ArcGIS Pro provides two dynamic aggregation methods for feature layers: binning and clustering. Both methods achieve similar goals but are visually and behaviorally different.
If the feature layer contains point features, you can aggregate the layer into clusters. Use clustering to dynamically aggregate point features that are geographically close to each other into single symbols to visually reveal useful patterns of information. You can also use it to avoid visually overlapping data.
Feature clustering
A cluster is a symbol that represents two or more point features. Feature clustering aggregates point features into clusters. In most cases, a cluster's symbol also displays a value indicating the number of point features it represents. When the number of features a cluster includes increases, the size or shape of the cluster symbol proportionally increases as well.
When you aggregate point features into clusters, the layer redraws and groups point features within a specified distance of one another on the map into one cluster. The specified distance, which is called the clustering radius, is the approximate distance a point feature must be to another point feature to be aggregated into a cluster. If a point feature is not within a cluster's specified radius, it is not aggregated into a cluster.
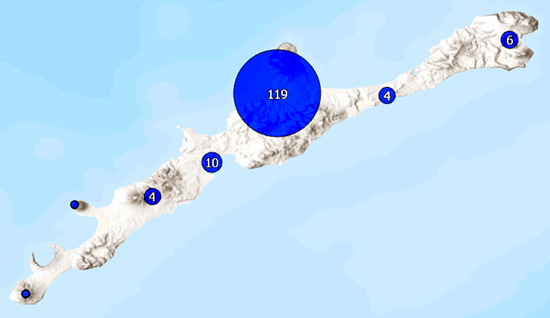
Clustering is used to simplify the symbology of a complex layer of cluttered points. Unique to feature clustering, the symbols have size, color, and text components, so they can visually display more than one variable from the data. Clustering can show patterns in the data that are difficult to visualize when a layer contains hundreds or thousands of points.
Examples of clustering include the following:
- Cluster a layer of geocoded student addresses to view the areas where most students live without visualizing their specific address.
- Categorize species into groups with unique values symbology clusters to view the most typically dominant trait in a national reserve.
- Visualize the most common value (mode) in a dataset of traffic incidents in a city to see at what time of day accidents are most prevalent.
Aggregate point features into clusters
Feature clustering is available for use with any point feature layer in a map. You can dynamically switch between feature clustering and feature binning from the Aggregation drop-down menu.
With a feature layer selected in the Contents pane, click the Feature Layer tab on the ribbon. In the Drawing group, click the Aggregation drop-down menu  and choose Clustering
and choose Clustering  .
.
Note:
Clustering point features based on their z-values is not supported.