ArcGIS Pro 3.6 keeps the focus on the application's performance, productivity, and usability. Some major enhancements—such as a new look for ModelBuilder and the ability to synchronize time display on maps—are summarized in the Highlights section. More quality improvements appear in the following sections. This release also emphasizes 3D visualization with Gaussian splat layers, the Google Photorealistic 3D basemap, improved terrain rendering in flood simulations, and enhancements to weather effects.
Video overview
This video was created by the ArcGIS Pro development teams and the product support teams to highlight new functionality in this release.
Highlights
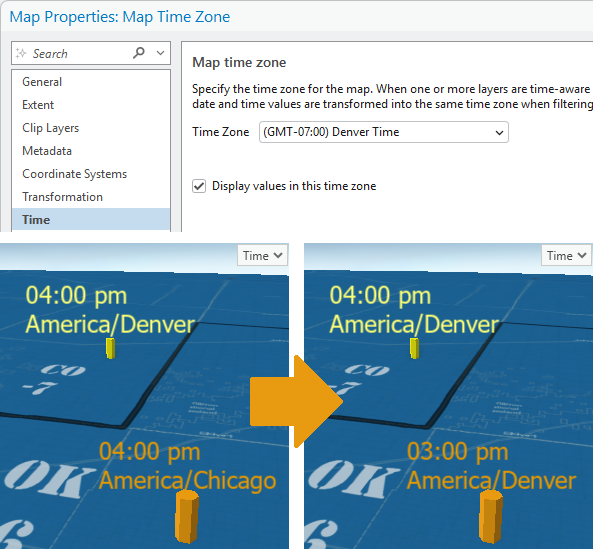
Display date-time values in the map's time zone
You can set map time properties to adjust temporal values in time-configured layers to align to a common time zone. This simplifies working with temporal content, as it ensures that time values in different time zones can be directly compared.
This option changes the displayed value only; the value stored in the data does not change. Layers must have a time zone defined for those temporal values to participate. The adjusted time values are applied everywhere data values are shown, including tables, the Attributes pane, labels, reports, and pop-ups. In the table, you can hover over a field header to show the time zone being displayed as well as the time zone of the data.
You can edit an adjusted temporal value in the defined time zone of the layer or in the map time zone. When editing using the Calendar control  , you can choose the time zone that is applicable to the date entered.
, you can choose the time zone that is applicable to the date entered.
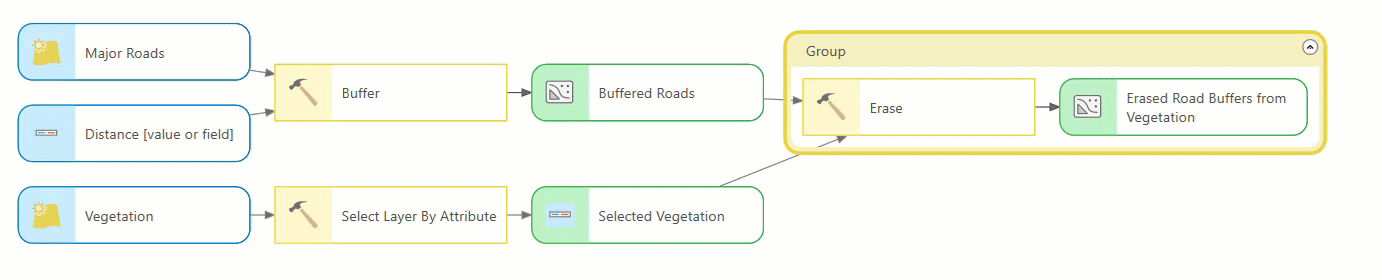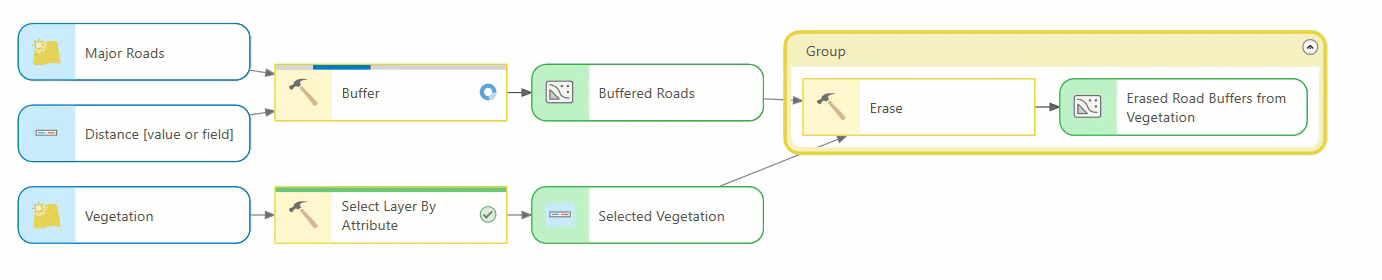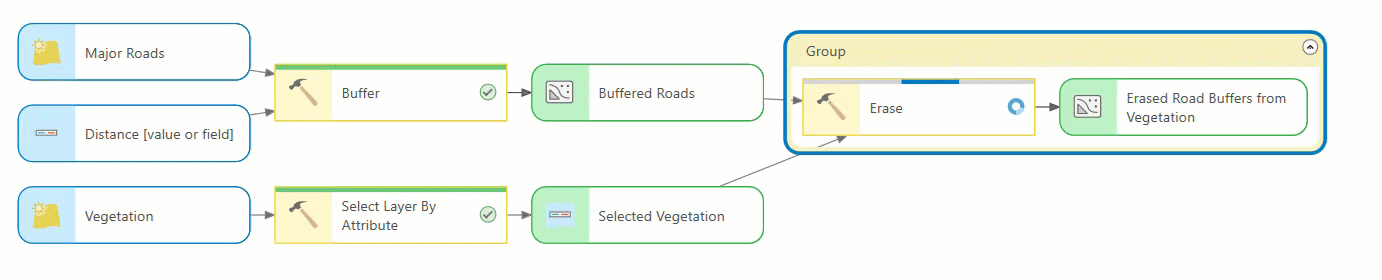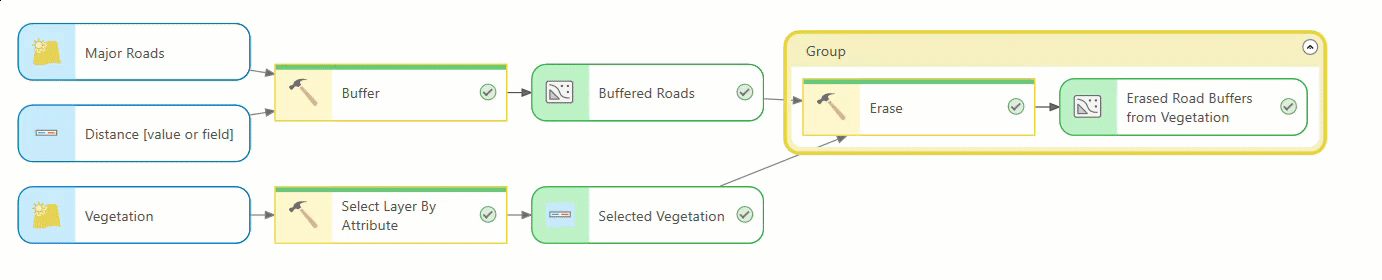
ModelBuilder redesign
ModelBuilder has a visually modern look that makes it more consistent with ModelBuilder in ArcGIS Online. The new design incorporates the following changes:
- Element nodes such as tools, variables, inputs, and outputs are now rounded rectangles. When you add new variables or tools, they appear in gray to indicate an invalid state.
- Tools and variables that are ready to run are shown in a pastel color scheme.
- Groups are represented in a new color to match the color theme of the other nodes and elements.
- Variables nodes display a data type icon, and tool nodes display an icon representing their tool type (built-in, model, or script). Connecting a data variable to a tool opens a new pop-up that lists the tool parameters and its icons.
- Tools show a progress bar as they run. Once complete, the tool shows a green check mark if it ran successfully or a red x if it failed. Groups show a corresponding red color if any tool in the group fails.
- The Variable Data Type dialog box uses visual aids to explain the single value, multiple value, and value table variable types. This helps you make informed decisions when creating variables.
View software announcements
When you start ArcGIS Pro, it now checks for software announcements related to your installed ArcGIS Pro products by default. Announcements include information about upcoming software changes, deprecation notices, and critical software defects. They appear as toast notifications and as items in the Notifications pane. Your computer must be connected to the internet to check for and receive announcements.
Geodatabase schema reporting
The Generate Schema Report geoprocessing tool has a new dynamic HTML output format. The schema report is produced using Calcite Design System components that give it a similar look and feel to ArcGIS Online. The report layout and navigation are significantly better than the tool's original standard HTML format.
Other benefits of the dynamic HTML output include the following:
- A familiar user interface
- A list view for quick scanning of schema elements and a traditional table view
- Search, sort, and filter options
- A single output .html file that is easy to share
The Compare Schema geoprocessing tool allows you to review the differences between the schemas of two geodatabases, schema reports, feature datasets, or individual feature classes or tables. The output is a dynamic HTML report that represents the differences between the schemas as inserts, updates, and deletes.

