Available with Image Analyst license.
A stereo map is a stereoscopy-enabled map that provides stereo vision through a stereo model, which is composed of two images of the same geographic area taken from two locations. Binocular stereo vision provides better image interpretation than singular mono vision. With stereo display, you can perceive 3D depth, such as slopes and topography, complex building structures, and feature heights and elevation. You can also collect 3D features from the stereo images in the ArcGIS Pro stereo map.
A stereo map's data source is a stereo model consisting of a stereo image pair or a collection of stereo models managed as a mosaic dataset. The stereo mosaic dataset is created as a workspace in the Ortho Mapping application and must be block adjusted to derive the stereo model.
The stereo map uses the left and right images in the stereo model to establish the stereo display. ArcGIS Pro supports three types of stereo display, described below.
- Anaglyph that uses red and cyan glasses. This approach is not recommended for prolonged use stereoscopically.
- Active shutter that uses active shutter glasses in conjunction with an infra-red emitter and 3D stereo monitor.
- Passive display that uses polarized glasses in conjunction with a 3D monitor that uses a beam splitter technology.
For the shutter eyewear requirements, see Stereo requirements.

A stereo map has a projection that is defined by the current stereo model. The spatial reference of the map cannot be changed, but the stereo map can display the supported layer in any projection. If the layers have a different coordinate system than the stereo map, they are projected on the fly to the spatial reference of the stereo map. The best practice is to avoid reprojection when possible.
When a stereo pair is loaded, the Stereo Map view displays two images in which the epipolar lines are parallel to the x-axis. The stereo cursor always returns to x, y, and z, which are displayed in the stereo view status in current projection units. If no vertical datum is defined, the z-unit will be the same as that defined in the mosaic dataset.
Stereo Map tab
The Stereo Map tab contains several groups: Clipboard, Navigate, Stereo Source, Layer, Stereo Display, Stereo Model, Cursor Type, Subviews, Inquiry and Input Device.

The Clipboard, Navigate, and Layer groups are duplicated from the map view. The Inquiry group contains the Locate tool. The other groups are unique to the stereo workflow.
Stereo Source group
The Stereo Source group exposes two tools; Set Source and Set DEM Source. The Set Source tool has a split button to set and clear the stereo source. When a stereo map is initiated, you need to identify the data source for the stereo project. The Set Source button  enables you to choose which stereo images to use in
a project. You can choose a mosaic dataset or an image pair. A mosaic dataset can also be added to the Stereo map using either of the methods listed below:
enables you to choose which stereo images to use in
a project. You can choose a mosaic dataset or an image pair. A mosaic dataset can also be added to the Stereo map using either of the methods listed below:
- Drag and drop a mosaic dataset into an opened Stereo Map.
- Right-click on a mosaic dataset, select Add to New, then choose New Stereo Map.
When the stereo source is loaded, the first stereo pair of the mosaic data is used by default. The stereo map also assigns the name of the mosaic dataset for project identification. Once you choose the stereo source, you can use the various stereo tools on the source images and perform the stereo workflow.
A stereo map can only have one stereo source. If the stereo map already has a stereo source defined, the new stereo source replaces the existing stereo source. If the source mosaic dataset does not have a stereo model built, a warning message appears indicating that a stereo model must be built before it can be used as a stereo source. When you use two images as a stereo source, ArcGIS Pro checks the files for rational polynomial coefficients (RPCs), frame camera models, and overlap between the two images. If any of the requirements are missing, you are notified.
The Set DEM Source option allows you to add a digital elevation model (DEM) to the source mosaic dataset to support terrain following functionality. The advantage of this functionality is that when activated by pressing T on your keyboard, it automatically keeps the cursor at terrain level as you move and pan. If this option is not activated, you must manually adjust the cursor height to support proper stereoscopic viewing. For additional information about terrain following functionality, see the Terrain Following section below. The Set DEM Source option is only available when working with a mosaic dataset as a stereo source. When selected, the Set DEM Source dialog box appears, which allows you to select a local DEM by browsing to the file on disk. Once the DEM is added to the mosaic dataset, the images are geometrically corrected. This may result in the shape and extent of the mosaic dataset being changed to match the extent of the applied DEM. This shape and extent change is apparent in the 2D map window but not in the Stereo Map view.
When you are finished using the current stereo source and want to remove it from the stereo map, use the Clear Source button in the menu below Set Source  .
.
Stereo Display group

