When you create or modify features that participate in a utility network, snapping, editing tools, and feature templates apply the rules and associations defined for your network.
The following sections summarize how editing tools work when you edit a utility network. To learn more about connectivity rules and associations, see the following topics:
For a basic workflow to get started, see Edit a utility network.
Group and preset templates
Group templates can be configured to generate associations between the features it creates when it contains a primary template that creates utility network features. Group template associations are limited to group features only and do not extend to the contents of preset templates assigned to the group.
Preset templates generate associations that were defined when the preset template was authored, independent of any group settings. This is true when you use them as component templates in a group template or as standalone templates.
For example, a group template with a primary template for a medium voltage line and a feature template for a medium voltage attachment as the snapping device can be configured to generate associations using these features.
If the group template in this example also contains a preset template for a transformer bank, the transformer bank components are placed in a map with the associations defined for them when the preset template was authored.
For step to create a group template, see Create a group template.
View attributes and associated assets
In the Attributes pane, you can view utility network attributes and associated assets for a selected feature. In the tree view, associations appear below the selected feature and report the total number of associated subfeatures.
In the selection list, you can right-click the association, and zoom to the associated features. Associated features are organized by layer and can contain multiple items. When you click an association—for example, a containment—information is reported on the Associations tab.
To learn more, see View utility network associations.
Move network features
When you use Move  to move a network feature, coincident features and features associated as container objects and structural attachments also move. For example, moving a duct bank also moves its contents, or moving a pole also moves a transformer attached to it.
to move a network feature, coincident features and features associated as container objects and structural attachments also move. For example, moving a duct bank also moves its contents, or moving a pole also moves a transformer attached to it.
Features that share a coincident endpoint, edge, or a vertex when midspan connections are permitted, are also edited. All coincident features move with the selected feature and linear features are stretched so that the visible feature topology remains contiguous.
Editing linear assets with tools such as Vertices  also edits other network features sharing the same x,y,z location and displays a rubber band line that stretches dynamically when you move a vertex.
also edits other network features sharing the same x,y,z location and displays a rubber band line that stretches dynamically when you move a vertex.
Note:
Utility networks use network topology to maintain connectivity among features and do not participate in map topology. Network topology enables you to trace a network and identify connected features, determine flow characteristics of a commodity such as water or electricity based on feature attributes, and perform other analytic operations.
To learn more, see About network topology.
Split network features
When you use Split  to split a utility network line feature, the resulting features are connected with a system junction feature at the location of the split. Asset types constrained by attribute domains are determined by the domain split policy defined for the utility network.
to split a utility network line feature, the resulting features are connected with a system junction feature at the location of the split. Asset types constrained by attribute domains are determined by the domain split policy defined for the utility network.
For example, container contents and associated attribute assignments are maintained based on the containment split policy defined for structure line feature classes.
To learn more, see Associations.
Junction and edge connections
Junction and edge connectivity rules are based on geometric coincidence and control the types of junction assets you can connect to specific edge assets.
Snapping
When you add or move a network feature, snap settings automatically change to settings that conform to junction and edge connectivity rules. You can turn snapping off, but you cannot change the layers or features to which you are snapping.
Tip:
When you create features, press T to view the snappable elements of a feature with respect to the connectivity rules.
To view connectivity rules, right-click the network in the Contents pane, click Properties  , and click the Network Properties tab.
, and click the Network Properties tab. 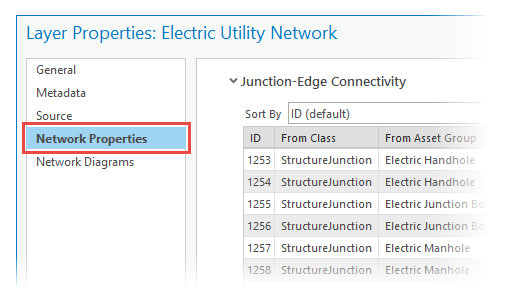
Midspan connections
When you place a network feature on a network linear feature segment or cross it with another linear network feature, the polyline is modified based on the junction and edge connectivity rules. How the polyline is modified is listed in the following table.
| Editing scenario | Midspan connection permitted | Midspan connection not permitted |
|---|---|---|
Point feature on a polyline feature | A vertex is added to the coincident polyline. | The segment is split, and the attributes and related records are copied to the new feature. |
Polyline feature crossing a polyline feature | A vertex is added at each intersection and where an endpoint touches the polyline. | The segment is split, and the attributes and related records are copied to the new feature. |
Junction and edge nonspatial objects
Junction and edge nonspatial objects model physical components contained inside network features such as strands inside a fiber cable or conductors inside an underground duct. You can also use them as container objects to contain other nested containers, features, and objects.
Nonspatial objects are stored in standalone tables and connected to network features using connectivity, containment, or structural associations.
To learn more, see Junction and edge objects.
Caution:
Editing tools that operate on selected features do not select nonspatial objects or layers that can't be edited.
To avoid unexpected results when selecting nonspatial objects, deactivate the current editing tool before executing the command. For example, press the Esc key after using the Move tool before selecting features by attributes in a standalone table or performing a network trace.
Edit attributes
To edit attributes for nonspatial objects in the Attributes pane, select the feature and expand the container.
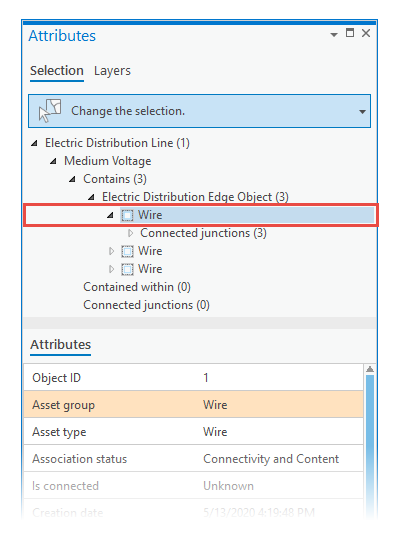
To remove a nonspatial object from a container feature in the Attributes pane, right-click the nonspatial object, and click Remove Association  .
.

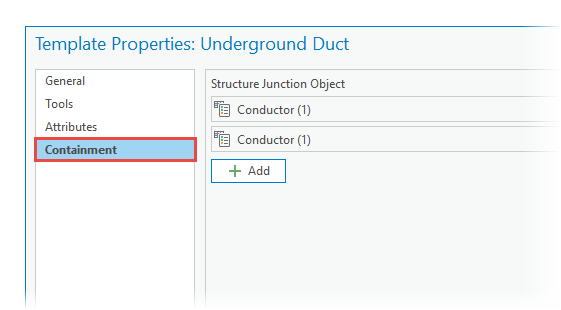
Create features
To include nonspatial objects when you create utility network features, add the table template to a feature template in Template Properties, on the Containment tab.