Learn more about generating schema reports and comparing schemas
Google Photorealistic 3D basemap
In local or global 3D scenes, you can access the Google Photorealistic 3D basemap when you are signed in to an ArcGIS Online organization that has enabled access to this basemap. In the scene, 2D basemap layers and the Esri WorldElevation3D/Terrain 3D layer are replaced by a single Google mesh elevation layer that provides a textured digital surface model of the entire planet.

Gaussian splat layers
Gaussian splat layers can be added to 3D scenes to provide highly realistic visualizations of complex geometry that can't be achieved with traditional photogrammetric approaches. Thin human-made structures such as railings or powerlines are easily distinguished, as are natural phenomena such as individual leaves on a tree. Effects such as fog, smoke, and reflections from windows or water can also be captured.

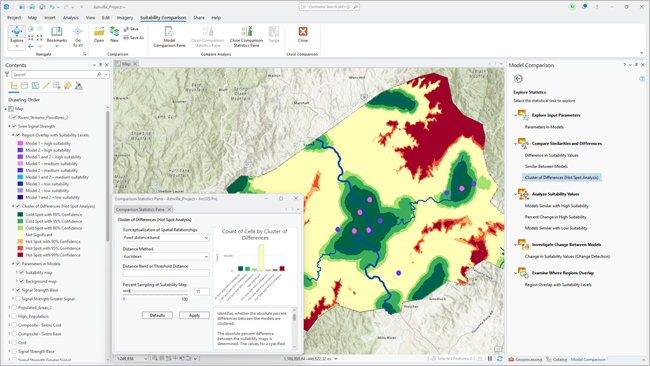
Suitability model comparison
The Model Comparison interface in the Suitability Modeler provides tools to compare models through the analysis of what-if scenarios. By changing inputs and parameters within and between models, you can explore scenarios such as the following:
- The effects of prioritizing environmental concerns over cost when locating a solar farm.
- The impact of altering the significance of land use in a bobcat habitat model.
- The influence of adjusting the transformation applied to the distance from power lines when siting a new corporate headquarters.
- The effects of changing the criteria relevant to locating a recycling center.
The Model Comparison interface allows you to visually and statistically evaluate a number of model variations. This minimizes subjectivity, refines the decision-making process, and grounds your choices in a deeper understanding of the alternatives.
Note:
The Suitability Modeler requires a Spatial Analyst license.
Performance and productivity
Many performance and productivity improvements were made in ArcGIS Pro 3.6, including those listed below.
Performance
- You can run geoprocessing tools on the application foreground thread to optimize performance. See what's new in Analysis and geoprocessing.
- The Zonal Statistics and Zonal Statistics as Table geoprocessing tools can use all available logical processors when reading input rasters. See what's new in the Image Analyst toolbox and Spatial Analyst toolbox.
- Performance was improved when selecting map features with complex masking configurations. See what's new in Mapping and visualization.
- In a feature services environment, you can filter the display of immediate evaluation attribute rules so that rules evaluated only on the server are not shown in the Attribute Rules view. See what's new in Geodatabases and databases.
- Stereo maps have increased draw speed and responsiveness, and were tuned to reduce eyestrain in all stereo workflows. See what's new in Stereo Maps.
- In 3D scenes, terrain changes more responsively, especially in flood simulations. Flood simulation animations also export faster. See what's new in Visual effects in scenes.
- The new Pairwise Polygon Neighbors geoprocessing tool may offer better performance than the Polygon Neighbors tool. See what's new in the Analysis toolbox.
Productivity
- You can add legend items from the legend context menu. See what's new in Layouts.
- Attribute tables have a Calculate Field Toolbar that makes field calculations easier. See what's new in Analysis and geoprocessing.
- You can search for colors and color schemes by keyword when you symbolize feature layers. See what's new in Symbology.
- Arcade uses an improved code editor. See what's new in ArcGIS Arcade.
- You can select features using a symbol class. See what's new in Mapping and visualization.
- You can export a selection from the Select By Attribute or Select By Location tool dialog boxes when you open the tools in a floating window. See what's new in Analysis and geoprocessing.
- Database name and username lengths are supported to the limit of what the database management system supports. See what's new in Geodatabases and databases.
On the Computer tab of the Catalog pane, context menus are available for root drives, mapped network drives, and Windows libraries. See what's new in Projects.
Get started
General
- During application startup, ArcGIS Pro can check for announcements relevant to your installed ArcGIS Pro products. See View software announcements in the Highlights section.
- When you update ArcGIS Pro to a new major or minor release, you can add optional features available in the new release. Patch releases do not deliver new features and do not prompt you about optional features.

Semantic search is installed during a software update. - A canceling status has been added to the Tasks tab in the Diagnostic Monitor window to indicate that cancellation of a task is in progress.
- You can keep the current ribbon tab active when switching views so that the same set of ribbon commands is available as you work.
Analysis and geoprocessing
General
- The attribute table view includes the Calculate Field Toolbar. Use the toolbar to make field calculations without opening the Calculate Field tool.

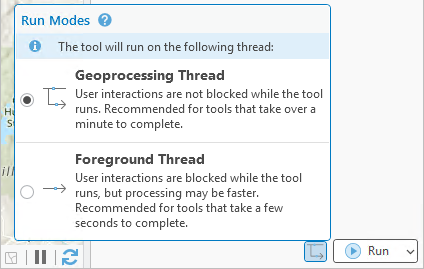
- You can run geoprocessing tools on the geoprocessing thread or on the foreground thread. The foreground thread may be faster but blocks interactions with ArcGIS Pro while the tool runs. The geoprocessing thread runs a tool in the background, keeping the interface unblocked. These options are available on the Run Modes button on tools opened in the Geoprocessing pane.
- Check the Show toggle to add output datasets to open map option in the Geoprocessing options to add the Add to Map toggle button to geoprocessing tools. You can use the toggle button to add tool output to the active map.
- The Select By Attributes and Select by Location tools, when opened in a floating window, include the Export Selection button, which you can use to save a selection as a new dataset.
- You can customize date parameters on custom tools with Date Only and Time Only controls by setting the parameter's controlCLSID property in the ToolValidator class.
Charts
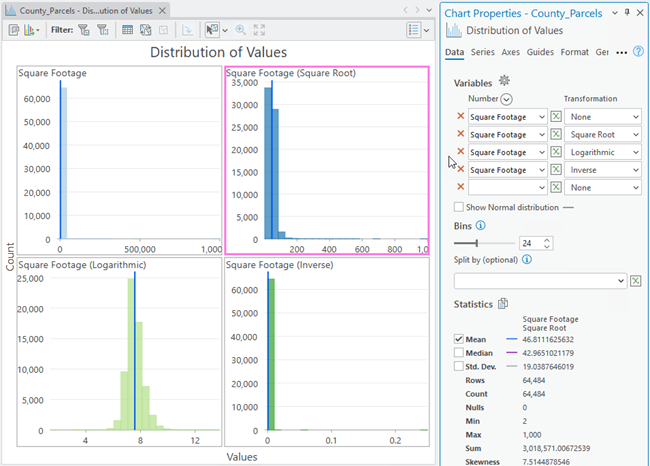
- Grid histograms can be created by selecting multiple numeric fields. Different transformations can be applied to each field.
- Series colors can be updated using a predefined color scheme.