The Stereo Display group has tools to set up selected image pairs for the stereo workflow. The Display Mode has a drop-down menu to choose how to display the stereo pairs. The Default option  displays both images. If you only want to see the left or the right image, click the Left Image Only button
displays both images. If you only want to see the left or the right image, click the Left Image Only button  or the Right Image Only button
or the Right Image Only button  , respectively. Click None
, respectively. Click None  if you do not want to display either of the stereo images.
if you do not want to display either of the stereo images.
If the stereo pairs are in the wrong order and you want to swap the images, click Invert  .
.
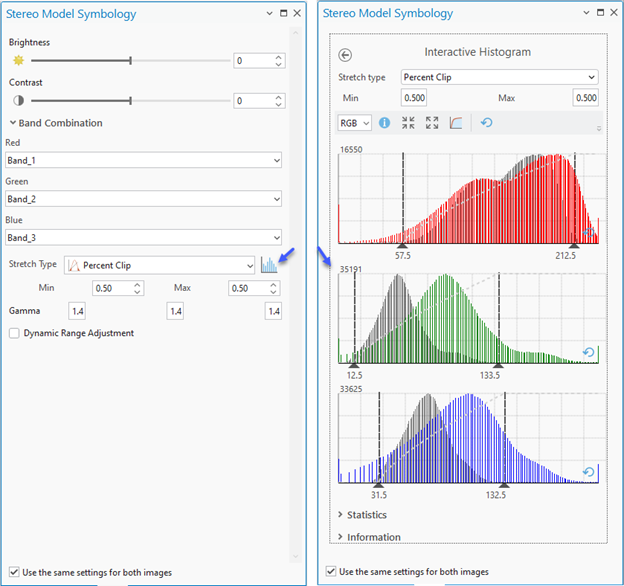
Stretch  opens the Stereo Model Symbology pane, allowing you to adjust the image display setting for both images. You can adjust the brightness, contrast, and gamma for each band of each image. Additionally, you can adjust symbology settings such as band combination, stretch type, histogram for each band, and dynamic range adjustment. If the settings for both images are the same, you can check the Use same settings for both images check box and make the display adjustments to both images simultaneously.
opens the Stereo Model Symbology pane, allowing you to adjust the image display setting for both images. You can adjust the brightness, contrast, and gamma for each band of each image. Additionally, you can adjust symbology settings such as band combination, stretch type, histogram for each band, and dynamic range adjustment. If the settings for both images are the same, you can check the Use same settings for both images check box and make the display adjustments to both images simultaneously.
Zoom to Model  updates the map display with the chosen stereo pair. This is helpful when you are exploring the map and want to return focus to the extent of the stereo pairs.
updates the map display with the chosen stereo pair. This is helpful when you are exploring the map and want to return focus to the extent of the stereo pairs.
The Resolution drop-down list allows you to set the display scale based on a factor of the current stereo model's resolution. These resolution choices help you work at the same level of detail for all your stereo models.
Stereo Model group

The stereo model collection can include many stereo pairs. The Stereo Model group has the tools to choose the stereo pair you want to work with in the stereo source. The Model Selector button  opens the Stereo Model Selector pane, which allows you to manage and select stereo pairs. The top of this pane displays the footprints of all the stereo pairs in the stereo source. The bottom of the pane lists all the available stereo pairs, which can be filtered by polygon, map extent, or attribute. For more information about the Stereo Model Selector pane, see Stereo Model Selector pane.
opens the Stereo Model Selector pane, which allows you to manage and select stereo pairs. The top of this pane displays the footprints of all the stereo pairs in the stereo source. The bottom of the pane lists all the available stereo pairs, which can be filtered by polygon, map extent, or attribute. For more information about the Stereo Model Selector pane, see Stereo Model Selector pane.

