Basemaps serve as a reference map on which you
overlay data from layers and
visualize geographic information. An individual basemap can be made of multiple feature, raster, or web layers. Basemaps are the foundation for your maps and provide context for your work. 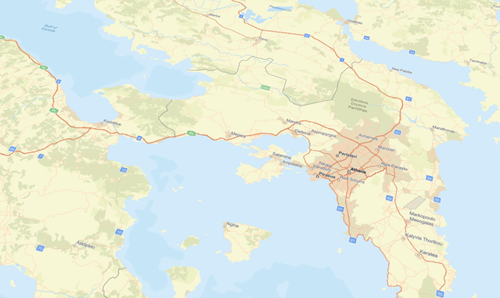
As 2D basemaps are designed for maps, 3D basemaps are designed for local and global scenes. They include scene layers such as buildings and trees. 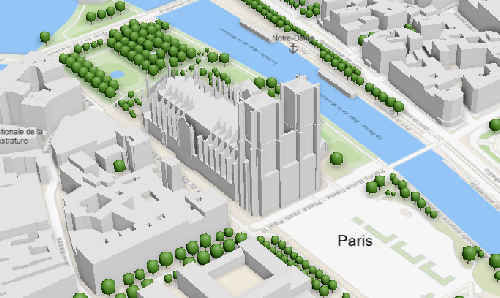
The ArcGIS Pro basemap gallery includes several curated 2D and 3D basemaps for you to use in your maps and scenes. After you add a map or scene to your project, the basemap can be changed from the Map tab.
Add a basemap to a map
To add or change the basemap in the active map, follow these steps:
- On the Map tab, in the Layer group, click Basemap
 to open the basemap gallery.
to open the basemap gallery. - Click a basemap in the gallery.
The basemap is updated or added to the map. Only one basemap can be used at a time per map.
Note:
Basemaps are authoritative maps that are either assembled, curated, or managed by Esri. Both vector and imagery-based basemap content are updated approximately every three weeks with any new data that is provided by authoritative sources or the greater community.
When a new basemap is added to a map, it includes an elevation surface. The elevation surface is included in case you want to use the basemap in a scene. When you add a custom basemap to a 2D map from the basemap gallery, the elevation surface is not included.
The other predefined basemaps included in the basemap gallery are designed to be used at multiple map scales so the basemap portrays appropriate content at each range of map scales. These basemaps are relatively static and are updated on an infrequent basis.
Some basemaps (such as the Terrain with Labels basemap) include an independent reference layer with labels, which allows you to turn on and off its labels. In other basemaps, the labels are included within the map layer.
In local and global scenes, the basemap gallery can include 3D basemaps with an active ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise portal connection. When a scene is converted to a map, the scene layers remain in the Contents pane but do not render in the map. If you choose a 2D basemap in the basemap gallery, any 3D layers are removed.
Set the default basemap
Your ArcGIS Online organization account settings determine your default basemap. However, you can change the default basemap that is added to new maps in map and scene options. You can choose to add a different (custom) basemap by default from the gallery. Or, you can specify that maps and scenes are created without a basemap. Depending on your organization settings, some basemaps may not be available for use.
You can also choose to use vector-based or raster-based basemaps in your ArcGIS Online organization settings. For more information, see Configure map.
Author a custom basemap
Authoring a custom basemap allows you to define reference and background layers. Reference layers draw on top of operational layers, while background layers draw below operational layers.
For example, you may include roads as a reference layer and base imagery as a background layer. Using this custom basemap, the roads layer would appear above any new layers added to the map, while the image layer would appear beneath.
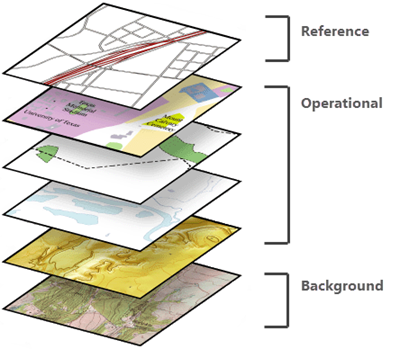
After you create a custom basemap, it is automatically saved and added to the Basemap gallery. From there, it can be used in other maps in the project, but it is not available in other projects.
Note:
Basemaps that contain both reference and background layers appear in the Contents pane in two independent lists.
- On the Insert tab, in the Project group, click the New Map drop-down arrow and click New Basemap
 .
. A new blank map view opens.
- Add the data that you want to comprise your basemap. On the Map tab, in the Layer group, click Add Data
 . Browse to your data, and add it to the basemap.
. Browse to your data, and add it to the basemap. You can also drag content into the map from the Catalog pane.
- With the basemap in view, in the Contents pane, click List By Drawing Order
 . Right-click a layer and click Set as Reference Layer to set all layers above the selected layer as reference
layers, and all layers below it as background layers.
. Right-click a layer and click Set as Reference Layer to set all layers above the selected layer as reference
layers, and all layers below it as background layers.
Convert a map to a basemap
In ArcGIS Pro, you can use a map and its layers as a basemap in another map. You can convert the map into a basemap, which allows you to use it in any other map in the project. To convert a map to a basemap, follow these steps:
- Open the map to convert in the view.
- On the View tab, in the View group, click Convert
 .
. - On the drop-down menu, choose To Basemap
 .
.
The map is converted to a basemap of the same name, with the suffix BM. The basemap icon  appears on the basemap's view tab. You can choose to add this basemap to other maps in the project from the basemap gallery.
appears on the basemap's view tab. You can choose to add this basemap to other maps in the project from the basemap gallery.
In the Contents pane, the map's layers have been copied to the basemap.
Note:
Layers not supported to draw in a map, for example, a scene layer, will automatically be removed from the basemap.
Choose a 3D basemap
If your active portal is set to ArcGIS Online, you can choose to use a 3D basemap. You can combine a 3D basemap with your own layers, and in overlapping areas, you can apply a mask. For example, if you have a single building such as a BIM model and you need to visualize it in the context of the surrounding buildings, to ensure the model does not overlap the building in the 3D basemap, you can exclude the building by applying a mask.
If you choose to use a different 3D basemap when there are masks already applied, you can keep the masks or discard them. The Apply Masks dialog box appears, and you can set which masks are associated with which operational layers.
Google Photorealistic 3D Basemap
If your active portal is set to ArcGIS Online and your organization has access, you can choose the Google Photorealistic 3D Basemap from the basemap gallery on the Map tab. This layer is a global dataset that replaces your 2D or 3D basemap layers as well as the Esri Terrain 3D. This mesh dataset appears as an elevation layer in Ground and provides both photorealistic textures and elevation values in one global dataset. As a global dataset, any existing elevation sources in the ground will not render while the Google Mesh layer is present. Some commands on the Elevation Surface Layer contextual tab are unavailable. The zero surface will not render while the Google Mesh layer is present for Ground. Switch to a different basemap to access properties on the Elevation Surface Layer contextual tab as well as render your custom elevation layers.