- Style options can be applied to multiple series at the same time by selecting the rows of interest in the series table.
- Text styles for series data labels and guide labels can be applied individually.
- A moving average overlay can be added to temporal line charts to smooth out temporal trends.
Data Engineering
- Data engineering can be performed on raster attribute tables.
Geoprocessing services and web tools
- The validate operation allows you to validate input and obtain updated parameter information and validation messages when you publish geoprocessing services and web tools to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 or later. You can enable validation when sharing a web tool, and create custom validation logic in script tools.
- You can publish geoprocessing services and web tools with the time unit data type to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 or later.
- The Content tab in the Share As Web Tool pane was redesigned to make sharing easier and faster.
ModelBuilder
ModelBuilder has a new look, making it both visually modern and more consistent with ModelBuilder in ArcGIS Online. See ModelBuilder redesign in the Highlights section.
Raster functions
The Linear Spectral Unmixing function was enhanced in the following ways:
- The Remove Continuum parameter specifies whether the spectra are or are not normalized from an image or reference data.
- The Training Feature parameter supports the Esri Spectral Library (.esl), and ENVI Spectral Library (.sli) file formats.
Spatial statistics
Geoprocessing tools
- See Spatial Statistics toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
3D Analyst extension
Lidar and LAS datasets
- LAZ support is provided in LAS datasets.
- Profile graph chaining includes the following enhancements:
- Specify groups, starts, directions, and other properties
- Options for line directionality and flipping
- Improved cursor tracking
- The ArcGIS Pro SDK supports LAS point selection.
- You can import TIN symbology from ArcMap or ArcScene.
- A new workflow topic, Classify transmission power lines in point clouds using deep learning, was added to the documentation.
- Click the Selected Features button on the status bar of a map or scene view to zoom to the selected features.