The other tools in the Stereo Model group provide different ways to choose the stereo pair to work with. Auto Load  displays the most appropriate stereo pair based on your location in the map display and the stereo model metadata. As you pan toward the edge of the model, the next best stereo pair is automatically loaded in the Stereo Map view. This means that you don't need to manually advance stereo pairs when working stereoscopically. The Auto Load toggle button can be turned on or off by clicking it or by pressing M on your keyboard.
displays the most appropriate stereo pair based on your location in the map display and the stereo model metadata. As you pan toward the edge of the model, the next best stereo pair is automatically loaded in the Stereo Map view. This means that you don't need to manually advance stereo pairs when working stereoscopically. The Auto Load toggle button can be turned on or off by clicking it or by pressing M on your keyboard.
Note:
Manually loading a stereo model deactivates the auto load functionality.
Next Stereo Model  displays the next stereo pair in the stereo model based on the current sorting order. Conversely, Previous Stereo Model
displays the next stereo pair in the stereo model based on the current sorting order. Conversely, Previous Stereo Model  displays the previous stereo pair in the stereo model based on the current sorting order. Undo Stereo Model
displays the previous stereo pair in the stereo model based on the current sorting order. Undo Stereo Model  goes back to the previous stereo pair that was displayed in the map. Redo Stereo Model
goes back to the previous stereo pair that was displayed in the map. Redo Stereo Model  shows the next stereo pair that you were working with in the stereo map.
shows the next stereo pair that you were working with in the stereo map.
Click Ignore Obliques  to filter out stereo pairs with oblique angles greater than 15 degrees. This option is particularly useful when performing feature extraction from a block of images comprised of nadir and oblique images. Ignore Obliques can also be activated from the Filter option
to filter out stereo pairs with oblique angles greater than 15 degrees. This option is particularly useful when performing feature extraction from a block of images comprised of nadir and oblique images. Ignore Obliques can also be activated from the Filter option  in the Stereo Model Selector pane using the Filter by attribute option.
in the Stereo Model Selector pane using the Filter by attribute option.

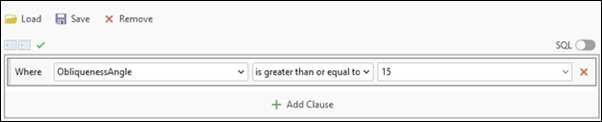
The number of models visible in the Stereo Model Selector pane after activating the Ignore Oblique filter will be equal to the filtered result. While activated, both Auto Load best pair and Next Stereo Model options will honor the filtered results. Clicking Ignore Obliques again will deactivate it.
Note:
The Build Stereo Model geoprocessing tool will need to be run on mosaic datasets built prior to ArcGIS Pro 3.4 for them to work with the Ignore Oblique capability.
Cursor group
The tools in the Cursor group help you pick the right cursor shape, size, and color for the data. They also allow you to set the cursor z-sensitivity.
Cursor type
The following cursor shapes are available:
- Box Dot

- Circle Dot

- Cross Dot

- Cross Only
- Dot

- X Dot

- X Only

Each cursor shape has advantages and disadvantages, but it is mainly a personal preference as to which one to use.
Cursor size and color
You can select the color and size of the cursor to increase its visibility in the stereo view. If you use the cyan/red anaglyph view, some colors show the height of the cursor better than others.
Cursor sensitivity
The cursor sensitivity page allows you to determine how much the z-value changes per scroll of the mouse wheel. The default value is the value set by the system based on data characteristics. It also allows you to set how the accelerator (Shift key) and decelerator (Caps Lock key) shortcuts will affect the change in z per scroll.
You can change the application default values for cursor sensitivity on the Navigation Options page.
Sub Views group

