster in a supported writeable format.
Click Run to create the final anomaly output as a raster dataset or feature class. The output can then be used to either focus on, or eliminate, anomalies in the input multiband or hyperspectral imagery for subsequent analysis.