This data is made available by the Danish Climate Agency and reused under the Creative Commons 4.0 license. - LAS dataset layers have new point symbol size options.
- The new Plane point selection tool is available to interactively select and edit LAS points.
Geoprocessing tools
- See 3D Analyst toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Business Analyst extension
- The Add Business Analyst data utility allows you to build datasets for a single level of geography by enriching standard geographies or hexagons with demographic data for use in ArcGIS Pro projects and analysis.
- Quantiles
and
Highlight Extremes
comparison methods were added to the
benchmark comparisons workflow to extend grouping and color-coding
analysis options. Benchmark comparison layers are context-driven
and can be repopulated with your last saved settings in the
Contents pane. Other workflow enhancements include the following:
- A View Results button.
- Site attributes contain icons that distinguish between numeric and text fields.
- Exporting results to Excel outputs all comparison methods in individual tabs.
- Table views in the Results pane include Flash, Zoom To, and Pan To commands, and indicators for sorted fields.
- Accessibility improvements were made in benchmark comparisons, suitability analysis, and the data source window.
- Place icons were added for points of interest searches with a local dataset.
Territory design
- Commands on the Territory Design ribbon tab open as floating geoprocessing tools, allowing for uninterrupted interaction with the Modify Territories pane.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Territory Design toolbox for enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Image Analyst extension
Spectral analysis
- The Spectral Library Browser pane allows you to open, browse, search, and view the selected spectral signatures in a spectral library.
- The Spectral Signature Viewer is used to view, analyze, measure, collect, and save spectral signatures from imagery and a spectral library file.
- The Spectral Signature Pane allows you to edit names and change colors of the spectral signatures, customize text for the viewer, and export to an Esri Spectral Library file (.sli).
- The Target Detection Wizard identifies pixels in hyperspectral or multispectral images that correspond to particular spectral signatures in a library.
Deep Learning
- The Review Training Data pane provides tools that allow you to review, approve, reject, and update labels or exported training data. These tools can help you perform both a visual review and an automated review based on quantitative assessments.
Motion imagery
- You can use the Static Sensor tool
 to generate video metadata for stationary videos that do not have the required metadata for motion imagery tools.
to generate video metadata for stationary videos that do not have the required metadata for motion imagery tools.
Stereo mapping
- ADS data supports labeling.
Synthetic aperture radar
- The SAR tab on the ribbon has tools and functionality to work with synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data. The tab has three groups to visualize, process, and analyze SAR data.
- InSAR coherence workflows are now available and include the following:
- The Feature Detection Wizard provides a guided workflow that is composed of best practices and a simplified user experience to perform SAR feature detection using Level-1 SAR data.
- The Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (DInSAR) workflow can be performed on Sentinel-1 SAR data. DInSAR is a remote sensing technique used to measure ground deformation by analyzing the phase differences between two or more SAR images acquired at different times.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Image Analyst toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Network Analyst extension
- Traffic capabilities on a network dataset are supported by the Support Traffic option on the Network Dataset Properties dialog box.
- You can change the vertical connectivity policy on a network dataset after it is created.
-
The Explore Locations tool
 allows you to see on a map where an input point is located on the network, or whether it is not located at all.
allows you to see on a map where an input point is located on the network, or whether it is not located at all. - The Waste Collection solver supports virtual depots, fractions, and renewal selection.
Geoprocessing tools and Python
- See Network Analyst module in the Python section for Network Analyst module enhancements.
Spatial Analyst extension
ArcGIS Suitability Modeler
- The Suitability Modeler Model Comparison interface allows you to compare suitability models through a statistical evaluation of their similarities and differences. See Suitability model comparison in the Highlights section.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Spatial Analyst toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Geoprocessing tools
3D Analyst toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Aspect, Geodesic Viewshed, and Slope—Accept the GPU ID and Processor Type environments.
- Extract Objects From Point Cloud—The Minimum Height Surface and Maximum Height Surface parameters can be used to filter the output points.
- Make LAS Dataset Layer—The Minimum Height and Maximum Height parameters allow you to apply a z-range filter to the output.
- Extract LOD2 Buildings:
- You can calculate the volumes of the generated buildings and write the values to an attribute field in the output.
- Overall geometry quality improvements were made.
- You can use point clouds in LAS format (.las file) or LAS dataset format (.lasd file) as the input height source.
- When an input raster with rectangular cells is processed by the following tools, the output raster has square cells with sides equal to the average of the length and width of the input cells: Aspect, Contour, Geodesic Viewshed, Plus,Slope, and Surface Parameters.
Analysis toolbox
New tools
- Pairwise Polygon Neighbors—Creates a table with statistics based on polygon contiguity (overlaps, coincident edges, or nodes) and may improve performance over the Polygon Neighbors tool when using complex and large polygon feature classes as an input.
Enhanced tools
- Spatial Join—The Join Features parameter supports multiple inputs and has a Join Count Field Name option to specify the name of the field that stores the count of join features matching each target feature.
- Near—The Field Names parameter has a Near Features option that you can use to add multiple distance fields when multiple Near Features values are specified.
- Pairwise Clip—You can use the Use maximum precision parameter to apply a level of accuracy during processing that is greater than the default for the input spatial reference.
Aviation toolbox
New tools
- Generate Procedure Leg Geometry—Generates geometry from procedure legs to correct loaded AIXM data that lacks proper geometry.
Bathymetry toolbox
Enhanced tools
- The BIS To Mosaic Dataset tool supports the Geographic Transformations environment.
Conversion toolbox
KML toolset
New tools:
- KML To Geodatabase—Converts .kml or .kmz files to feature classes and converts KML attributes in an Extended Data node into individual attribute fields.
Data Management toolbox
Attribute Rules toolset
New tools:
- Calculate Geometry Fields Attribute Rule—Generates an attribute rule that calculates a feature's geometry information and writes it to a specified field.
Fields toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Add Fields (multiple)—The Field Properties parameter includes additional field properties: Field Precision, Field Scale, Field supports null values, and Field is required.
- Calculate Field—The Expression parameter interprets high precision date values as IS0 8601 string values instead of strings that use regional date and time settings.
- Calculate Fields (multiple)—The SQL expression type is supported for mobile and file geodatabases.
General toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Append—The Update Geometry parameter is supported when the Optimize performance for feature services parameter is enabled.
- Delete Identical—The Field parameter supports the big integer field type.
- Find Identical—The Field(s) parameter supports the big integer field type.
Geodatabase Administration toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Migrate Object ID To 64 Bit—Supports attribute rule validation tables as input datasets.
Package toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Create 3D Object Scene Layer Content—Supports multipatch feature classes as input datasets.
- Generate Level Of Detail—Supports layers as input datasets.
- Upgrade Scene Layer—Supports layers as input datasets.
Raster toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Alter Mosaic Dataset Schema—Two supported satellite sensor options were added to the Raster Types parameter: EnMAP and PACE OCI.
Table toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Get Count—Performance is improved when using enterprise geodatabase datasets and feature services as input.
Toolbox toolset
Enhanced tools:
- Analyze Tools For Pro—For Python 2 to Python 3 upgrade issues, this tool uses the fissix module to review Python code. The fissix module is a modernized backport of the deprecated Python lib2to3 library.
Workspace toolset
New tools:
- Compare Schema—Compares two schema reports or geodatabase schemas and produces a dynamic HTML report. See Geodatabase schema reporting in the Highlights section.
- Create Parquet Cache—Creates a local persistent cache of the data for the input Apache Parquet file.
Enhanced tools:
- Generate Schema Report—Creates a dynamic HTML report with improved layout and navigability. See Geodatabase schema reporting in the Highlights section.
Data Reviewer toolbox
The new Data Sampling toolset contains tools for selecting random data samples and reselecting previously generated samples.
New tools
- Reselect Sample—Reselects a previously generated random selection from a feature layer or table view.
- Select Random Sample—Selects a random sample of the input features or rows based on the specified sampling method.
Editing toolbox
New tools
- Simplify By Tangent Segments—Simplifies polygon and line features by removing collinear and co-circular vertices from straight and curved lines.
Enhanced tools
- Update COGO—Updates COGO on lines with different direction types.
Geocoding toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Assign Streets To Points:
- The Country or Region parameter supports Brazil (BRA) and Poland (POL).
- The Language Code parameter supports Portuguese (POR) and Polish (POL).
- Create Locator:
- Locators for Brazil can be created in Portuguese. The Country or Region parameter supports Brazil (BRA), and the Language Code parameter supports Portuguese (POR).
- Locators for Poland can be created in Polish. The Country or Region parameter supports Poland (POL), and the Language Code parameter supports Polish (POL).
Image Analyst toolbox
The new Surface toolset contains the Calculate Cut Fill Volume tool.
New tools
- Apply Complex Data Filter—Smooths the phase component of the complex input synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data and outputs complex radar data.
- Calculate Cut Fill Volume—Calculates the cut and fill volumes between a base elevation surface and an elevation raster.
- Detect Target Using Spectra—Identifies pixels in an image that match a spectral signature.
- Generate Interferogram—Creates an interferogram by differencing the phase of the reference and secondary single look complex (SLC) inputs.
- Generate Masked SAR Raster—Generates an output SAR dataset that preserves radar measurements for the entire original input extent, while masking out a specified region of interest.
- Generate Multitemporal Coherence—Generates a false color composite image using ground range detected and the coherence products. Each band in the composite is composed of different SAR acquisitions, which are derived from complex radar products.
- Resample Library Spectra—Resamples the bands of a spectral library to match the bands of a target spectral library or image, producing a new spectral library file.
- Transform Image Shapes—Transforms features from image space to map space.
- Unwrap Phase—Removes the phase ambiguities and solves for continuous phase values for SLC data.
Enhanced tools
- Apply Coregistration—The DEM Raster parameter was changed from required to optional.
- Convert SAR Units—The Conversion Type parameter has an Unwrapped phase to displacement option. With this option, the unwrapped interferogram phase in radians is converted to displacement using the sensor's wavelength.
- Generate Radiometric Terrain Corrected Data—Optional Username, Password, and Cloud Storage Connection parameters were added.
- Linear Spectral Unmixing:
- The Remove Continuum parameter specifies whether the spectra are or are not normalized from an image or reference data.
- The Spectral File or Training Features parameter supports the Esri Spectral Library (.esl), and ENVI Spectral Library (.sli) file formats.
- Train Deep Learning Model—The 3D-RCNet model option was added to the Model Type parameter. It inherits the strength of ConvNet and ViT, resulting in high-performance hyperspectral imagery classification.
- Zonal Statistics and Zonal Statistics as Table—Improvements were made in the parallelization of reading input rasters. The Parallel Processing Factor environment limit was changed from four logical processors to all that are available (100 percent). If no value is provided in the environment, all available cores will be used.
- When an input raster with rectangular cells is processed by the following tools, the output raster has square cells with sides equal to the average of the length and width of the input cells: Abs, Cell Statistics, Con, Pick, Plus, Reclassify, and Slice.
Indoor Positioning toolbox
New tools
- Add Geometry To Indoor Positioning Dataset—Generates traversability information necessary to enable geometry-aided indoor positioning.
Indoors toolbox
New tools
- 360 Video To Oriented Images—Extracts 360-degree images from 360-degree videos to an oriented imagery dataset.
- Extract Floor Plan Features From PDF—Creates polyline features representing floor plan elements from an input .pdf file. The output can be used as an input to the Import Features To Indoor Dataset tool to populate an Indoors model with facilities, levels, units, and detail features.
Enhanced tools
- Import Features To Indoor Dataset:
- The Door Identifier parameter can be used to select input polyline features using an SQL query that defines doors that should be closed to create unit features.
- The Elevation Of Level parameter can be used to define the z-value of output level, unit, and detail features.
Knowledge Graph toolbox
New tools
- Create Knowledge Graph—Creates a knowledge graph on the active portal and configures its parameters.
- Load Table To Knowledge Graph—Loads data from a table or feature class into a knowledge graph.
Location Referencing toolbox
New tools
The new Data Products toolset contains the following tools:
- Generate Linear Referenced Feature Count—Creates a feature count data product for routes in an LRS Network without an LRS data template.
- Generate Linear Referenced Length Summary—Creates a length data product for routes in an LRS Network without an LRS data template.
- Generate Linear Referenced Route Log—Creates a route log data product for routes in an LRS Network without an LRS data template.
Enhanced tools
- Append Events:
- The Append even if there are conflict prevention locks parameter supports appending events when locks are present.
- The mapping of the FromDate and ToDate fields is optional for the Load Type parameter's Add option.
- Append Routes—The Allow partial loading of routes parameter supports partial loading of routes, even if certain source routes fail validation.
- Generate Intersections—The Generate intersections even if there are conflict prevention locks parameter supports generating intersections when locks are present on intersecting routes.
- Generate LRS Data Product—You can specify more than one Effective Date parameter value to obtain the delta or change in length or feature count between each pair of effective dates.
- Overlay Events—Performance was improved when running the tool with data from a feature service.
Maritime toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Export S-101 Cell—Creates an S-101 exchange set.
- Validate S-57 File—Flags S-58 Check 531 for individual S-57 datasets.
- Copy S-57 Features—The Copy Dataset Name Field parameter allows you to include the dataset name field in the attributes of copied S-57 features.
Network Diagram toolbox
New tools
- Add Diagram Feature Selection To Layout—Allows you to select the diagram features to which the next active layout configured on the diagram template will apply.
- Create Geoprocessing Model From Diagram Template—Accepts any diagram template as an input and creates a geoprocessing model detailing the sequence of network diagram configuration tools used to set up the rules and layouts for the template.
Enhanced tools
- Create Diagram Layer Definition—The Merging With Existing Layer Definitions parameter allows you to add sublayers related to the same network source class when refining existing diagram sublayers.
- Add Trace Rule—The Output Asset Types and Output Conditions parameters allow output filtering of the traced network elements.
- Apply Smart Tree Layout and Add Smart Tree Layout—The Order tree branches according to an attribute, Attribute Availability, Attribute Name, and Attribute Sort Order parameters allow you to order tree branches according to attributes available on edges or junctions.
Oriented Imagery toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Generate Service From Oriented Imagery Dataset:
- The Virtual Cache Directory parameter specifies the location of the cloud store registered on the server.
- The Allow Deep Learning parameter specifies whether the deep learning workflows can be run on the published service.
- Add Images To Oriented Imagery Dataset—Supports the following inputs:
- Mosaic datasets built using aerial imagery raster types
- .csv files using the FrameCamera table schema
Parcel toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Add Parcel Type—The Use for strata parcels parameter specifies whether the parcel type is used to store strata parcels.
Reality Mapping toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Reconstruct Surface—The Products parameter has a Gaussian Splats option that renders points in a dense 3D point cloud with a Gaussian distribution.
Server toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Upload Service Definition—Supports publishing knowledge graph service definitions to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 or later.
Spatial Analyst toolbox
New tools
- Adjust Stream to Raster—Generates a stream feature output that matches the resolution of an input raster.
- Locate Depressions—Locates areas that are topographically lower than the surrounding terrain based on spatial characteristics.
- Topographic Position Index—Calculates the topographic position index value for each cell within a specified neighborhood.
- Value Percentile Contours—Creates polygons that enclose the top (or bottom) percentile of the map by raster value that provides a clean, area-based view of the extremes.
- Volume Percentile Contours—Creates polygons that enclose the top (or bottom) percentile by volume of a probability density distribution.
Enhanced tools
- Band Collection Statistics:
- The Compute histogram parameter calculates and adds histogram statistics to the output statistics file Checking this parameter enables the following parameters: Number of Histogram Bins, Output Histogram Table, and Output Histogram Name.
- The Output Statistics File parameter can output .csv and .md files.
- The tool accepts the following environments: Cell Size, Cell Size Projection Method, Extent, Geographic Transformations, Mask, Output Coordinate System, and Snap Raster.
- Linear Spectral Unmixing:
- The Remove Continuum parameter specifies whether the spectra are or are not normalized from an image or reference data.
- The Spectral File or Training Features parameter supports the Esri Spectral Library (.esl), and ENVI Spectral Library (.sli) file formats.
- Feature Solar Radiation and Raster Solar Radiation—Accept the GPU ID and Processor Type environments.
- Aspect, Feature Preserving Smoothing, Geodesic Viewshed, Multiscale Surface Deviation, Multiscale Surface Difference, Multiscale Surface Percentile, and Slope—Accept the GPU ID and Processor Type environments.
- Zonal Statistics and Zonal Statistics as Table—Improvements were made in the parallelization of reading input rasters. The Parallel Processing Factor environment limit was changed from four logical processors to all that are available (100 percent). If no value is provided in the environment, all available cores will be used.
- When an input raster with rectangular cells is processed by the following tools, the output raster has square cells with sides equal to the average of the length and width of the input cells: Abs, Aspect, Cell Statistics, Con, Contour, Derive Continuous Flow, Extract by Mask, Flow Direction, Geodesic Viewshed, Pick, Plus, Reclassify, Slice, Slope, and Surface Parameters.
Spatial Statistics toolbox
New tools
- Evaluate Bin Sizes for Point Aggregation—Evaluates multiple hexagonal or square bin sizes for aggregating point data, and recommends a bin size that balances internal uniformity within bins and a variety of point counts across bins.
- Evaluate Predictions with Cross-validation—Evaluates predictive model performance using cross-validation. The tool allows models created using the Forest-based and Boosted Classification and Regression, Generalized Linear Regression, and Presence-only Prediction (MaxEnt) tools.
- Prepare Data for Prediction—Enhances data for predictive workflows by splitting features into training and testing sets, balancing categorical data, and spatially thinning to reduce sampling bias.
Enhanced tools
- Generate Spatial Weights Matrix:
- The Input Features parameter accepts feature layers.
- The Unique ID Field parameter accepts object ID fields such as OID, FID, and OBJECTID.
- For polygons, neighbors can be defined using higher-order contiguity. For example, second-order contiguity includes all neighbors that share an edge or border with the focal feature (the first-order neighbors) and all polygons that share an edge or border with the first-order neighbors.
- Neighbors can be weighted using distance-based kernels, field values, or the length of shared border (for polygons).
- Weights can be defined between each feature and itself (self-weighting).
Territory Design toolbox
Enhanced tools
- Solve Territories—The Number of Territories Method parameter includes the following options:
- Maximize Territories Count—Calculates territories to create a larger number of territories. Territories are smaller in size.
- Minimize Territories Count—Calculates territories to create a smaller number of territories. Territories are larger in size.
Topographic Production toolbox
New tools
- Apply Element Values—Applies values from the Guide To Numbered Features surround element in a layout to the respective feature attributes.
- Download Job Files—Downloads and extracts job files from a topographic production server for manual operations during an ArcGIS Workflow Manager workflow step.
- Update Topographic Production Service Database—Updates the database that an instance of the Topographic Production Service is using.
- Upload Job Files—Uploads a packaged job file to a topographic production server during an ArcGIS Workflow Manager workflow step.
Enhanced tools
- Unzip MGCP Cell And Import—Supports the Multinational Geospatial Co-production Program (MGCP) Urban Vector Data (MUVD) schema.
- Apply Building Offsets—Supports grouped symbol values.
ArcGIS Reality for ArcGIS Pro
- ArcGIS Reality for ArcGIS Pro is now installed with ArcGIS Pro. You do not need to install it separately.
- You can create Gaussian splat layers in the product generation wizards and tools.
- You can use aerial lidar when generating DSM, True Ortho, DSM Mesh and 3D Mesh products.
- You can generate ArcGIS Reality mapping products using reflectance data.
- Focused reprocessing of affected areas reduces product regeneration time when correcting errors.
- The addition of Worldview Legion 5 and Worldview Legion 6 completes support for the full constellation of Legion satellites.
- Cross-platform satellite imagery support was added. For example, Worldview Legion and Pleiades Neo imagery can be combined in a single project to support your derived product requirements.
- Ground control point (GCP) workflows were improved in the following ways:
- You can manually tag GCPs on more than one image before initiating GCP autocorrelation.
- GCP autocorrelation accuracy was enhanced.
- Following manual or semi-automatic GCP tagging, the image list can now be sorted based on a quality score in ascending or descending order.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Reality Mapping toolbox for enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Data management and workflows
BIM
- The BIM file workspace now includes the Control Devices and Plumbing Equipment Mechanical Elements categories.
- The BldgFloor field has been added to BIM features to support the concept of building floors.
CAD
- Multipoint feature layers are supported in the Export To CAD geoprocessing tool and the reading of DWG and DXF drawing files.
- The Surface Contour feature layer was added to support Autodesk Civil 3D proxy contours.
- The Model to World Transformation dialog box was added to geoposition CAD and BIM files using translate, scale, and rotate values common in ground to grid workflows.
- User defined parameters (UDPs) from Civil 3D drawings are now supported as feature layer attributes.
- M-values are supported in the reading and exporting of data to polyline feature layers in DWG and DXF files for use in ArcGIS for AutoCAD.
Data Reviewer
- The Valency check and Composite check are available as Run Data Checks.
- The Feature on Feature Run Data Check supports the evaluation of a feature's z-value when assessing its spatial relationship to other features.
- The Duplicate Feature check supports evaluation of a feature's z-values when determining whether it is a duplicate for attribute validation rules and Run Data Checks.
- The filtering field Category was added to the Error Inspector pane to support error management in automated and visual quality control workflows.
- The Valency check is available with the Export to Attribute Rules tool.
- ArcGIS Pro 3.6 is the final release to support Data Reviewer workflows and related tools that work with ArcMap. See Release notes for ArcGIS Pro 3.6.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Data Reviewer toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Geocoding
- Two new
Match Options properties are supported by locators published to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0.
- Include match narrative returns detailed information about how a geocoding result was obtained. The match narrative can be viewed at the bottom of the Show Details pop-up for the geocode result in the Locate pane.
- Return associated features returns collections of feature types associated with the input address. When the property is enabled, you can do the following when searching for addresses and places in the Locate pane:
- Search and discover more addresses at a geocoded location.
- List all businesses located at a specific address.
- Return all addresses that exist within a postal code.
- Additional default output fields are returned by the locator in the geocode results:
- Building Complex (BldgComp)
- Room Type (RoomType)
- Room Name (RoomName)
- Wing Type (WingType)
- Wing Name (WingName)
- Match ID (MatchID)—Contains an ID value representing a unique address or place that can help find and eliminate duplicate addresses or find duplicate entries in the reference data used to build the locator.
- Potential ID (PotentialID)—Similar to MatchID, but includes additional information about classified but unmatched subunit components in a request.
- The following locator role fields are available for the Point Address and POI roles in the Create Locator tool to help build more powerful locators: Building Complex, Room, Room From, Room To, Room Type, Wing, and Wing Type.
- Find Address Candidates and Geocode Addresses are publishing capabilities that can be set independently of each other when configuring the service before publishing a locator to ArcGIS Server 12.0 or later or configuring the portal item before sharing a locator to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 or later.
- The Search Within drop-down menu in the Locate pane allows you to filter searches by feature collection type when using the ArcGIS World Geocoding Service. You can return a collection of POIs, point addresses, or subaddresses associated with the input address.