The Sub Views group has tools to help you view stereo imagery in the Overview and Magnifier windows.
The Overview window  shows the zoomed-out location of the current extent. This can help you navigate around the stereo pairs in a project without leaving the current stereo display resolution. The Magnifier window
shows the zoomed-out location of the current extent. This can help you navigate around the stereo pairs in a project without leaving the current stereo display resolution. The Magnifier window  shows a zoomed-in view of the location of the cursor. This can help you view an object closely, without leaving the current stereo display resolution.
shows a zoomed-in view of the location of the cursor. This can help you view an object closely, without leaving the current stereo display resolution.
Input Device group
The Input Device group includes a View Button Mapping option that enables a quick view of the Stealth or Softmouse 3D input device button assignments. New button assignments can also be changed from this group and saved by clicking the OK button.
Stereo map navigation
In the Stereo Map view, you can change the cursor's location by moving it to the desired x,y location. To change the z-location (height), you can rotate the mouse wheel to change the cursor's z-value. Click the mouse button to enter the current 3D point.
You can use the standard Pan and Zoom tools to navigate around a stereo map. The multiple predefined pixel resolution scales allow you to navigate to the desired display scale. The 1 : Square root of 2 scale is often an optimal scale for stereo display clarity.
You may need to adjust the x-parallax manually or automatically using F8 key to see the features clearly or if you want to zoom in to or out from features. You can also adjust the y-parallax if the adjustment accuracy of the stereo model is limited.
The following table lists the navigation keys used to manipulate the cursor and the display:
| Keyboard shortcut | Action | Comment |
|---|---|---|
Ctrl+Alt+S | Activate the Select tool. | |
Ctrl+Alt+C | Activate the Explore tool. | |
Click and drag | Pan the map. | |
Shift | Accelerate change in x,y. | Move the pointer in the direction you want. Press Shift again to return to the standard speed of change in x,y. |
Caps Lock | Decelerate change in x,y. | Move the pointer in the direction you want. Press Caps Lock again to return to the standard speed of change in x,y. |
Q | Roam. | Move the pointer in the direction you want. |
Plus sign (+) or Ctrl+Mouse wheel | Zoom in. | Zoom in on the map. |
Hyphen (-) or Ctrl+Mouse wheel | Zoom out. | Zoom out on the map. |
Z and move pointer horizontally or Z+Mouse wheel | Change the z-value. | To increase the z-value, rotate the mouse wheel backward or press Z while dragging the pointer to the right. To decrease the z-value, rotate the mouse wheel forward or press Z while dragging the pointer to the left. |
Shift+Z and move pointer horizontally or Shift+Mouse wheel | Accelerate change in z. | Press Shift while rotating the mouse wheel. Alternatively, to change the z-value 15 times faster, press Shift+Z while moving the pointer either left or right. |
Caps Lock+Z and move pointer horizontally or Caps Lock+Mouse wheel | Decelerate change in z. | Press Caps Lock while rotating the mouse wheel. Alternatively, to change the z-value five times slower, press Caps Lock and then press Z while moving the pointer either left or right. |
B | Turn surface snapping on or off. | Surface snapping provides on-demand positioning of the floating mark to the elevation surface at the current stereo pointer location. This provides the z-value at the stereo pointer position. This feature requires the images to have statistics calculated and pyramids built with either bilinear or cubic resampling. |
T | Turn terrain following on or off. | Terrain following automatically keeps the stereo pointer on the surface of the stereo model as you pan the stereo image pair. This feature is useful in navigating the stereo display. |
H | Change selected vertex height. | |
F8 | Switch between roaming pointer mode and fixed pointer mode. | |
F9 | Hide feature layers on the map. | |
Tilde (~) | Temporarily turn off fixed pointer mode. | This turns off the fixed pointer mode to allow you to perform other tasks. To return to the fixed pointer mode, press the Tilde key again. Note:There is no need to press the Shift key. This shortcut applies to United States standard keyboards. Other types of keyboards may have a different character on the key. For detailed information, verify which key the VK_OEM_3 (Microsoft virtual key code) is mapped to for your keyboard. |
Ctrl+Left arrow key or Ctrl+Right arrow key; or V and move pointer left or right | Adjust the x-parallax. | The two images move toward or away from each other in the x (horizontal) direction. |
Ctrl+Up arrow key or Ctrl+Down arrow key | Adjust the y-parallax. | The two images move toward or away from each other in the y (vertical) direction. |
Ctrl+F7 | Reset to the default parallax. | |
M | Activate Auto Load. | Turn on and off the automatic loading of the best stereo pair based on image metadata. |
E | Pan to the center of the stereo pair. | |
Ctrl+Shift+M | Open the Modify Features pane. | |
