Synthèse
A PointGeometry object is a shape that has neither length nor area at a given scale.
Discussion
Dans de nombreux workflows de géotraitement, vous devez éventuellement exécuter une opération spécifique à l'aide d'informations sur les coordonnées et la géométrie, sans vouloir nécessairement créer une nouvelle classe d'entités (temporaire), la remplir avec des curseurs, l'utiliser, puis la supprimer. Les objets géométrie peuvent alors être utilisés en entrée et en sortie afin de simplifier le géotraitement. Les objets géométrie peuvent être entièrement créés à l'aide des classes Geometry, Multipoint, PointGeometry, Polygon ou Polyline.
During the creation of a geometry object, a simplification process is performed to make the geometry topologically consistent according to its geometry type. For instance, it rectifies polygons that may be self-intersecting or contain incorrect ring orientations. Coordinates may move within the resolution of the geometry's spatial reference.
The following operators can be used in place of geometry methods:
| Python operator | Geometry method |
|---|---|
+ | intersect |
| | union |
- | difference |
^ | symmetricDifference |
== | equals |
!= | not equals |
For example, to union two geometry objects, g3 = g1 | g2 is equivalent to g3 = g1.union(g2).
The + operator will use the geometry type (dimension) of the first geometry to determine the geometry type of the output.
Syntaxe
PointGeometry (inputs, {spatial_reference}, {has_z}, {has_m}, {has_id})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
inputs | A Point object used to create the object. | Point |
spatial_reference | The spatial reference of the new geometry. (La valeur par défaut est None) | SpatialReference |
has_z | Specifies whether the geometry will be z-enabled. (La valeur par défaut est False) | Boolean |
has_m | Specifies whether the geometry will be m-enabled. (La valeur par défaut est False) | Boolean |
has_id | Specifies whether the geometry will support point IDs. (La valeur par défaut est False) | Boolean |
Propriétés
| Propriété | Explication | Type de données |
| JSON (Lecture seule) | An Esri JSON representation of the geometry as a string. Conseil :The returned string can be converted to a dictionary using the json module's loads function. | String |
| WKB (Lecture seule) | The well-known binary (WKB) representation for OGC geometry. This property provides a portable representation of a geometry value as a contiguous stream of bytes. | Bytearray |
| WKT (Lecture seule) | The well-known text (WKT) representation for OGC geometry. This property provides a portable representation of a geometry value as a text string. Any true curves in the geometry will be densified into approximate curves in the WKT string. | String |
| area (Lecture seule) | The area of a polygon feature. The area is zero for all other feature types. | Double |
| centroid (Lecture seule) | The true centroid if it is within or on the feature; otherwise, it is the label point. | Point |
| extent (Lecture et écriture) | The extent of the geometry. | Extent |
| firstPoint (Lecture seule) | The first coordinate point of the geometry. | Point |
| hasCurves (Lecture seule) | Specifies whether the geometry has a curve. | Boolean |
| hullRectangle (Lecture seule) | A space-delimited string of the coordinate pairs of the convex hull rectangle. | String |
| isMultipart (Lecture seule) | Specifies whether the number of parts for the geometry is more than one. | Boolean |
| labelPoint (Lecture seule) | The point at which the label is located. This point is always located within or on a feature. | Point |
| lastPoint (Lecture seule) | The last coordinate of the feature. | Point |
| length (Lecture seule) | The length of the linear feature. The calculation uses 2D Cartesian mathematics. For point and multipoint geometry, the length will be zero. For polygon geometry, the length will be the 2D length of the boundary. | Double |