- The performance of batch geocoding jobs was improved by enhancements to the Geocode Table pane.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Geocoding toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
- See Geocoding module in the Python section for geocoding module enhancements.
Geodatabases and databases
Attribute rules
- You can write a feature's geometry information to a field using the Calculate Geometry Fields attribute rule template.
- You can choose whether the Attribute Rules view shows rules that are excluded from application evaluation. This option applies to feature services only.
Cloud data warehouses
- You can use a programmatic access token (PAT) as a password when you connect to Snowflake.
- ArcGIS supports username lengths up to the limit of what the cloud data warehouse supports.
Document databases
- Connections to Elasticsearch support using an API key for authentication when you create a .dbconn file.
- You can publish web layers from Elasticsearch or OpenSearch. For more information, see the Share your work section.
Enterprise geodatabases and databases
- ArcGIS supports PostgreSQL 17.x.
- If you upgrade your IBM Db2 11.5 database to 11.5.9 Fix Pack 0 Cumulative Special Build 58840, you can enable an enterprise geodatabase in the database.
- ArcGIS supports database name and username lengths up to the limit of what the database management system supports.
- When you create an attribute index in ArcGIS Pro, the name you specify can contain up to the maximum number of characters supported by the database management system.
Mobile geodatabases
- When you create an attribute index in ArcGIS Pro, the index name can contain up to 128 single-byte characters.
File geodatabases
- When you create an attribute index in ArcGIS Pro, the index name can contain up to 255 single-byte characters.
Indoor positioning
- Options to configure an IPS-aware map were renamed; the functionality remains the same.
- The ArcGIS IPS Information Model was updated as follows:
- The IPS_Beacons feature class can store images as attachments.
- A field named GEOMETRY_AIDED was added to the IPS_Positioning_Datasets feature class.
- When a geometry-enabled IPS positioning dataset is shared using the Share Indoor Positioning Data Service geoprocessing tool, the Geometry-Aided tag is added to the service.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Indoor Positioning toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Indoors
- The floor filter includes a Floor Visibility option in 3D scenes, allowing you to isolate the selected floor or view it in context with the floors below it.
- A new domain value added to the ArcGIS Indoors Information Model supports organization area managers in Indoors Space Planner.
- You can configure floor awareness for additional layers on the Map Properties dialog box.
- You can use .ebc files to define walkable levels information for BIM files.
ArcGIS Knowledge
- When analyzing a knowledge graph's data, the Filtered Find Path pane allows you to add path costs to further enhance a link chart analysis.
- The Load Table tool
 supports the following capabilities:
supports the following capabilities:- Merging entities using the shape property and combining geometries when merging.
- A Multiple Type Lookup option that allows you to define relationships in the event the source table does not contain entity types, or if you are working with entities and relationships in separate tables.
- Missing Values settings that can be configured to handle missing or null values in your data.
Geoprocessing tools
See Knowledge Graph Toolbox for new geoprocessing tools.
Offline mapping
- A Refresh button on the Offline Map Areas dialog box allows you to view the current content of offline map areas and their status.
- You can specify the download location for map areas prepared ahead of time in the Share and Download options.
- When you download offline map areas prepared ahead of time, ArcGIS Pro honors the Tile package on the device and Tile package from my organization settings in the web map's offline options.
- You can use the Include only related rows for stand-alone tables check box when downloading a map to filter stand-alone tables that relate to features in the current map extent.