Ctrl+Shift+C | Open the Create Features pane. | |
Ctrl+Shift+S | Open the Stereo Model Selector pane. | |
O | Open the Overview window. | |
W | Open the Magnifier window. |
For more keyboard shortcuts, see Keyboard shortcuts for navigation and Keyboard shortcuts for editing.
The Stereo Map view supports two cursor modes: a roaming cursor and a fixed cursor. A roaming cursor shows typical cursor behavior: when you move the mouse, the cursor moves. This is the default behavior. A fixed cursor stays in the center of the display, and the imagery roams in the direction you move the mouse. The fixed cursor is efficient when collecting features since it reduces the need to pan on the map. While in the fixed cursor mode, you can temporarily switch to the roaming cursor mode by pressing the F8 key.
Terrain following
Terrain following automatically keeps the stereo cursor on the surface of the stereo model as you pan the stereo image pair. This feature is useful in navigating the stereo display. Terrain following is supported in two ways:
- Image correlation
- Using a DEM attached to the mosaic dataset or image collection
If no DEM is attached to the mosaic dataset, terrain following using image correlation is available. When a DEM is attached to the mosaic dataset, terrain following based on the DEM is used by default.
When using terrain following based on image correlation, consider the following:
- When using a very large image over a remote network connection, it is recommended that you do not use the image correlation method since there may be significant delays for the system to retrieve the correlation information.
- It is recommended that you do not use the image correlation method in the fixed cursor mode with images that have frequent and dramatic surface change, such as a digital surface model (DSM) with dense buildings.
- The images must have statistics calculated and pyramids built with either bilinear or cubic resampling.
When using terrain following based on a DEM, consider the following:
- A DEM can be attached to a mosaic dataset using the Set DEM Source option in the Stereo Source group.
- The attached DEM must have the same vertical coordinate system (VCS) as the stereo model or image collection.
- The accuracy of the terrain following is directly related to the accuracy of the DEM. It is recommended that you use a DEM extracted from the current model or block to support accurate terrain following. The DEM can be derived using the DEM extraction tools in the Ortho Mapping product generation wizard or using the ArcGIS Reality for ArcGIS Pro extension.
Features in a stereo map
Features can be added to the stereo map using the Add Data button or by dragging the file onto the map. Once added to the stereo view, features are overlaid on top of the stereo model that is being viewed and are clipped to the stereo model. New Labeling and Data contextual tabs are added to the ArcGIS Pro main menu, from which additional vector-specific capabilities are available.
Feature labeling allows you to superimpose features on imagery and display labels for improved feature identification. To enable labeling, click the Labeling tab, and select Label, or you can right-click the feature in the Contents pane and select Label from the drop-down menu. To adjust label properties—such as size, color, and weight—select Labeling Properties from the drop-down menu or from the Labeling tab on the main menu.
Note:
Labeling is not supported on ADS sensor imagery.
A feature that is added to the map is visible only if a source has been set. The display of all features in the Stereo Map view can be switched on or off by pressing the F9 key.
Stereo map properties
To access the stereo map properties, right-click the stereo map in the Contents pane and click Properties. The Stereo tab in the Map Properties: Stereo pane allows you to view source information about the images comprising the stereo model and set the orientation direction of the stereo models displayed in the stereo map.
Stereo source information
The stereo source information section shows the source information about the images comprising the stereo model that is currently displayed in the stereo map. These images can be two images making up a stereo pair or two items in a collection of images. The type of information displayed includes the location of the data, name of the dataset, type of workspace, and the ID of the left and right images of the stereo pair.
Stereo model orientation
Stereo models are displayed in certain configurations due to the nature of stereoscopic viewing. The images are displayed with one image designated as the left image and the second image designated as the right image. Image collection flight lines are typically collected in an east-west or west-east direction, where north is up or down in the map, or a north-south or south-north direction, where north is left or right in the map. Consider both of these factors when orienting imagery for stereo viewing.
In ArcGIS Pro, you can choose the way stereo models are oriented when displayed in the stereo map. You can orient stereo models using the Up or Right, Up or Left, Down or Right, and Down and Left options to reflect where north is.