| length3D (Lecture seule) | The 3D length of the linear feature. The calculation uses 3D Cartesian mathematics. For point and multipoint geometry, the length will be zero. For polygon geometry, the length will be the 3D length of the boundary. Attention :The operation does not perform unit conversion between the horizontal and the vertical coordinate systems. The x, y, and z coordinates are assumed to be in the same linear unit. Attention :This property is only available for projected data. | Double |
| partCount (Lecture seule) | The number of geometry parts for the feature. | Integer |
| pointCount (Lecture seule) | The total number of points for the feature. | Integer |
| spatialReference (Lecture seule) | The spatial reference of the geometry. | SpatialReference |
| trueCentroid (Lecture seule) | The center of gravity for a feature. | Point |
| type (Lecture seule) | The geometry type: polygon, polyline, point, or multipoint. | String |
Vue d’ensemble des méthodes
| Méthode | Explication |
| angleAndDistanceTo (other, {method}) | Returns a tuple of angle and distance to a point or polygon. |
| boundary () | Constructs the boundary of the geometry. 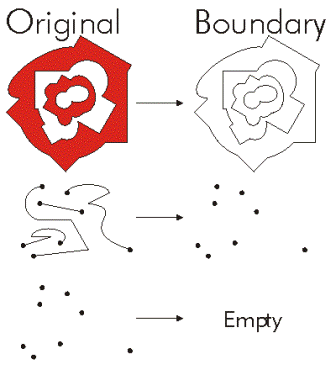 |
| buffer (distance) | Constructs a polygon at a specified distance from the geometry. 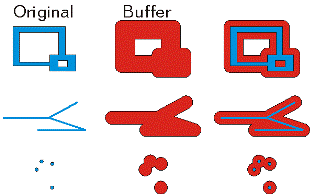 |
| clip (envelope) | Constructs the intersection of the geometry and the specified extent. 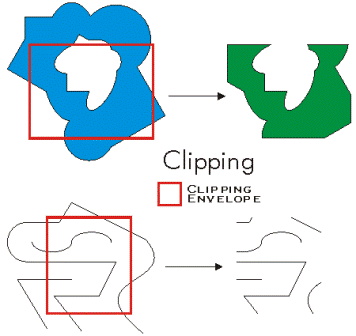 |
| contains (second_geometry, {relation}) | Indicates if the base geometry contains the comparison geometry. contains is the opposite of within. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 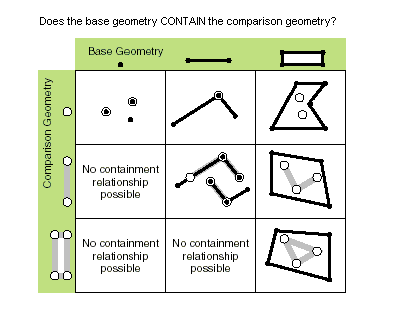 |
| convexHull () | Constructs the geometry that is the minimal bounding polygon such that all outer angles are convex.  |
| crosses (second_geometry) | Indique si les deux géométries s'intersectent dans une géométrie de type de forme inférieure. Deux polylignes se croisent si elles partagent uniquement des points, dont au moins un n'est pas une extrémité. Une polyligne et un polygone se croisent s'ils partagent une polyligne ou un point (pour une ligne verticale) à l'intérieur du polygone qui n'est pas équivalent à la polyligne entière. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 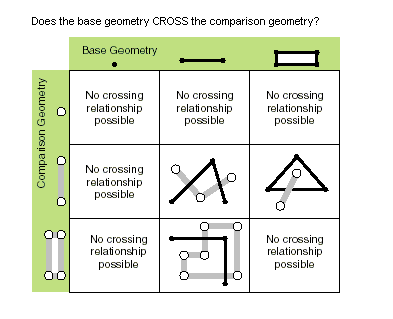 |
| difference (other) | Constructs the geometry that is composed only of the region unique to the base geometry but not part of the other geometry. The following illustration shows the results when the red polygon is the source geometry. 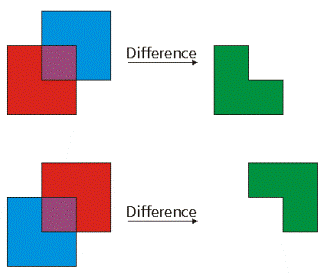 |
| disjoint (second_geometry) | Indique si la géométrie de base et la géométrie de comparaison n'ont aucun point en commun. Deux géométries s'intersectent si la propriété disjoint renvoie False. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 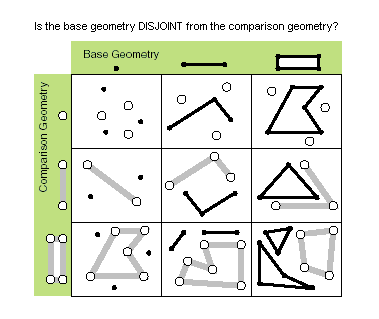 |
| distanceTo (other) | Returns the minimum distance between two geometries. The distance is in the units of the geometry's spatial reference. If the geometries intersect, the minimum distance is 0. Both geometries must have the same projection. |
| equals (second_geometry) | Indicates if the base and comparison geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. This is a 2D comparison only; M and Z values are ignored. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 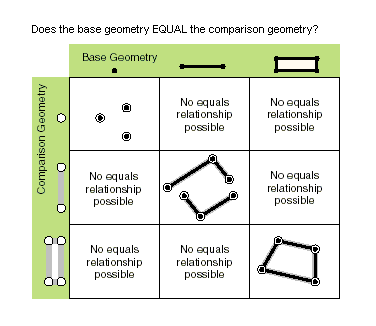 |
| getGeohash (precision) | Converts a PointGeometry in geographic coordinate system coordinates of latitude and longitude to a geohash string that is accurate to an arbitrary precision within a bounding box in the geohash grid. |
| getPart ({index}) | Returns an Array object of Point objects for a particular part of the geometry if an index is specified. If an index is not specified, an Array object containing an Array of Point objects for each geometry part is returned. The getPart method is equivalent to indexing an object; that is, obj.getPart(0) is equivalent to obj[0]. |
| intersect (other, dimension) | Constructs a geometry that is the geometric intersection of the two input geometries. Different dimension values can be used to create different shape types. The intersection of two geometries of the same shape type is a geometry containing only the regions of overlap between the original geometries. 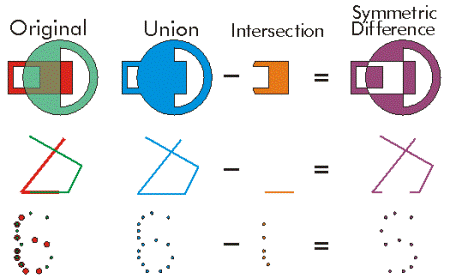 For faster results, test if the two geometries are disjoint before calling intersect. |