Parquet
- To reduce the time it takes to create a cache for smaller Parquet files, ArcGIS Pro creates an in-memory cache when you access a file that contains fewer than 500,000 records.
- You can browse to a Parquet file in either a local folder or cloud storage connection from geoprocessing tools. Previously, you could only drag the map layer to geoprocessing tools to use a Parquet file as input.
- The location on disk where local persistent caches are stored has changed. The first time that you browse to the file or open a project containing the file cache after you upgrade to ArcGIS Pro 3.6, the cache is moved to the new location. When you run the CreateParquetCache ArcPy function, the persistent cache is created in the new location.
- The Zstandard (Zstd) compression format is supported for Parquet files used in ArcGIS Pro.
- The following additional cloud storage services are now supported for accessing a Parquet file:
- Google Cloud storage
- Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
- Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
- After you add data from a Parquet file to a map, you can publish hosted web layers from the data. For a list of supported web layer types, see the Share your work section.
- ArcGIS can consume field names from a Parquet file that contain up to 128 single-byte alphanumeric characters.
Workflow Manager
- All workflow item feature services must be shared to enable access to workflow items with an item version of 25.2.0.0 or later.
- Users from an ArcGIS Online partnered organization can participate in your organization’s workflows.
- The Workflow Client namespace in the ArcGIS Pro SDK 3.6 for .NET can be used to subscribe and unsubscribe to job notifications to get automatic updates from ArcGIS Workflow Manager Server for jobs and steps.
- The jobForceStop privilege allows you to cancel a step being run by another user.
Editing
General
- The Nudge commands
 move features by a small distance up or down or to the left or right. The commands are available on the context menu when you edit a feature with the Move tool
move features by a small distance up or down or to the left or right. The commands are available on the context menu when you edit a feature with the Move tool  or Annotation tool
or Annotation tool  .
. - Reverse Direction
 is available as a stand-alone tool in the Modify Features pane.
is available as a stand-alone tool in the Modify Features pane. - The Streaming tool
 contains options for setting the number of vertices grouped into a single Undo
contains options for setting the number of vertices grouped into a single Undo  step, and for enabling or disabling the active snapping settings.
step, and for enabling or disabling the active snapping settings. - When streaming vertices in a stereo map, you can scroll the mouse wheel to set the stereo cursor z-value, or hover over a location and press the B key to set it to the z-value stored with the image at the cursor location.
- The Transfer Attributes tool
 allows you to choose multiple overlapping target features with the pointer or on the selection chip.
allows you to choose multiple overlapping target features with the pointer or on the selection chip. - When you edit a feature using the Edit Vertices tool
 , the feature symbol displays in its original location until the edit is finished.
, the feature symbol displays in its original location until the edit is finished. - The Store Templates command
 is available in the Manage Templates pane on the context menu when you right-click a map in the template view.
is available in the Manage Templates pane on the context menu when you right-click a map in the template view. - The Attributes pane
 includes a drop-down unit selector for existing COGO line attribute values. Changing the unit converts the value.
includes a drop-down unit selector for existing COGO line attribute values. Changing the unit converts the value. - The Error Inspector table view allows you to filter feature classes and geodatabase topology rule types.
- The Copy command on the Error Inspector menu bar copies selected rows to the clipboard and allows you to paste them to external applications such as Microsoft Excel.
Parcel fabric
- When reconciling a version with parcel edits, if updates to the same parcels have since been posted to the default version, the resolve parcel conflicts functionality can be used to automatically resolve parcel geometry and parcel lineage conflicts.
- The default layer organization for historic parcels can be changed by adding an IsRetired field with a subtype on both the parcel polygons and parcel lines for the parcel type. If an IsRetired field is added to both the polygon and line feature classes, the parcel polygon and parcel line layer will be displayed using the subtypes on the field.
- When you build parcels for an active record, if there are only connection lines in the active record, the record polygon will be created to match the extent of the connection lines.
Imagery and remote sensing
General
- Two new SAR imagery stretch types are available: Square Root and Logarithm.
Oriented imagery
- You can digitize features directly on top of images using the Oriented Imagery Viewer.
- You can navigate between images in the Oriented Imagery Viewer using sequence-based or direction-based navigation.
- You can measure distance, area, and location by intersecting vectors from measurement points captured from two different viewpoints.
- You can point the Oriented Imagery Viewer to a JavaScript Maps SDK API that is locally hosted or hosted on an ArcGIS Enterprise portal. This allows you to work with oriented imagery offline.
- In ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0, you can access imagery stored securely in Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure private cloud environments.
- The Oriented Imagery Viewer now supports browser-compatible video playback. You can interact with videos using play, pause, video slider, and volume controls.
Raster data types and sensors
- The following sensors and raster types are supported:
- Sentinel-1C satellite sensor.
- Tanager hyperspectral satellite sensor and raster type.
- The EnMAP raster type supports imagery from the Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program (EnMAP) hyperspectral sensor.
- WorldView Legion raster type, including support for Legion 3 and Legion 4 satellites.
- The PACE OCI raster type supports imagery from the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) on the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) satellite.
- Satellogic raster type.
- The enhanced Sentinel-2 raster type supports Sentinel-2C, satellite SM, SentinelHUB, Copernicus Dataspace, and Brazil Data Cube.
- Theos-2 raster type.
- The HEIF/HEIC image compression format is supported.
- Image properties support JSON as an export format.
SpatioTemporal Asset Catalog (STAC)
- You can create a mosaic dataset and improve performance using the Add all items to Mosaic Dataset button.
- You can filter dynamic catalog searches based on the description of the STAC connection.
- Multiple level STAC catalogs are supported when the STAC URL points to the root catalog, which can have multiple catalogs or collections in it. Each catalog can have other catalogs or collections, displaying the hierarchical STAC catalog structure.
Stereo Maps
- When changing stereo pairs manually or using Auto Load
 , the current image is kept until the new image is loaded, resulting in less flashing and visual interruption of the stereo view.
, the current image is kept until the new image is loaded, resulting in less flashing and visual interruption of the stereo view. - Imagery sources for stereo maps use a new rendering pipeline. This results in better performance and fewer blank areas when zooming and panning quickly.
- Vector features rendered in a stereo map use a new rendering pipeline that supports symbolization regardless of the stereo model type, and reduces the time to load and interact with these features in a Stereo Map view.
- The cursor sensitivity page has a new Scale synchronized option that changes the cursor sensitivity based on the viewing scale.
Geoprocessing tools and raster functions
- See Raster toolset in the Data Management toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
- See Reality Mapping toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
- See Oriented Imagery toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
- See Raster functions for new and enhanced raster functions.
Mapping and visualization
General
- The data sources of feature datasets are shown on the List By Data Source tab
 of the Contents pane.
of the Contents pane. - Horizontal and vertical scrollbars can be added to the edges of a map. This is not available in scenes.
- Feature selection can be shown using feature geometry instead of feature symbology.
- You can select features by right-clicking a symbol class in the Contents pane of a map.

