Available with Business Analyst license.
Summary
Creates a multigeography-level, scale-dependent choropleth layer from a variable describing a business, demographic, consumer, or landscape characteristic.
Illustration
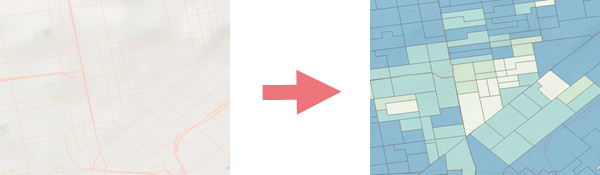
Usage
Map appearance will vary based on the classification method employed. Detailed explanations of each are contained in the parameter syntax documentation.
The default number of classification fields is 5. This can be changed within the Number of Classes parameter. Typically, the number of breaks ranges from 3 to 7.
The geography level displayed will automatically adjust to the optimal geography level as map scale changes.
You can specify three classes for a field whose values range from 0 to 300; the application will create three classes with ranges of 0–100, 101–200, and 201–300.
The Geometric Interval method uses an algorithm that creates class breaks by minimizing the sum of squares of the number of elements in each class. This ensures that each class range has approximately the same number of values with each class and that the change between intervals is consistent.
Natural breaks are divided into classes whose boundaries are set where there are relatively big differences in the data values.
Quantile assigns the same number of data values to each class. There are no empty classes or classes with too few or too many values.
Business Analyst Data, used in summarizations and reports, is specified through the geoprocessing Data Source environment setting.
Syntax
ColorCodedLayer(classification_variable, out_layer_name, classification_method, number_of_classes)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
classification_variable | Select one variable to display as a color-coded map. | String |
out_layer_name | The name of the color-coded layer that will be added to the map. | String |
classification_method | The method that will be used to calculate the class breaks.
| String |
number_of_classes | The number of data classification breaks that appear on the map. The default value is 5. | String |
Derived Output
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_layer | A container for the output layer. | Group Layer |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the ColorCodedLayer tool.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.baDataSource = "ONLINE;US;"
arcpy.ba.ColorCodedLayer("networth.mednw_cy", "CCL_NetWorth", "NATURAL_BREAKS", 5)The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the ColorCodedLayer tool with Statistical Data Collection variables.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.baDataSource = "USA_ESRI_2018"
arcpy.ba.ColorCodedLayer(r"c:\users\<User ID>\documents\arcgis\projects\my_project\bayarea_proprietarydata.sdcx/sales_s01_sales", "sales_s01_sales Layer", "NATURAL_BREAKS", 5)Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Requires Business Analyst
- Standard: Requires Business Analyst
- Advanced: Requires Business Analyst