| move ({dx}, {dy}, {dz}) | Moves a geometry by specified distances along the x-, y-, and z-axes to create a new geometry. |
| overlaps (second_geometry) | Indique si l'intersection des deux géométries possède le même type de forme que l'une des géométries en entrée et qu'elle n'est pas équivalente à l'une des géométries en entrée. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration.  |
| pointFromAngleAndDistance (angle, distance, {method}) | Returns a point at a given angle in degrees and distance in the units of the geometry's spatial reference using the specified measurement type. |
| projectAs (spatial_reference, {transformation_name}) | Projects a geometry from one spatial reference to another. When the geometry object and the destination spatial reference do not have a common datum, specify a transformation_name parameter value. For more information, see Geographic datum transformations and ListTransformations. A vertical transformation will be performed when the following criteria are met:
When the transformation_name parameter value is a vertical transformation, and neither the geometry object nor the destination spatial reference have a vertical coordinate system, the function will fail with a ValueError exception. If either the geometry object or the spatial_reference parameter value have an unknown spatial reference, the output geometry's spatial reference will be that of the spatial_reference parameter value. Use of unknown spatial reference is not recommended for analysis. The projectAs method will not modify m-values, if present. |
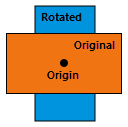
| rotate ({origin}, {rotation_angle}) | Rotates a geometry around a specified origin by the degrees given in radians. The rotation is applied relative to the origin, so that the geometry rotates around the origin. The position of the rotated geometry is significantly affected by the choice of origin. Rotate does not apply to the z-direction. The following describes a few possible choices for the origin and its affect on the output:
|
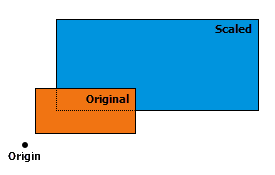
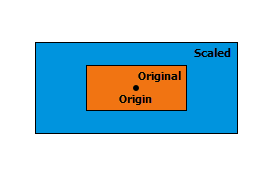
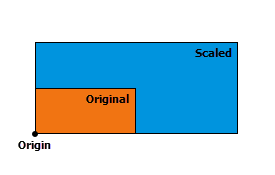
| scale ({origin}, {sx}, {sy}, {sz}) | Scales a geometry from a specified origin by specified factors along the x-, y-, and z-axes to create a new geometry. The position of a transformed point (or vertex) is given by The transformation is applied relative to the origin, so that the origin remains stationary while the geometry expands or contracts around it. The position and the direction of the expansion or contraction for the resulting geometries is significantly affected by the origin. The following describes a few possible choices for the origin and its affect on the output:
|
| symmetricDifference (other) | Constructs the geometry that is the union of two geometries minus the instersection of those geometries. The two input geometries must be the same shape type.  |
| toCoordString (notation) | Converts a PointGeometry to the selected coordinate system notation. |
| touches (second_geometry) | Indicates if the boundaries of the geometries intersect. Two geometries touch when the intersection of the geometries is not empty, but the intersection of their interiors is empty. For example, a point touches a polyline only if the point is coincident with one of the polyline end points. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 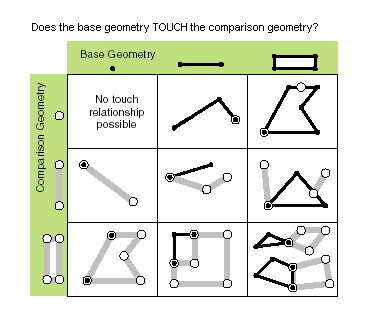 |
| union (other) | Constructs the geometry that is the set-theoretic union of the input geometries. The two geometries being unioned must be the same shape type.  |
| within (second_geometry, {relation}) | Indicates if the base geometry is within the comparison geometry. within is the opposite operator of contains. Only True relationships are shown in this illustration. 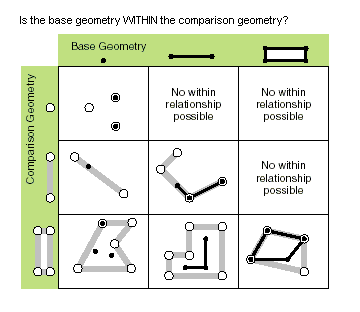 The base geometry is within the comparison geometry if the base geometry is the intersection of the geometries and the intersection of their interiors is not empty. within is a Clementini operator, except in the case of an empty base geometry. |