- The state of the selection tool is persisted after the application is closed.
- Feature selection performance was improved in maps with complex masking configurations and when the source data is in enterprise geodatabases.
3D scenes and layers
- You can visualize high fidelity photorealistic scenes with Gaussian splat layers. See Gaussian splat layers in the Highlights section.

- The Google Photorealistic 3D basemap provides access to textured buildings and terrain anywhere on earth. See Google Photorealistic 3D basemap in the Highlights section.
- You can change the displayed distance unit from the coordinate display at the bottom of a scene.
- Profile views can be created along a line or along a selection.
- 3D polygons in scenes draw using an improved tessellation method that results in more consistent and better triangulation.
- The Data tab on the ribbon for point cloud scene layers and integrated mesh scene layers allows access to geoprocessing tools.

Animation
- The following dynamic text formats have been added for camera viewpoints and map range overlays:
- separator="false"
- showPlusSign="true"
- padDecimal="true"
Annotation and labeling
- When managing annotation feature classes, you can sort the symbols and annotation classes and import symbols from different annotation feature classes in the Feature Class Properties pane.
- When managing dimension feature classes, you can sort the dimension styles and import dimension styles from different dimension feature classes in the Feature Class Properties pane.
- Field formatting applied to Date, Date Only, Time, and Time Offset fields is respected for label expressions in languages other than ArcGIS Arcade.
- The Labeling Summary report includes a notification when the Never remove (place overlapping) label placement parameter is enabled.
ArcGIS Arcade
- ArcGIS Arcade 1.34 is supported. For a summary of new features, see the Arcade release notes for versions 1.32 and later.
- Arcade expressions are edited in an enhanced code editor that includes code completion, inline warning hints, and formatting capabilities.
Coordinate systems and transformations
- Coordinate systems saved as projection files use the newer WKT2 standard by default. The original Esri WKT standard is still available for use in earlier releases of ArcGIS Pro.
- Available coordinate systems and transformations were updated to EPSG v12.018.
- The ArcGIS Coordinate Systems Data supplementary files include new geographic transformation grids for Canada, Greece, Latvia, and Japan, as well as new vertical transformation models for Germany, Greece, Japan, and Mexico.
- The anchor epoch date parameter is listed for list of supported geographic and vertical coordinate systems with semi-dynamic datums. Anchor epoch information from the source and target geographic coordinate reference systems is used with the new NTv2 velocity grid transformation method. Transformations using this method were added for Canada.
- The lists of list of supported geographic and vertical coordinate systems and list of supported projected coordinate systems contain tables of deprecated coordinate systems. An explanation of why a coordinate system may be deprecated is included with each table.
ENC layers
- Multiple selected sublayers can be converted simultaneously to feature layers.
- S-101 Edition 2.0.0 ENC cells can be viewed as a group layer of feature layers and tables.
Layouts
- You can add a layer to a legend from the legend context menu.
- Scale bars include an Ends and first division number frequency display option.
- Dynamic text tags for page width, page height, page unit, and page size name were added.
- Formatting tags for displaying time zones in date and time dynamic text elements were added.
- Formatting tags for displaying MGRS and USNG parts in coordinate dynamic text elements were added.
Pop-ups
- Flood simulation element information can be included in a pop-up Fields element.
- Image, chart, and carousel elements support alternative text.
- Chart elements fill their available space, and the 10-field maximum has been removed.
- You can right-click a feature or record in the results list to select the layer or table in the Contents pane.
- Display expressions are listed in the Field drop-down menu as {expression/displayExp}.
- Utility network association elements that have been configured online are visible but read-only.
Presentations
- You can insert multiple map pages by selecting multiple maps and scenes.
- You can create multiple image or video pages by selecting multiple image or video files.
- You can add speaker notes to a presentation that are visible only to the presenter.
- You can interact with a video page displayed in full screen in the following ways:
- Control automatic playback.
- Mute sound.
- Use a progress bar to go to specific points.
Print and export maps and layouts
- Export alerts indicate when export parameters are not compatible with the map contents.
- Print alerts indicate when errors arise when communicating with the printer driver during a print request.
Reports
- The Details subsection can be configured to contain multiple columns.
- Two new mailing label templates are included by default.
- Graphics that cross a page break are clipped proportionally at the break instead of being pushed to the next page.
Simulation
- Flood simulation element information can be included in a pop-up Fields element.
- A simulation can be duplicated at a specific moment in time to run different mitigation scenarios.
- Simulation elements can be given custom names.
- Water rate and duration configurations for water sink and water source areas can be saved or imported.
- The simulation cache can be cleared independently of the local cache.
- You can export only the currently displayed state of a simulation.
Styles
- Additional tags were added to the colors and color schemes in the ArcGIS Colors system style to support searching.
Symbology
- You can update or remove symbology headings for graduated colors, graduated symbols, proportional symbols, unclassed colors, and charts symbology in the Symbology pane.
- On the Map and Scene tab of the application Options dialog box, the Legend size patch limit setting now supports line and polygon symbols to better handle symbol effects.
- When you choose colors and color schemes for feature layers, you can now search for those style items by keyword.
Symbols
- Physically based rendering (PBR) of material properties in glTF markers was enhanced to support additional PBR extensions (KHR_MaterialsIOR,
KHR_MaterialsSpecular,
KHR_MaterialsClearcoat,
and KHR_MaterialsTransmission). This allows realistic rendering of transparent, tinted, or translucent glass, specular highlights, and clear coat properties.

- Advanced compression for mesh geometry, defined by the KHR_draco_mesh_compression extension, allows smaller transmission sizes of glTF markers.
Tables
- You can export a table to Excel from the options menu
 on the table.
on the table.
Time
- You can adjust temporal values in time-configured layers to a common time zone. See Display date-time values in the map's time zone in the Highlights section.
- Layers can have a time zone defined without being time aware. The time zone of the layer can be applied to all temporal fields.
Visual effects in scenes
- Clouds in scenes with weather effects have more realistic lighting in low light or no light situations. The lighting changes based on the sun position.