Méthodes
angleAndDistanceTo (other, {method})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
other | The second geometry. If the geometry is a polygon, the distance is measured to the centroid of the polygon. | PointGeometry |
method | The method used to measure distance.
(La valeur par défaut est GEODESIC) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| tuple | Returns a tuple of angle (in degrees) and distance (in meters) to another point. |
boundary ()
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | A polygon's boundary is a polyline. A polyline's boundary is a multipoint, corresponding to the endpoints of the line. A point or multipoint's boundary is an empty point or multipoint. |
buffer (distance)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
distance | The buffer distance. The buffer distance is in the same units as the geometry that is being buffered. A negative distance can only be specified against a polygon geometry. | Double |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Polygon | The buffered polygon geometry. |
clip (envelope)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
envelope | An Extent object used to define the clip extent. | Extent |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | An output geometry clipped to the specified extent. |
contains (second_geometry, {relation})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | The spatial relationship type.
(La valeur par défaut est None) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean |
A return Boolean value of True indicates this geometry contains the second geometry. |
convexHull ()
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | The resulting geometry. The convex hull of a single point is the point itself. |
crosses (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Une valeur booléenne renvoyée True indique que les deux géométries s'intersectent dans une géométrie de type de forme inférieure. |
difference (other)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
other | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | The resulting geometry. |
disjoint (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Une valeur booléenne renvoyée True indique que les deux géométries n'ont aucun point en commun. |
distanceTo (other)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
other | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Double | The distance between the two geometries. |
equals (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean |
A return Boolean value of True indicates that the two geometries are of the same shape type and define the same set of points in the plane. |
getGeohash (precision)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
precision | The precision length of the hash string to return for the PointGeometry. The minimum length is 1 and the maximum length is 20. The default length is 8. (La valeur par défaut est 8) | Integer |
| Type de données | Explication |
| String | getGeohash returns a geohash string based on the input point geometry latitude and longitude coordinates and the length of precision. |
The spatial reference of the point geometry must be in a geographic coordinate system to return an accurate geohash.
import arcpy
# Spatial reference set to GCS_WGS_1984
spatial_reference = arcpy.SpatialReference(4326)
pnt = arcpy.Point(-88.236, 40.096)
pnt_geometry = arcpy.PointGeometry(pnt, spatial_reference)
print(pnt_geometry.getGeohash(6)) # dp1k05getPart ({index})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
index | The index position of the geometry. | Integer |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Array | The resultant Array object. |
intersect (other, dimension)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
other | The second geometry. | Object |
dimension | The topological dimension (shape type) of the resulting geometry.
| Integer |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | A new geometry (point, multipoint, polyline, or polygon) that is the geometric intersection of the two input geometries. |
move ({dx}, {dy}, {dz})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
dx | The distance the geometry will be moved along the x-axis. (La valeur par défaut est 0.0) | Double |
dy | The distance the geometry will be moved along the y-axis. (La valeur par défaut est 0.0) | Double |
dz | The distance the geometry will be moved along the z-axis. The geometry must be z-aware and have z-values. (La valeur par défaut est 0.0) | Double |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Geometry | An output geometry, moved by the specified distances along the x-, y-, and z-axes. |
overlaps (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | Une valeur booléenne renvoyée True indique que l'intersection des deux géométries a la même dimension que l'une des géométries en entrée. |
pointFromAngleAndDistance (angle, distance, {method})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
angle | The angle in degrees to the returned point. | Double |
distance | The distance in the units of the geometry's spatial reference to the returned point. | Double |
method | PLANAR measurements reflect the projection of geographic data onto the 2D surface (in other words, they will not take into account the curvature of the earth). GEODESIC, GREAT_ELLIPTIC, LOXODROME, or PRESERVE_SHAPE measurement types can be chosen as an alternative if desired.
(La valeur par défaut est GEODESIC) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| PointGeometry | Returns a point at a given angle and distance in degrees and meters. |
projectAs (spatial_reference, {transformation_name})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
spatial_reference | The spatial reference to which the geometry will be projected. The value can be a SpatialReference object or the coordinate system name. | SpatialReference |
transformation_name | The geotransformation name. With ArcGIS Pro, if you do not specify a transformation, none will be applied. With ArcGIS Server, if you do not specify a transformation, a fallback transformation will be applied. | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | The projected geometry. |
rotate ({origin}, {rotation_angle})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
origin | The origin of the transformation. The argument can be either an arcpy.Point object or an arcpy.PointGeometry object. The default origin, arcpy.Point(0.0, 0.0), will usually be located outside the target geometry. (La valeur par défaut est arcpy.Point(0.0, 0.0)) | Point |
rotation_angle | The angle, in radians, to rotate the geometry around its origin. The default rotation angle is 0.0 radians (no rotation). (La valeur par défaut est 0.0) | Float |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Geometry | An output geometry rotated by the specified angle around the specified origin. |
scale ({origin}, {sx}, {sy}, {sz})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
origin | The origin of the transformation. The argument can be either an arcpy.Point object or an arcpy.PointGeometry object. The default origin, arcpy.Point(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), will usually be located outside the target geometry. (La valeur par défaut est arcpy.Point(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) | Point |
sx | The factor that will be used to scale the geometry along the x-axis. (La valeur par défaut est 1.0) | Double |
sy | The factor that will be used to scale the geometry along the y-axis. (La valeur par défaut est 1.0) | Double |
sz | The factor that will be used to scale the geometry along the z-axis. The geometry must be z-aware and have z-values. (La valeur par défaut est 1.0) | Double |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Geometry | An output geometry scaled from the specified origin and by specified factors along the x-, y-, and z-axes. |
symmetricDifference (other)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
other | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | The resulting geometry. |
toCoordString (notation)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
notation | The coordinate system notation to be generated.
| None |
| Type de données | Explication |
| String | The point in the specified coordinate system notation. |
touches (second_geometry)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | A return Boolean value of True indicates the boundaries of the geometries intersect. |
union (other)
| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
other | A second geometry. | Object |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Object | The resulting geometry. |
within (second_geometry, {relation})| Paramètre | Explication | Type de données |
second_geometry | A second geometry. | Object |
relation | The spatial relationship type.
(La valeur par défaut est None) | String |
| Type de données | Explication |
| Boolean | A return Boolean value of True indicates this geometry is contained within the second geometry. |
Exemple de code
Create a point feature class from scratch.
import arcpy
# Create a spatial reference from a wkid
spatial_ref = arcpy.SpatialReference(32145)
# A list of coordinate pairs
feature_info = [[1, 2], [3, 5], [7, 3]]
# A list to hold the PointGeometry objects
features = []
# For each coordinate pair, create a PointGeometry object
for pt in feature_info:
point = arcpy.Point(*pt)
point_geometry = arcpy.PointGeometry(point, spatial_ref)
features.append(point_geometry)
# Persist a copy of the PointGeometry objects using CopyFeatures
arcpy.CopyFeatures_management(features, "c:/geometry/f.gdb/points")Rubriques connexes
Vous avez un commentaire à formuler concernant cette rubrique ?