- Fog and haze in scenes with weather effects were improved to remove artifacts at their edges.
- Lighting and color reproduction in scenes uses a new tone mapping algorithm that provides improved color representation balance.
- The terrain changes more responsively, especially in high-resolution flood simulations. In addition, animations of flood simulation export faster.
Production
Airports
In the ArcGIS Aviation Airports product data files, the Update Aviation Geodatabase Schema add-in is available.
Aviation Charting
In the ArcGIS Aviation Charting product data files, the following are available:
- Create Aviation AOIs utility
- Update Aviation Geodatabase Schema add-in
Aviation Charting geoprocessing tools
- See Aviation toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Bathymetry
- ArcGIS Bathymetry supports S-102 v. 3.0.0.
- S-102 products can be exported using the Export To S-102 tool in the S-102 toolbox in the ArcGIS Bathymetry product data files. An Add S-102 Fields Python script tool that can be used to customize the S-102 feature attribute table is also included in the toolbox.
Clearing Grids
- The workflow to insert number features in a series has been improved to allow subsequent feature values to be incremented and to specify when the incremented values stop.
- Customization options have been improved and combined into a single options dialog box.
Maritime
- The S-100 Exchange Set Editor tool can be used to package, encrypt, and digitally sign S-100 exchange sets.
- Maritime S-100 schemas now use four characters to represent agency codes for S-100.
- The paper chart color scheme was updated with new colors. The RGB values provided in Annex A—BSPT Recommended Baseline Chart Colors have been converted to CMYK colors. The following files are updated to reflect this change:
- Nautical.lyrx
- ZOCDiagram.lyrx
- INT1.stylx
- Symbol layer drawing was updated in the Nautical.lyrx file. New features with no symbols (<all other values>) draw on top of all other symbols.
- The S101FeatureClassSubtypeMapping.xml file was moved from the ArcGIS Pro Resources folder to the ArcGIS Maritime product files.
- The following files have been added to the ArcGIS Maritime product files:
- S-100 GML Tools folder—Contains the Export Feature to S-100 Product tool and supporting files
- S-124 Feature Catalogue—Available in XML and HTML formats (124_FC_2.0.0.xml and 124_FC_2.0.0_webview.html)
- S-401FeatureClassSubtypeMapping.xml
Geoprocessing tools
- See Maritime toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Pipeline Referencing
- The integration between ArcGIS Pipeline Referencing and ArcGIS Utility Network were enhanced in the following ways:
- In the LRS Hierarchy pane, the LRS Schema node
 is denoted as LRS Schema (with Utility Network).
is denoted as LRS Schema (with Utility Network). - You can verify which fields are configured with a utility network in the centerline properties.
- In the LRS Hierarchy pane, the LRS Schema node
- The Process Edits tool
 supports generating intersections when locks are present on intersecting routes if the Generate intersections even if there are conflict prevention locks option is checked in the Location Referencing options.
supports generating intersections when locks are present on intersecting routes if the Generate intersections even if there are conflict prevention locks option is checked in the Location Referencing options.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Location Referencing toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Roads and Highways
- The integration between ArcGIS Roads and Highways and the Address Data Management solution was enhanced in the following ways:
- In the LRS Hierarchy pane, the Address Schema node
 contains the address range and site address point feature classes.
contains the address range and site address point feature classes. - You can verify which fields are configured with the Address Data Management solution in the centerline or LRS event properties.
- You can view the properties of the site address point feature class.
- In the LRS Hierarchy pane, the Address Schema node
- The Process Edits tool
 supports generating intersections when locks are present on intersecting routes if the Generate intersections even if there are conflict prevention locks option is checked in the Location Referencing options.
supports generating intersections when locks are present on intersecting routes if the Generate intersections even if there are conflict prevention locks option is checked in the Location Referencing options.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Location Referencing toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Topographic Mapping
ArcGIS Topographic Mapping is a new extension introduced in ArcGIS Pro 3.6. It integrates capabilities previously available in the Defense Mapping and Production Mapping extensions, which were removed at this release.
- Manual workflow tasks performed in ArcGIS Pro can be configured as part of topographic production workflows for data collection, data editing, and quality control using services-based ArcGIS Workflow Manager.
Product data files
- The consolidation of the two former extensions means that there is now one product file installer.
- Several updates, including rule files and map templates, were made to the ArcGIS Topographic Mapping product files to align with industry data model schema specifications.
Geoprocessing tools
Review Topographic Production toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Projects
General
- When a project you open is missing a required item, such as the default geodatabase or toolbox, you can choose how to repair the default item. You can have ArcGIS Pro create a new default item, or you can browse to an existing item. You can also create a new item in a location you choose.
- When you search a project, the total number of results is displayed in the Catalog pane. Up to 100 search results can be displayed at a time. You can click links to display more results or all results.
- When you select and rename a file-based item in the Catalog pane or a catalog view, its file extension is not selected.
- On the Computer tab of the Catalog pane, context menus are available for items under Windows Home, local drives and network shares under This PC, libraries, and desktop folders.
- You can use view scroll buttons to see open views that are not currently visible.

- You can create an ArcGIS Server connection file using an ArcPy script or the ArcGIS .NET SDK.
- You can use keyboard shortcuts to do the following:
- Left arrow key—In the Catalog pane, a catalog view, or browse dialog box, select container items, such as folder or geodatabases, and collapse their contents.
- Backspace—In a catalog view or browse dialog box contents list, perform the same function as the Back button
 .
.
Portal projects
- To use an existing portal project with ArcGIS Pro 3.6, you must upgrade the portal project.
- In the options for creating projects on an ArcGIS Enterprise portal, you can control the duration of conflict resolution messages and the number of saved local copies of the project on your computer. Previously, these settings could only be made using a Pro.settingsConfig file.
- New status messages on the Info page provide explanations when a project is not ready to save.
Sign in to your organization
- You can connect to portals that require identity-aware proxy authentication, such as those secured with Google Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy or Microsoft Entra Application Proxy.
Share your work
- The Reference registered data and Copy all data configurations are available when sharing a web scene.
- You can share web scenes containing Google Photorealistic 3D basemaps to ArcGIS Online.
- You can share Gaussian splat layers to ArcGIS Online.
- Stand-alone videos can be shared as video layers to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 or later.
- The following properties are available when you share a web feature layer:
Property Description Supported portals Enable Shared Template Editing
Allows others to add templates and update or delete templates they own.
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.4 or later
- ArcGIS Online
Enable Append
Allows others to append data.
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.5 or later when referencing registered data
- ArcGIS Enterprise 11.1 or later when copying data to the server
- ArcGIS Online
- Elasticsearch or OpenSearch query layers can be shared as map image layers or web feature layers that reference registered data to ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 or later.
- You can share data from Apache Parquet files as one of the following web layers that copy all data to ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise 12.0 and later:
- Web feature layer
- Vector tile layer with an associated web feature layer
- Web scene layer with an associated web feature layer
- Hosted table
- Link charts that include content from knowledge graphs can be shared as web link charts to ArcGIS Online.
- An option to assign unique numeric IDs to web layers in new maps by default is included in the map and scene options.
Network diagrams
Diagram layouts
- The Smart Tree layout can arrange branches according to attribute values available on diagram edges or diagram junctions.
- Layouts configured on a diagram template to be applied during diagram generation can now be applied to a diagram feature selection.
Diagram rules
- The Trace rule supports output filtering parameters. For example, output filtering can be set up on a first Trace rule to filter specific traced network elements from others that you do not want in the diagrams. A second Trace rule can then be set up to retrieve other network elements from just these filtered network elements.
- Diagram rules that can be applied using network categories are no longer restricted to diagram templates related to Utility Network version 7 and later. They can be set up on templates related to previous utility network versions.
Diagram layer definition
- You can reorder diagram sublayers by dragging them up or down in the Contents pane.
- You can add multiple sublayers related to the same network source class when refining existing diagram sublayers.
Diagram template settings
You can create template geoprocessing models detailing the sequence of network diagram configuration tools used to set up the rules and layouts on existing templates.
Geoprocessing tools
- See Network Diagram toolbox for new and enhanced geoprocessing tools.
Python
General
- The default Python environment includes the following updates and additions. See the full list of Python libraries in the default ArcGIS Pro Python environment.
- Python was upgraded from version 3.11.11 to version 3.13.7.
- NumPy was upgraded from version 1.26.4 to version 2.2.0. See the NumPy 2.0 migration guide for details on updating from NumPy 1.x to NumPy 2.x.
- When debugging ArcGIS Pro Python tools with Microsoft Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code, the attaching process was streamlined. Setting debug mode is no longer required. Visual Studio Code users can attach using the ArcGIS Pro Debugger extension for Visual Studio Code. No extension is required for Visual Studio users.
- conda env commands now work from PowerShell.
ArcPy
- The AddMessage function supports adding clickable links in a message.
- The EnvManager class can be used as a function decorator to set environment settings for the duration of a function.
- The following context managers were added. Each can also be used as a function decorator.
- LogHistory—Controls whether information about the operation of geoprocessing tools is written to an external log file.
- LogMetadata—Controls whether metadata is included when running geoprocessing tools.
- SeverityLevel—Controls how geoprocessing tools raise exceptions.
Data access module
- The CreateTable function creates a table or feature class with a defined set of fields in a specified location.
- The Editor class includes a version argument to set the version that is associated with the edit session. The Editor object's workspace argument accepts an arcpy.Describe().workspace object, which contains version information and a layer for common script workflows.
Geocoding module
- The Locator object's geocode method supports the following new parameters:
- matchNarrative—Specifies whether detailed information is returned regarding how a geocoding result was obtained by describing the way that each portion of an input string was processed, or classified, by the locator.
- searchWithin—Specifies the feature types that are returned for a collection of places that are related to a geocoded location.
- start—Defines the index number of the first entry in a searchWithin collection of candidates to be returned in the return value.
- num—Defines the number of searchWithin collection candidate results to be returned in each page.
- matchID—Allows searching for an ID value representing an address or place.
- comprehensiveZoneMatch—Specifies whether input addresses that do not exactly match the city name will return candidates.
Mapping module
- The getSymbologyDefinition and setSymbologyDefinition methods on the Layer class can be used to modify renderers or colorizers when specific class properties are not available.
- The elevation property on the Layer class returns the LayerElevation class, and it can be used to get and set elevation modes for 3D layers.
Network Analyst module
- New distance units of Centimeters, Millimeters, Decimeters, and Inches were added to the DistanceUnits enumeration.
ArcGIS Pro SDK
The ArcGIS Pro SDK allows you to extend ArcGIS Pro with your own unique tools and workflows using SDK add-ins and configurations. See What's New for Developers at 3.6.
Roadmap
To learn more about near-term, mid-term, and long-term development goals, refer to the latest ArcGIS Pro roadmap.
Deprecated functionality
See Release notes for ArcGIS Pro 3.6 for information about functionality that has been removed at ArcGIS Pro 3.6 or will be removed in a future release.
